LED grow lamps have developed significantly within a very short time. The technology required to generate enough usable light for plants was not available until recently. Unfortunately, many LED manufacturers also claimed that their LED grow lights were more powerful than HID (High-Intensity Discharge ) lights, when in fact they weren’t. These early misleading statements about Grow LED lights created negative consumer sentiment that continues today.
We have been growing and testing LED grow lights for 4 years. We have tested many of the early LED grow lights which have been more than disappointing and often disastrous for the test plants intended to grow under them. In recent years there has been a significant change in the LED grow technology available. This has opened the gates for high-quality, high-output LED grow lights on the market.
Today, LED grow light technology is still more expensive than traditional HID (high-intensity discharge) lamps, but it can now replace your current MH & HPS grow lights. This statement will probably be viewed with some skepticism, however with the current LED technology over 10 grow cycles we have found that we have had no loss in crop yields. In some cases, we even saw a slight increase in income.
You don’t have to believe us, LED is now as good as HID lighting. We will explain the LED power output confusion in this post and you will be able to see it for yourself.
How do you calculate the LED wattage required to flower cannabis?
The traditional power measurement for grow lights was watts, which made things easy until the development of LEDs. One watt of power corresponds to 1 watt of light output. The confusion arises when trying to measure LED grow lights in watts.
With LEDs, one watt of lamp power does not equal one watt of light output. Because LEDs are much more efficient than incandescent bulbs, we need to use a different measurement to determine the light output produced by the LED grow light.
You may have heard or read about the term “ PAR ” as it refers to LED grow lights. This is the actual measurable value of the usable spectrum of light produced by an LED.
LEDs achieve their effectiveness by not converting as much energy into heat compared to HID lamps ( NDL & MHL ). This means that more of the energy consumed by the LED lamp is converted into actually usable grow light.
PAR, PPF and PPFD for LED grow lamps
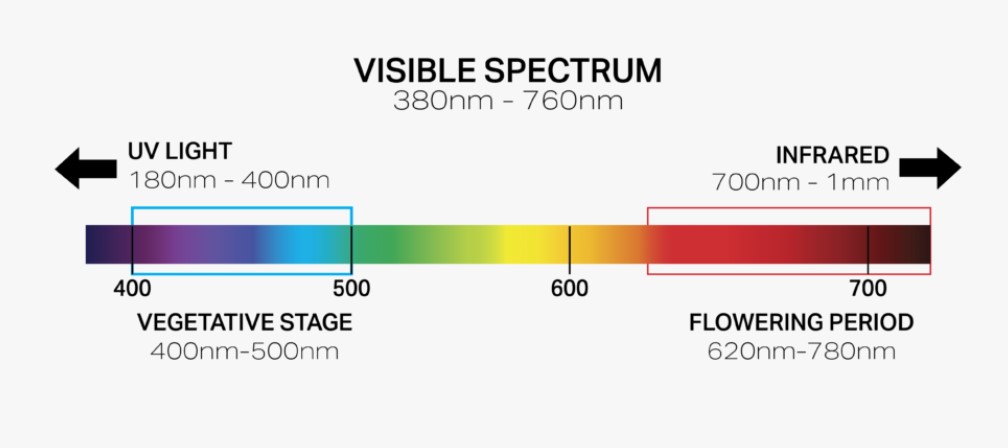
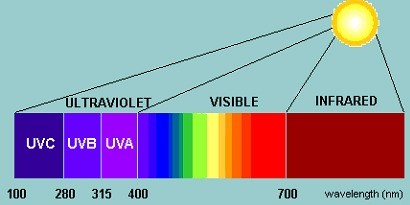
” PAR ” stands for Photosynthetically Active Radiation, which emits light in the electromagnetic spectrum between 400 nm and 700 nm, while humans can only see wavelengths of light between 500 nm and 600 nm.
Plants can convert light wavelengths between 400 nm and 700 nm into energy through photosynthesis. That still doesn’t show the whole picture though, because we haven’t talked about light intensity yet.
This is where things get a little more complex. The next term you need to know is ” PPF ” or photosynthetic photon flux. It sounds like a term from a sci-fi movie, but it only describes the amount of light produced by a light source per second.
This leads us straight to the next term, ” PPFD “ which stands for Photosynthetic Photon Flux Density. This is the measurement of the number of synthetic photons falling on the plant surface per second.
So how can you find out what size LED bulbs you need? Well, you could do the calculations that most people aren’t interested in doing, or you can use this chart to estimate.
The average LED grow light requires around 32 watts for 0.1 square meters of flowering cannabis plants. We use cannabis plants in the flowering phase to calculate the energy requirement, as they require significantly more energy. For comparison, a typical HID lamp would draw about 45 watts per square foot.
