Table of Contents
Part One: Understanding Cannabis Leaves
- Introduction to Cannabis Leaves
- Anatomy of Cannabis Leaves
- Importance of Leaves in Plant Health
- Cannabis Leaf Phyllotaxy: Arrangement on a Plant Stem
- Phyllotactic Patterns in Cannabis
- Influence of Light Conditions on Leaf Growth
- Cannabis Photosynthesis: Why Leaves Change Colors
- Chlorophyll and Photosynthesis
- Environmental Factors Impacting Leaf Color
- Common Cannabis Leaf Pattern Mutations
- Webbed Leaves and Their Significance
- Whorled Phyllotaxy and Its Characteristics
- Australian Bastard Cannabis: A Unique Mutation
- Less Common Cannabis Leaf Mutations
Part Two: Identifying and Utilizing Cannabis Leaves
- Identifying Cannabis Leaf Issues: Signs of Growing Mishaps
- Blistered, Twisted Leaves: Possible Mite Infestation
- Spotted Leaves: Indicates Deficiency, Likely Calcium
- Leaf Discoloration: Magnesium Deficiency
- White or Bright Yellow Edges and Inner Leaf Purplishness: Copper Deficiency
- Curling, Folding, and Heat Stress
- Drooping Leaves: Underwatering and Overwatering
- Common Uses of Cannabis Leaves
- Making Cannabis Leaf Tea
- Juicing Cannabis Leaves for Health Benefits
- Crafting Thai Sticks: Utilizing Leaves for Smoking
- Creative Culinary Uses: Incorporating Cannabis Leaves in Recipes
Understanding Cannabis Leaves:
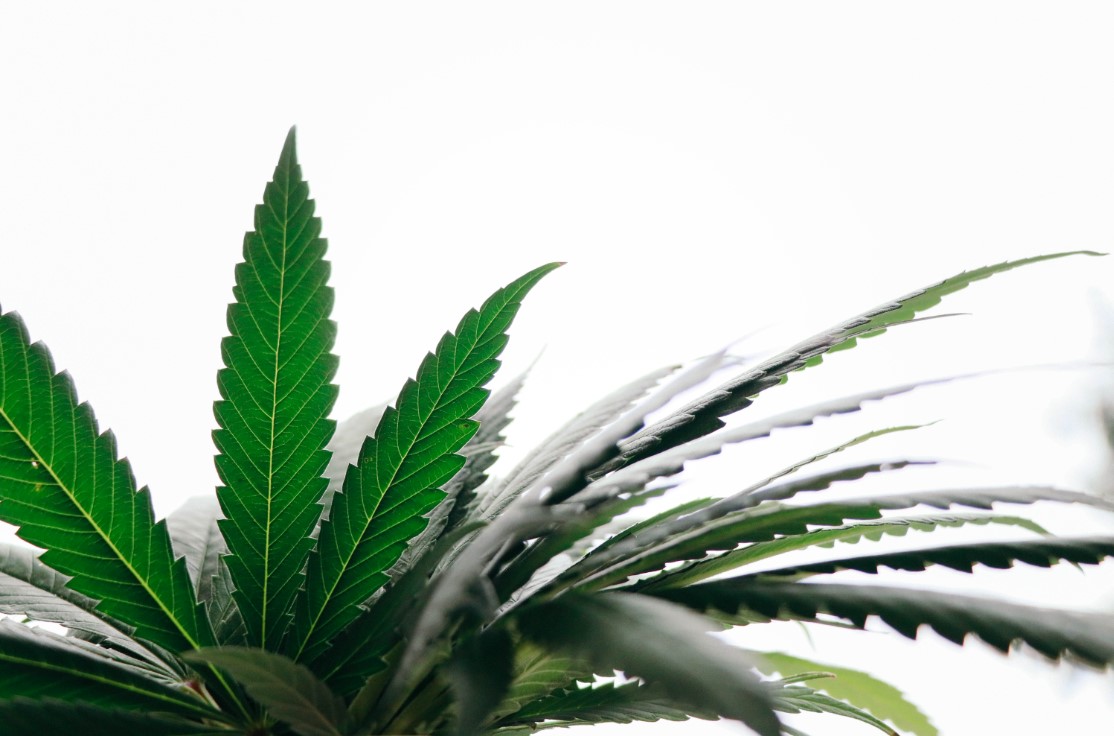
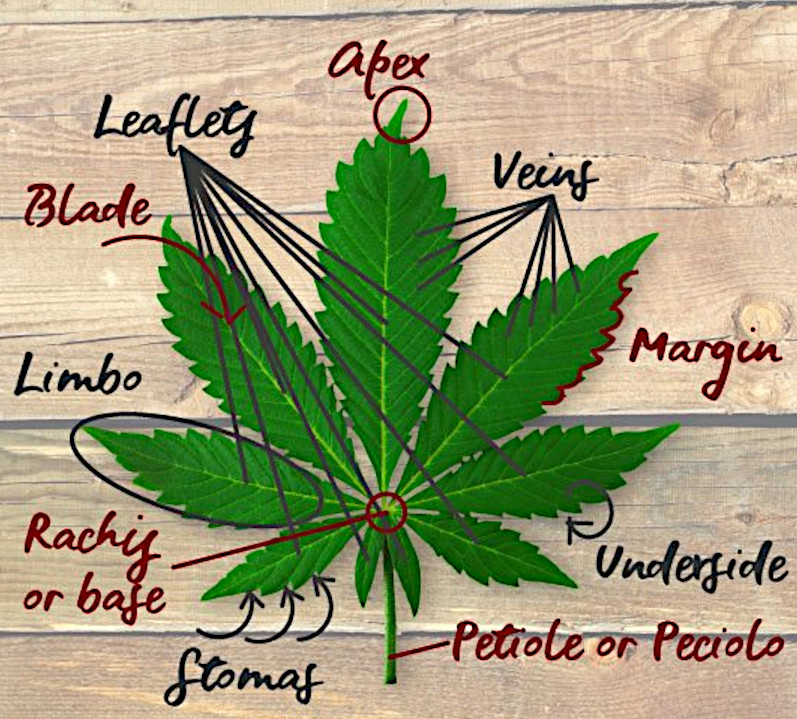
Anatomy of Cannabis Leaves
Cannabis leaves possess a complex structure comprising various components that are crucial to the plant’s physiological processes. Understanding the detailed anatomy of a cannabis leaf provides valuable insights into its functions and adaptations. Let’s examine the specific components that constitute a cannabis leaf:
Cannabis Leaf Structure:
Cannabis Leaf Anatomy:
- Petiole (Peciolo): Resembling the stem, it connects the leaf to the main trunk. Its length varies among different cannabis varieties, sometimes barely visible.
- Rachis (Base): The central axis of the leaf, where the petiole ends and the leaflets begin to form.
- Leaflets: Comparable to fingers on a hand, these are the separate parts into which a cannabis leaf is divided.
- Veins: Vascular lines visible on the leaf surface, divided into the major vein or midrib (main line separating leaflets) and minor or secondary veins (branching from the major vein).
- Limbo: The surface of each leaflet, divided into sections delimited by veins.
- Blade: The visible part of the leaf, thicker and darker on the upper side (adaxial) compared to the underside.
- Underside: The thinner, lighter inner side of the leaflet, housing stomata responsible for gas exchange.
- Stomata: Microscopic openings on the leaf’s underside for gas exchange.
- Margin: The leaf’s edge, often serrated in cannabis, with distinct tips.
- Apex: The tip of the leaflet, opposite to the rachis, also found at the tip of each cannabis leaflet.
Leaf Types and Varieties:
Sativa Cannabis Leaves:
- Leaf Structure: Sativa leaves are long and slender, often with pronounced serrations, giving them a jagged, spiky appearance. The leaves have a complex structure, consisting of multiple leaflets arranged along a central vein.
- Leaflet Count: Sativa leaves can have a higher number of leaflets, providing a larger surface area for photosynthesis. This characteristic supports the plant’s energy production during the growth phase.
- Color Variation: Sativa leaves exhibit a wide range of colors, from bright lime green to darker shades, occasionally bordering on blackish-green. The vibrant green hues signify healthy chlorophyll levels, essential for photosynthesis.
Indica Cannabis Leaves:
- Leaf Structure: Indica leaves are broader and more compact compared to Sativa leaves. They generally have fewer leaflets, usually ranging from seven to nine, giving them a fuller, rounder appearance.
- Leaflet Count: Indica leaves have a reduced number of leaflets compared to Sativa, maintaining efficient photosynthetic capabilities despite the compact structure.
- Color Variation: Indica leaves primarily exhibit deep olive-green hues. While lighter green varieties exist, they are relatively rare. The rich green color indicates the plant’s robust health and effective nutrient absorption.
Ruderalis Cannabis Leaves:
- Leaf Structure: Ruderalis leaves are palmately compound, usually consisting of three leaflets. These leaflets are wide and rounded, with serrated edges. This characteristic leaf structure distinguishes them from the more common five to seven leaflets found in Sativa and Indica strains.
- Adaptability: Ruderalis leaves possess adaptive traits that enable the plant to thrive in harsh climates. These leaves contribute to the plant’s resilience, allowing it to withstand challenging environmental conditions.
- Color and Texture: Ruderalis leaves commonly feature a medium green color and a relatively smooth texture, efficiently contributing to the plant’s photosynthetic processes.
Hybrid Cannabis Leaves:
- Leaf Characteristics: Hybrid cannabis leaves display a diverse range of traits, combining features from both Sativa and Indica parent strains. The leaf shape, size, and serration patterns vary widely, reflecting the genetic blend of the specific hybrid.
- Leaflet Count: Hybrid leaves can have a balanced number of leaflets, integrating traits from both parent strains. Some hybrids may exhibit a more pronounced influence from one parent, resulting in unique leaf patterns.
Understanding the diverse anatomy of cannabis leaves is essential for cultivators, as it provides valuable insights into the plant’s genetic makeup, growth patterns, and adaptability. Each strain’s unique leaf characteristics offer clues about their origin and environmental adaptations, empowering growers to make informed decisions and cultivate healthy, thriving cannabis plants.
Importance of Leaves in Plant Health
Cannabis leaves are vital components of the plant, serving essential functions that are crucial for its overall health and growth. Understanding the significance of leaves in the cannabis plant’s lifecycle is fundamental for any cultivator.
**1. ** Photosynthesis and Respiration: Leaves are the powerhouses of the cannabis plant, facilitating the process of photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, leaves absorb light energy, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen. This energy conversion sustains the plant’s growth and provides the necessary nutrients. In addition to photosynthesis, leaves also play a role in respiration, where they exchange gases with the environment, ensuring the plant has the oxygen required for metabolic processes.
**2. ** Nutrient Absorption: Cannabis leaves contain tiny pores called stomata, through which they absorb carbon dioxide necessary for photosynthesis. Additionally, leaves can absorb nutrients directly when sprayed with foliar feed solutions. This foliar feeding is a common practice among growers to provide essential nutrients to the plant, ensuring robust growth.
**3. ** Transpiration and Water Regulation: Leaves are involved in transpiration, the process through which plants lose water vapor to the atmosphere. This helps in regulating the plant’s internal water balance, preventing water stress. Proper hydration is essential for nutrient uptake and overall plant health, making leaves instrumental in maintaining the plant’s water equilibrium.
**4. ** Indicator of Plant Health: The appearance of cannabis leaves can indicate various aspects of the plant’s well-being. Changes in leaf color, texture, and structure can signal nutrient deficiencies, diseases, or environmental stress. Experienced growers often inspect leaves meticulously, interpreting the plant’s health status and adjusting cultivation practices accordingly.
**5. ** Protection and Defense: Leaves also serve as a shield, protecting the plant from external elements. They can deter herbivores and pests, preventing damage to the vital parts of the plant. Trichomes, tiny hair-like structures present on leaves, produce cannabinoids and terpenes, acting as a natural defense mechanism against predators and pathogens.
Understanding the importance of cannabis leaves empowers growers to create optimal growing conditions, ensuring healthy plants and bountiful harvests. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the various aspects of cannabis leaves, exploring their diverse forms, functions, and the intricate details that make them essential components of the cannabis plant.