Estimate based on 0.1 square meters per plant
| Max Number of plants | Area (square meters) | Minimum LED Wattage |
| 1 | 0.1 | 32 |
| 2 | 0.2 | 64 |
| 4 | 0.4 | 128 |
| 6 | 0.55 | 192 |
| 8 | 0.75 | 256 |
| 10 | 1.0 | 320 |
What does it mean when you talk about full-spectrum light?
We have mentioned ” PAR ” in this guide, which stands for Photosynthetically Active Radiation. This light measurement is often referred to as full-spectrum light. Full-spectrum lights have light whose wavelengths are between 440nm and 700nm, which includes ultraviolet and infrared. Cannabis plants use this full spectrum to photosynthesize light to convert it into simple sugars.
When you buy an LED grow light you will find that all the higher-priced systems will be full spectrum. Be careful when looking for cheaper grow lights, as manufacturers sometimes claim their lamps are full-spectrum, but do not have IF and IR LED chips built into their units.
Are full-spectrum LED grow lights absolutely necessary?
You can grow plants without ultraviolet and infrared, but this could introduce unwanted problems like mould and mildew. Ultraviolet light is a natural sterilizer even used to kill viruses.
When growing in a small space like a grow tent, it’s really important that you have ultraviolet light to reduce the risk of disease.
Full-spectrum LED grow lights generally have two modes of operation; vegetation and flowering. In veg mode, the grow light consumes 40% less energy and uses less red light. This is because the vegetation (growth phase) does not require as much energy as the flowering phase of a plant.
Likewise, flowering plants need more red light to develop healthy and strong buds. When you want to start flowering your plants, simply switch the operating mode to flowering. The lamp does not need to be changed.
What is also certain is that a full spectrum LED grow light will produce a higher yield than a non-full spectrum LED grow light. We have grown with both lights and the full spectrum grow light really takes the grow to the next level.
Light Color In Nano Meters:
- Yellow – 580nm
- Orange – 610 nm
- Red – 630nm
- Deep Red – 660nm
- Blue – 460nm
- Royal Blue – 430nm
- UV – 410nm
- Infrared (IR) – 730nm
Heat development
It is true that LED grow lights generate around 40% less heat than traditional incandescent lights. LEDs achieve this by only producing useful spectrums of light for plants. They eliminate all white light, greatly reducing the heat generated.
LED, short for Light Emitting Diode, is solid-state electronics. As with all electronics, heat is the enemy. With LED grow lights, excessive heat means the electronics can be damaged. LED chips, which are typically rated to last 50,000 hours or more, can significantly reduce their lifespan through overheating.
High-quality LED grow light manufacturers equip their devices with fans and heat sinks that dissipate heat efficiently. Heat is drawn into the heatsinks where cooler air is drawn into the light assembly and over the surfaces. This results in a great reduction of heat in the LED grow light as well as for the entire growing area.
The heat left over from the LED grow light is generally easily managed by simply ventilating your grow box (grow room).
Light scattering in the growing area
LED grow lights use lenses to emit light from the LED structure onto your plants. All LEDs have a main lens to ensure this. Some manufacturers add a second lens to their grow lights to spread the light wider (spread) for greater coverage, or into narrow beams for greater intensity.
Each time a lens is added in front of an LED, the power of the LED is reduced by 8-10%, but the increase in effectiveness for the plants offsets the small loss of energy.
These optical lenses are generally made of plastic or glass and have a focus between 90 and 120 degrees.
Some rogue manufacturers advertise that their lenses increase the intensity of transmitted light, but this is not possible. Intensity can only be increased with more power, while the lenses decrease the intensity by increasing the spread angle of the lights, or increase the intensity by reducing light spread.
Is the price of an LED grow light worth it?
It is true that the upfront investment in an LED grow light is higher than that of an HPS (high-pressure sodium) grow light set. The traditional NDL is just a fancy bulb with ballast to prevent flickering.
An HPS system requires the bulbs to be replaced after approximately 6 months of continuous operation. An HPS system also requires around 40% more power to run at full capacity compared to an LED grow light in flower mode.
LEDs have an expected lifetime of 50,000 to 75,000 hours or 5.7 years of continuous use. That’s a lot of grow cycles, coupled with the 40% lower electricity costs and you have a pretty straightforward answer.
But the savings go even further. Due to the lower operating temperature of an LED grow light, less air conditioning is required for the grow. You need less energy to control the temperature and humidity in a grow room.
You’ll quickly find that you’ll recoup the higher initial cost of LED grow lights in no time.
The time for LED grow systems has come! Over the next year or two, more and more people will be investing in this technology, which will drive development even further. We wouldn’t wait for further improvements as LED technology is already able to increase the yields and potency of cannabis plants.
Do some research and read some LED grow light reviews for yourself and you will surely be satisfied with the switch to LED grow lights.