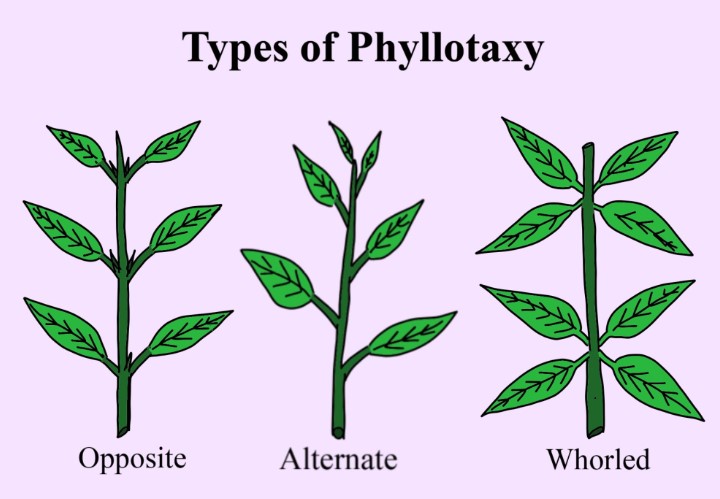
Cannabis Leaf Phyllotaxy: Arrangement on a Plant Stem
Phyllotactic Patterns in Cannabis
The arrangement of leaves on a cannabis plant stem, known as phyllotaxy, follows specific patterns that are essential to the plant’s growth and development. Understanding these patterns provides valuable insights into the plant’s biology and aids cultivators in optimizing their cultivation techniques.
1. Opposite-Decussate Phyllotaxy: Cannabis leaves typically exhibit an opposite-decussate phyllotactic pattern. In this arrangement, leaves emerge in pairs, with each new pair positioned at a right angle to the previous one. This pattern provides an efficient distribution of leaves along the stem, ensuring maximum exposure to sunlight for photosynthesis. Opposite leaves emerge symmetrically, one on each side of the stem, creating a distinctive and recognizable pattern.
2. Alternate Phyllotaxy during Flowering: Interestingly, as cannabis plants transition to the flowering stage, some may display an alternate phyllotactic pattern. During this phase, leaves emerge singly from the stem, swapping sides as they progress upward. This alteration in phyllotaxy is a natural response to the plant’s changing energy requirements, redirecting resources from leaf growth to flower development.
3. Environmental Influences on Phyllotaxy: Environmental factors such as light intensity and duration can influence phyllotactic patterns. Studies have shown that cannabis plants exposed to low light conditions during the vegetative stage may exhibit alternate leaf growth. As sunlight hours increase, the plant reverts to its opposite-decussate pattern. This adaptability demonstrates the plant’s resilience and ability to adjust to changing environmental cues.
4. Significance of Phyllotactic Patterns: Phyllotactic patterns are not merely aesthetic; they play a vital role in optimizing the plant’s energy capture and overall health. By arranging leaves in specific configurations, cannabis plants can efficiently utilize sunlight, ensuring adequate photosynthesis for growth and development. Observing phyllotactic patterns can also be an indicator of a plant’s overall vitality, with healthy plants displaying well-organized and uniform leaf arrangements.
Understanding the intricate phyllotactic patterns in cannabis provides growers with valuable insights into their plants’ behavior. By recognizing these patterns and their environmental triggers, cultivators can make informed decisions, fostering healthier plants and enhancing crop yields.
Influence of Light Conditions on Leaf Growth
Light, a fundamental environmental factor, plays a pivotal role in shaping the phyllotactic patterns and overall leaf growth of cannabis plants. The intricate dance between light intensity, duration, and the plant’s response mechanisms profoundly influences how leaves are arranged on the stem.
1. Phototropism and Leaf Orientation: Cannabis plants exhibit phototropism, a phenomenon where they grow towards a light source. During vegetative growth, cannabis leaves position themselves to maximize light absorption. Phototropism ensures that leaves are oriented in a way that captures the optimal amount of sunlight, enabling efficient photosynthesis. The plant’s ability to adjust the angle and orientation of leaves in response to light intensity contributes to the uniform distribution of light energy among leaves.
2. Role of Light Intensity: Light intensity directly affects leaf size and shape. Cannabis plants grown under high-intensity light typically develop larger and broader leaves. In contrast, plants exposed to lower light intensity produce smaller, narrower leaves. This variance in leaf morphology reflects the plant’s adaptation to available light levels, with broader leaves maximizing light capture in high-intensity environments and smaller leaves minimizing water loss through transpiration in low-light conditions.
3. Photoperiodic Effects on Phyllotaxy: The duration of light exposure, known as photoperiod, significantly influences leaf arrangement. Cannabis plants transition from opposite-decussate to alternate phyllotactic patterns in response to changes in photoperiod. Longer periods of light exposure during the vegetative stage promote opposite-decussate arrangement, optimizing light capture for robust growth. As the plant shifts to the flowering stage with shorter daylight hours, an alternate leaf arrangement emerges, channeling energy towards flower production.
4. Impacts of Light Stress: Extreme light conditions can stress cannabis plants, leading to irregular leaf growth patterns. High-intensity light, especially in indoor cultivation setups, can cause leaf bleaching and scorching. Prolonged exposure to intense light may disrupt normal phyllotactic patterns, hindering the plant’s ability to photosynthesize effectively. Conversely, insufficient light results in stretched, elongated stems and sparse foliage, indicating a lack of light energy for optimal growth.
5. Artificial Light Optimization: Indoor cannabis cultivation relies on artificial lighting systems to mimic natural sunlight. Growers often use techniques such as light spectrum adjustment and controlled photoperiods to optimize leaf growth and phyllotactic patterns. By providing tailored light conditions, cultivators can influence leaf development, ensuring healthy, well-arranged foliage conducive to robust photosynthesis.
Understanding the nuanced relationship between cannabis plants and light conditions is essential for growers. By carefully managing light intensity, duration, and quality, cultivators can harness the plant’s natural responses, promoting balanced leaf growth and maximizing overall plant health. In the subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into the physiological processes underlying leaf development and explore practical applications for cultivators aiming to optimize their cannabis crops.
Cannabis Photosynthesis: Why Leaves Change Colors
Chlorophyll and Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis, the fundamental process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, is orchestrated by the pigment chlorophyll. Cannabis leaves undergo a remarkable transformation during photosynthesis, and understanding the role of chlorophyll is crucial to unraveling the reasons behind these color changes.
1. Chlorophyll: The Green Mastermind: Chlorophyll, the green pigment abundant in cannabis leaves, is instrumental in capturing light energy and converting it into chemical energy. There are several types of chlorophyll, but chlorophyll-a and chlorophyll-b are the primary pigments responsible for photosynthesis. These pigments absorb light in the blue and red parts of the electromagnetic spectrum while reflecting and transmitting green light, giving plants their characteristic green color.
2. Absorption and Reflection: During the growing season, cannabis leaves are lush green due to the high concentration of chlorophyll, which absorbs sunlight to power photosynthesis. However, as environmental factors change, such as decreasing daylight hours and cooler temperatures in autumn, chlorophyll production slows down. As a result, the green pigment begins to degrade and is not replenished at the same rate, leading to its gradual disappearance from the leaves.
3. Unmasking Other Pigments: As chlorophyll breaks down, other pigments present in cannabis leaves become more visible. Carotenoids, responsible for yellow and orange hues, are unmasked as the green chlorophyll diminishes. Anthocyanins, responsible for red, purple, and blue colors, can also be produced in response to certain environmental stressors, creating stunning visual displays in cannabis plants.
4. Environmental Triggers: Various environmental factors influence the rate of chlorophyll breakdown and the production of alternative pigments. Shortened daylight hours, cooler temperatures, and changes in light quality signal to the plant that winter is approaching. In response to these cues, cannabis plants prepare for the colder months by withdrawing nutrients from leaves and shedding those no longer essential, leading to the vibrant autumnal colors often observed in deciduous plants.
5. Significance in Cultivation: For cannabis cultivators, understanding the interplay between chlorophyll, carotenoids, and anthocyanins can offer valuable insights. Monitoring leaf color changes provides clues about the plant’s health, environmental conditions, and nutrient status. Healthy, green leaves indicate robust photosynthesis, while abnormal coloration may signal nutrient deficiencies, stress, or disease.
Environmental Factors Impacting Leaf Color
The captivating spectrum of colors exhibited by cannabis leaves is profoundly influenced by a myriad of environmental factors. These factors interact in intricate ways, leading to the diverse and visually striking array of hues seen in cannabis plants.
1. Light Intensity: Light intensity is a primary environmental factor affecting leaf color. Cannabis leaves exposed to higher light levels tend to develop darker green hues due to increased chlorophyll production. In contrast, lower light levels result in paler green leaves. Adequate light is essential for photosynthesis, and its intensity directly correlates with the plant’s ability to synthesize chlorophyll.
2. Temperature Fluctuations: Temperature fluctuations, especially during the flowering period, can impact leaf coloration. Cooler temperatures often enhance the development of anthocyanins, the pigments responsible for red and purple hues. In colder climates or during autumn, cannabis plants may display vibrant shades of purple as a response to chilly nights.
3. Nutrient Availability: The availability of essential nutrients profoundly influences leaf color. Nitrogen deficiencies, common in poorly nourished plants, lead to yellowing leaves, a condition known as chlorosis. On the other hand, excess nutrients, especially nitrogen, can cause dark green leaves. Proper nutrient balance is crucial to maintaining healthy leaf coloration.
4. pH Levels in Soil or Growing Medium: pH levels in the soil or growing medium significantly affect nutrient uptake by cannabis plants. Imbalanced pH levels can lead to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, both of which impact leaf color. Monitoring and adjusting pH levels in the growing medium ensures optimal nutrient absorption and vibrant leaf color.
5. Watering Practices: Inconsistent or excessive watering can stress cannabis plants, affecting their overall health and leaf color. Water stress can lead to wilting, leaf curling, and changes in color. Proper watering practices, tailored to the specific needs of the plant, help maintain consistent leaf coloration.
6. Genetics and Strain Variation: Genetic factors play a pivotal role in determining leaf color variation among cannabis strains. Certain strains are genetically predisposed to exhibit specific colors, ranging from deep purples to bright oranges. Cultivators often select strains based on their desired color characteristics, leading to the wide variety of colorful cannabis plants available.
Understanding these environmental factors provides valuable insights for both cultivators and enthusiasts. By carefully managing light exposure, temperature, nutrient levels, pH, watering, and selecting suitable strains, cultivators can influence and enhance the vibrant palette of colors displayed by cannabis leaves. Observing and interpreting these color changes also enables growers to gauge the plant’s health and adjust cultivation practices accordingly.
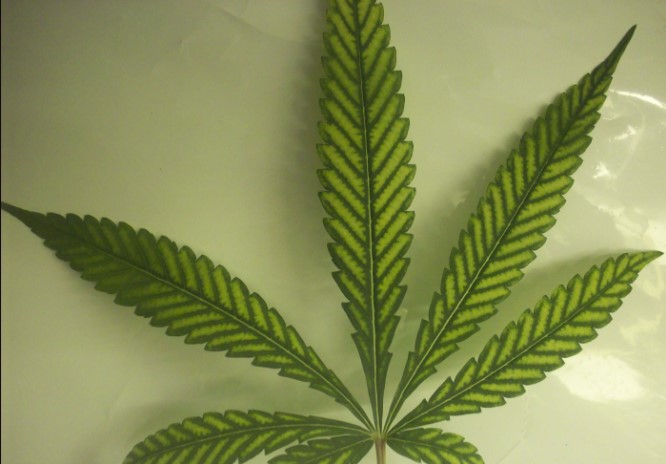
Common Cannabis Leaf Pattern Mutations
Webbed Leaves and Their Significance
One of the intriguing mutations observed in cannabis plants is the occurrence of webbed leaves, a phenomenon where the leaflets appear fused, resembling a web. While webbed leaves are not common, they hold significance in the world of cannabis cultivation for several reasons.
Significance and Desirable Traits:
- Concealment: Webbed leaves, being visually distinct from typical cannabis leaves, provide a degree of camouflage. In regions where cannabis cultivation is illegal, such unique traits help growers conceal their crops more effectively, minimizing the risk of detection.
- Genetic Variation: The presence of webbed leaves showcases the rich genetic diversity within cannabis populations. These mutations highlight the plant’s adaptability and ability to develop unique characteristics under various environmental pressures.
- Cosmetic Appeal: Some cultivators and enthusiasts find webbed leaves visually appealing. The distinct appearance adds an exotic and novel element to the plant, making it desirable for certain niche markets and collectors.
Challenges and Breeding Efforts:
- Stabilization Challenges: Despite the allure of webbed leaves, stabilizing this trait for commercial cultivation has proven challenging. Breeders have attempted to create stable webbed varieties like Ducksfoot, but achieving consistent and reliable webbed leaf expression has been elusive.
- Genetic Research: The study of webbed leaves contributes to ongoing genetic research in cannabis. Understanding the underlying genetic mechanisms behind this trait can provide valuable insights into the plant’s biology and evolution.
Cultivation Considerations:
- Selective Breeding: While webbed leaves are not widespread, breeders continue to explore selective breeding techniques to enhance and stabilize this trait. By carefully selecting plants with webbed leaves and crossbreeding them, there is potential to create more stable webbed varieties in the future.
- Hybridization Experiments: Some breeders experiment with hybridization, combining webbed leaf cannabis varieties with high-potency strains. These experiments aim to create unique hybrids that possess both the webbed leaf trait and desirable cannabinoid profiles.
In summary, webbed leaves in cannabis represent a captivating aspect of the plant’s genetic diversity. While these mutations have practical applications in concealment and a cosmetic appeal to certain enthusiasts, the challenges associated with stabilizing this trait underscore the complexity of cannabis genetics. Ongoing research and breeding efforts continue to unravel the mysteries behind webbed leaves, shaping the future of cannabis cultivation and diversity.
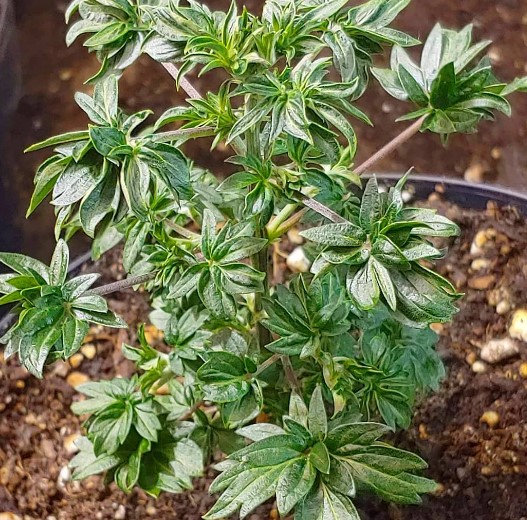
Whorled Phyllotaxy and Its Characteristics
Whorled phyllotaxy is another intriguing leaf pattern mutation observed in cannabis plants. Unlike the standard arrangement where leaves emerge singly or in pairs along the stem, whorled phyllotaxy is characterized by multiple leaves originating from the same node in a circular or spiral pattern around the stem.
Characteristics and Identification:
- Circular Arrangement: In plants exhibiting whorled phyllotaxy, leaves emerge in a circular formation around the stem. This unique arrangement sets them apart from the typical opposite or alternate leaf patterns.
- Spiral Configuration: Whorled leaves can also appear in a spiral pattern, where each leaf is positioned at a consistent angle from the previous one, creating a spiral effect along the stem.
- Increased Leaf Density: Due to the multiple leaves originating from the same node, cannabis plants with whorled phyllotaxy often have a higher leaf density in specific sections of the plant.
- Visual Distinctiveness: Whorled phyllotaxy is visually distinct and easily identifiable upon close inspection of the plant’s structure.
Significance and Cultivation Implications:
- Cosmetic Appeal: Whorled phyllotaxy is considered visually appealing by some cultivators and enthusiasts. The unique arrangement of leaves adds an exotic and ornamental quality to the plant, making it desirable for certain niche markets and collectors.
- Research Interest: The study of whorled phyllotaxy contributes to botanical research and genetic exploration. Understanding the genetic basis of this mutation provides valuable insights into plant development and morphology.
- Selective Breeding: Some breeders experiment with selective breeding techniques to enhance and stabilize the whorled phyllotaxy trait. By carefully selecting plants exhibiting this pattern and crossbreeding them, breeders aim to create stable whorled leaf varieties.
Challenges and Future Prospects:
- Stabilization Efforts: Similar to other leaf pattern mutations, stabilizing whorled phyllotaxy for consistent expression poses challenges. Breeders continue to work on developing stable varieties that reliably exhibit this trait.
- Hybridization Studies: Hybridization experiments involving cannabis plants with whorled phyllotaxy and high-potency strains are ongoing. These studies explore the potential synergy between unique leaf patterns and desirable cannabinoid profiles.
In summary, whorled phyllotaxy in cannabis represents a captivating deviation from the standard leaf arrangement. While this mutation primarily holds aesthetic appeal, its unique characteristics contribute to the plant’s genetic diversity and the ongoing exploration of cannabis genetics. Cultivators and researchers alike remain intrigued by the potential applications and genetic mechanisms underlying whorled phyllotaxy in cannabis plants.
Australian Bastard Cannabis: A Unique Mutation
Australian Bastard Cannabis (ABC) stands out as one of the most distinctive mutations observed in cannabis plants. This unique variation features hairless, succulent leaflets, usually with no more than five leaflets to a leaf, making it markedly different from the typical cannabis leaf morphology.
Characteristics and Identification:
- Hairless Leaflets: ABC plants have smooth, hairless leaflets, unlike the fine trichomes found on the surface of regular cannabis leaves. This lack of hair gives the leaves a unique texture and appearance.
- Limited Leaflet Count: Typically, ABC leaves have a lower number of leaflets, often not exceeding five per leaf. This reduction in leaflet count contributes to the plant’s distinct look.
- Succulent Texture: The leaflets of Australian Bastard Cannabis have a succulent texture, indicating a higher water content compared to the standard cannabis leaves. This trait is particularly noteworthy in arid or semi-arid regions where water retention is vital for plant survival.
Origin and Geographic Distribution:
- First Observations: Australian Bastard Cannabis was first observed in escaped cannabis populations around Sydney, Australia. The mutation likely occurred spontaneously in the wild, leading to the development of this unique trait.
- Limited Commercial Availability: Despite its intriguing characteristics, ABC remains rare in commercial cannabis cultivation. Efforts to stabilize and commercialize this mutation have faced challenges, limiting its availability in the market.
Cultivation and Research Interest:
- Genetic Research: Australian Bastard Cannabis has piqued the interest of researchers and geneticists due to its unusual leaf morphology. Studies aim to unravel the genetic basis of this mutation, shedding light on the underlying genetic mechanisms.
- Limited Cultivation: While some enthusiasts cultivate ABC for its novelty and unique appearance, widespread cultivation remains limited. Challenges in stabilizing the mutation and ensuring consistent expression have impeded large-scale production.
Potential Applications and Future Prospects:
- Genetic Exploration: The study of Australian Bastard Cannabis contributes to genetic diversity research in cannabis. Understanding the genetic factors responsible for this mutation enhances our knowledge of cannabis genetics and evolution.
- Ornamental and Medicinal Potential: ABC’s unique appearance makes it desirable for ornamental horticulture. Additionally, exploring potential medicinal properties associated with this unique variation remains an area of interest for researchers.
In conclusion, Australian Bastard Cannabis stands as a testament to the incredible diversity within the cannabis species. Its rare and distinctive characteristics continue to captivate researchers, cultivators, and enthusiasts alike, showcasing the intricate and fascinating world of cannabis mutations. While challenges in stabilization persist, the allure of this unique mutation fuels ongoing research and cultivation efforts within the cannabis community.
Less Common Cannabis Leaf Mutations
- Fused Leaflets: This mutation causes adjacent leaflets to fuse together, forming a single, broader leaflet.
- Variegation: Variegated leaves have irregular patterns of different colors, often appearing as patches or streaks of white, yellow, or light green on a predominantly green leaf.
- Cannabis Witches’ Broom: This mutation leads to the abnormal growth of multiple branches or shoots from a single node, resembling a broom. It is often caused by pathogens or genetic factors.
- Cannabis Rosette: Plants with this mutation exhibit tightly packed, distorted growth, forming a rosette-like structure. It is typically caused by genetic abnormalities or viral infections.
- Cannabis Monstrose: Monstrose plants display abnormal, contorted growth patterns, leading to a highly unusual and often ornamental appearance. This mutation can be caused by genetic factors or environmental stress.
- Cannabis Variegated Fan Leaves: This mutation results in fan leaves with irregular color patterns, similar to variegation but specifically affecting the fan leaves.
- Cannabis Crested Growth: Also known as cristation or fasciation, this mutation causes stems, leaves, or flowers to flatten and elongate, creating a crested or fan-like appearance. It occurs due to abnormal cell division.
Identifying Cannabis Leaf Issues: Signs of Growing Mishaps
Blistered, Twisted Leaves: Possible Mite Infestation
Blistered and twisted leaves are often indicative of a mite infestation, specifically the notorious cannabis spider mites. These tiny arachnids, barely visible to the naked eye, feed on cannabis plants by piercing the plant cells and extracting their contents. As a result, the affected leaves develop a blistered appearance, and in severe cases, they may appear twisted or curled.
Spider mites are more prevalent in dry and warm conditions. They thrive in environments with low humidity, making indoor cannabis grows especially susceptible. Infestations can escalate rapidly, leading to extensive damage if not promptly addressed.
How to Identify:
- Blistered Appearance: Affected leaves develop small blisters or bumps, giving them a raised, uneven texture.
- Twisted or Curled Leaves: Leaves may exhibit twisting or curling, especially around the edges.
- Tiny Specks and Webbing: Look for tiny specks on the leaf surface, which are mites, and fine webbing between leaves and buds, indicating their presence.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Maintain Proper Humidity: Keeping the humidity levels in check can discourage spider mite infestations. Regularly misting plants can create a less favorable environment for mites.
- Natural Predators: Introducing natural predators like ladybugs or predatory mites can help control spider mite populations organically.
- Neem Oil: Neem oil, a natural insecticide, can be used to treat spider mite infestations. Dilute it with water and spray it on the affected plants(ONLY DURING VEGETATIVE GROWTH STAGE).
- Isolate Affected Plants: If you identify an infestation, isolate the affected plants immediately to prevent the mites from spreading to other cannabis plants.
By closely monitoring your cannabis plants and promptly addressing any signs of blistered, twisted leaves, you can effectively manage mite infestations and ensure the health of your crop.
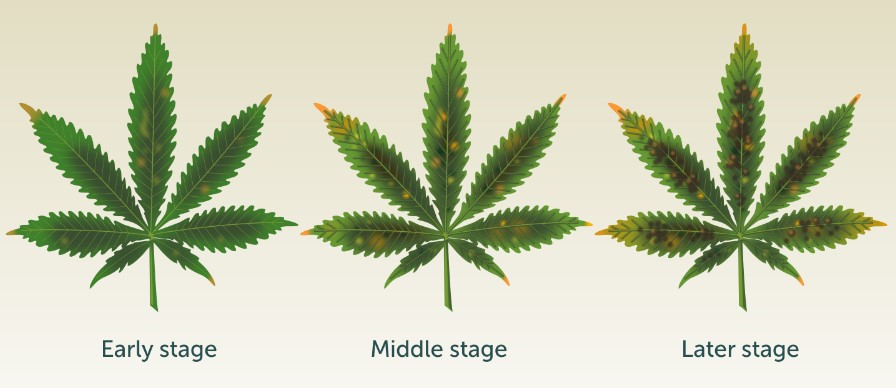
Spotted Leaves: Indicates Deficiency, Likely Calcium
Spotted leaves on cannabis plants are a common indicator of nutrient deficiencies, with calcium deficiency being a likely cause. Calcium is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in cell structure and function. When cannabis plants lack sufficient calcium, it can lead to the development of spotted or discolored leaves.
How to Identify:
- Small Brown or Yellow Spots: Spots appear on the leaves, usually starting as small, pale yellow or brown dots.
- Spots Enlarge and Merge: Over time, these spots can enlarge and merge, forming irregular patterns on the leaves.
- Leaf Tips and Edges Affected: Calcium deficiency often affects the tips and edges of the leaves first before spreading to the entire leaf surface.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Balanced Nutrient Solution: Ensure your cannabis plants receive a well-balanced nutrient solution that includes sufficient calcium. Many fertilizers formulated for cannabis cultivation contain adequate calcium levels.
- pH Regulation: Maintain the pH of the soil or hydroponic system within the optimal range (usually around 6.0 to 6.5). Fluctuations in pH can affect nutrient absorption, including calcium.
- Calcium Supplements: If deficiency symptoms persist, consider using calcium supplements specifically designed for plants. These supplements can be added to the watering solution to provide an additional source of calcium.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly monitor the leaves for any signs of deficiency. Early detection allows for timely intervention and prevents the issue from worsening.
Addressing calcium deficiencies promptly is essential for ensuring healthy cannabis growth and maximizing yield. By understanding the signs and taking appropriate measures, growers can prevent and mitigate nutrient deficiencies, promoting robust and vibrant plant development.
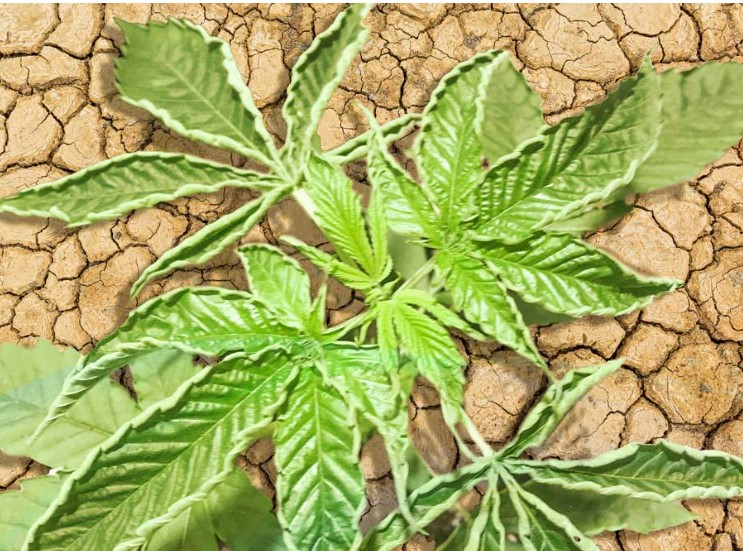
Leaf Discoloration: Magnesium Deficiency
Leaf discoloration in cannabis plants is a common symptom of magnesium deficiency. Magnesium is a vital nutrient responsible for various physiological processes within the plant, including chlorophyll production. When cannabis plants lack sufficient magnesium, it can lead to distinctive discoloration patterns on the leaves.
How to Identify:
- Yellowing Between Veins: The area between the veins on the leaves turns yellow while the veins remain green, creating a mottled appearance.
- Leaf Tips Affected: The tips of the leaves may start turning yellow or brown, progressing inward from the edges.
- Leaf Curling: In severe cases, leaf edges may curl upward or downward, indicating stress caused by magnesium deficiency.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Balanced Nutrient Solution: Ensure your cannabis plants receive a well-balanced nutrient solution containing adequate magnesium. Balanced fertilizers formulated for cannabis cultivation typically include magnesium.
- pH Regulation: Maintain the pH of the growing medium within the optimal range (around 6.0 to 6.5). Fluctuations in pH can affect nutrient availability, including magnesium.
- Magnesium Supplements: If magnesium deficiency is confirmed, magnesium supplements can be added to the watering solution. These supplements provide an additional source of magnesium, aiding in the correction of the deficiency.
- Epsom Salt Solution: A natural source of magnesium is Epsom salt (magnesium sulfate). Prepare a diluted Epsom salt solution and apply it to the plants’ roots to supplement magnesium levels.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly inspect the leaves for signs of nutrient deficiencies, including discoloration. Early detection allows for timely corrective action, preventing further damage to the plants.
By addressing magnesium deficiency through appropriate measures, growers can restore the plants’ health and vitality. Monitoring nutrient levels and providing necessary supplements ensure robust cannabis growth and enhance overall crop quality.
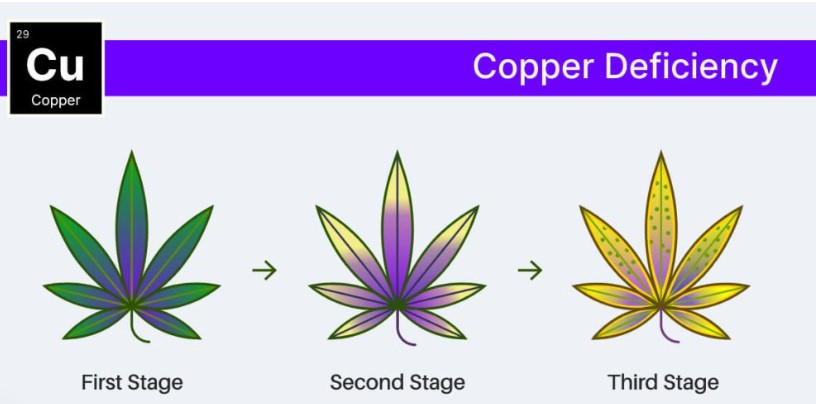
White or Bright Yellow Edges and Inner Leaf Purplishness: Copper Deficiency
Copper deficiency in cannabis plants can manifest through distinct leaf symptoms, including white or bright yellow edges and purplish discoloration on the inner leaves. Copper is an essential micronutrient that plays a crucial role in various enzymatic processes and overall plant health. When cannabis plants lack copper, it results in specific visual cues that indicate the deficiency.
How to Identify:
- White or Bright Yellow Edges: The edges of the leaves turn white or bright yellow, giving the leaves a distinctive appearance.
- Inner Leaf Purplishness: Along with the white or yellow edges, the inner part of the leaves may develop purplish or dark blue discoloration.
- Shiny or Curling Leaves: Affected leaves might appear shiny, and in some cases, they may curl or turn under due to stress caused by copper deficiency.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Copper Supplements: To address copper deficiency, copper supplements can be added to the nutrient solution. These supplements provide an additional source of copper, aiding in the correction of the deficiency.
- Balanced Fertilization: Ensure that your cannabis plants receive a balanced fertilizer that contains essential micronutrients, including copper. Regularly check the nutrient composition to prevent micronutrient imbalances.
- pH Regulation: Maintain the pH of the growing medium within the optimal range (around 6.0 to 6.5). Fluctuations in pH can impact nutrient availability, including copper.
- Observation and Monitoring: Regularly inspect the leaves for signs of copper deficiency. Early detection allows for timely corrective action, preventing further damage to the plants.
- Consultation with Experts: If symptoms persist despite corrective measures, consider consulting with experienced cannabis cultivators or horticulturists. They can provide specialized guidance based on the specific conditions of your cultivation setup.
By addressing copper deficiency promptly and providing the necessary supplements, growers can promote healthy cannabis growth, vibrant foliage, and optimal bud development. Monitoring nutrient levels and ensuring a well-balanced environment are essential practices for successful cannabis cultivation.
Curling, Folding, and Heat Stress
Curling, folding, and discoloration in cannabis leaves are common symptoms of heat stress, a condition that occurs when plants are exposed to excessively high temperatures. Heat stress can impair plant growth, reduce yields, and negatively impact overall plant health. Proper identification and management of heat stress are essential for successful cannabis cultivation.
How to Identify:
- Curling Leaves: Cannabis leaves affected by heat stress often curl upward or inward along their edges. The curling can be uniform across the leaf or concentrated on specific parts.
- Folding: In response to heat stress, leaves might fold or crinkle, resembling a wilted appearance. The folding can occur horizontally or vertically, depending on the severity of the stress.
- Discoloration: Heat-stressed leaves may exhibit discoloration, turning yellow or brown at the edges or tips. In severe cases, the entire leaf might change color due to cellular damage.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Temperature Regulation: Maintain an optimal temperature range for cannabis cultivation. Indoors, use cooling systems such as fans, air conditioning, or ventilation to control the ambient temperature. Outdoors, consider shading techniques to shield plants from direct sunlight during the hottest parts of the day.
- Proper Watering: Adequate irrigation helps regulate the plant’s internal temperature. Ensure consistent watering practices to prevent both underwatering, which can exacerbate heat stress, and overwatering, which can lead to root problems.
- Humidity Control: Manage humidity levels within the growing environment. High humidity combined with high temperatures can intensify heat stress. Use dehumidifiers if necessary to maintain optimal humidity levels.
- Shading: Employ shading methods such as cloth covers or shade nets to diffuse sunlight and reduce the intensity of light exposure. This can help mitigate heat stress during periods of intense sunlight.
- Observation and Adjustment: Regularly monitor the plants for signs of heat stress. If symptoms are observed, take immediate action to adjust environmental conditions and provide relief to the stressed plants.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure proper airflow and ventilation within indoor grow spaces. Good air circulation helps dissipate heat and maintain a stable environment for the plants.
By implementing these preventive measures and closely monitoring the growing conditions, cannabis cultivators can minimize the risk of heat stress, ensuring healthy and vigorous plant growth throughout the cultivation cycle.
Drooping Leaves: Underwatering and Overwatering
Cannabis leaves can droop due to issues related to watering, specifically underwatering and overwatering. Proper watering is crucial for maintaining plant turgidity and overall health. Leaves droop as a response to changes in the water balance within the plant cells.
How to Identify:
- Underwatering: When plants don’t receive enough water, their leaves may droop and appear wilted. The drooping is often accompanied by dryness in the soil and can affect both older and newer leaves.
- Overwatering: Excessive watering can lead to waterlogged soil, suffocating the roots and impeding their ability to absorb oxygen. Overwatered cannabis plants may exhibit drooping leaves, which can be soft and limp to the touch. Overwatering also often causes yellowing of leaves and root rot.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Proper Watering: Establish a consistent watering schedule based on the specific needs of the cannabis plant and the environmental conditions. Allow the soil to partially dry out between watering sessions to prevent both underwatering and overwatering.
- Check Soil Moisture: Use a moisture meter or the finger test to assess soil moisture levels. Insert your finger into the soil up to an inch deep. If it feels dry, it’s time to water; if it’s still moist, wait before watering again.
- Drainage: Ensure the pots or planting area have adequate drainage to prevent water accumulation at the root level. Well-draining soil and pots with drainage holes help excess water escape, reducing the risk of overwatering.
- Observation: Regularly observe the plants for signs of drooping leaves. Adjust the watering frequency based on the plant’s response and environmental conditions.
- Root Health: Monitor the roots for signs of rot or disease. Healthy roots are essential for water absorption. If root issues are suspected, consider repotting the plant into fresh, well-draining soil.
By being attentive to the plant’s water requirements and addressing issues related to underwatering and overwatering promptly, cannabis cultivators can maintain upright, healthy leaves, promoting optimal growth and development.
Common Uses of Cannabis Leaves
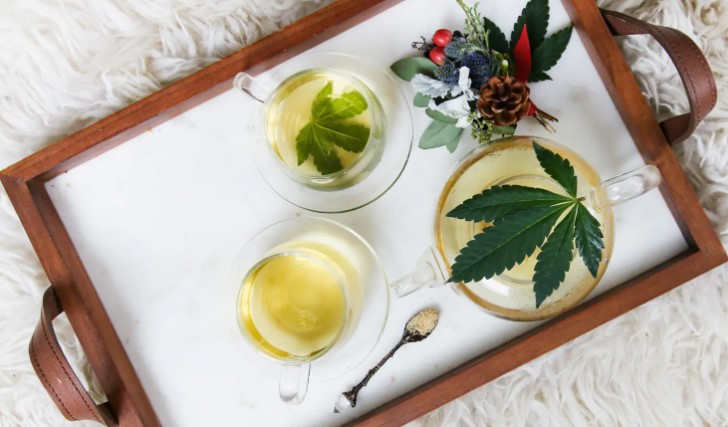
Making Cannabis Leaf Tea
Cannabis leaves, often overlooked compared to the flowers, have various practical applications. One creative and beneficial use is making cannabis leaf tea. This soothing beverage not only offers a unique taste but also provides potential health benefits without the psychoactive effects commonly associated with cannabis consumption.
Ingredients:
- Fresh or Dried Cannabis Leaves: About 1-2 tablespoons of fresh leaves or 1 teaspoon of dried leaves per cup of tea.
- Water: 1 cup of water per serving.
- Optional Add-ins: Honey, lemon, cinnamon, or ginger for flavor enhancement.
Steps:
- Prepare the Leaves:
- If using fresh leaves, ensure they are clean and free of any contaminants.
- If using dried leaves, measure the appropriate amount.
- Boil Water:
- Bring water to a gentle boil. Use a clean pot or kettle to ensure the purity of your tea.
- Steep the Leaves:
- Place the cannabis leaves in a teapot or a cup.
- Pour the hot water over the leaves, covering them completely.
- Steeping Time:
- Let the leaves steep for about 5-10 minutes. The longer you steep, the stronger the flavor.
- Optional Add-ins:
- Enhance the taste by adding honey, a splash of lemon juice, a pinch of cinnamon, or slices of fresh ginger.
- Strain and Serve:
- After steeping, strain the tea to remove the leaves, making it easier to drink.
- Pour the tea into your favorite cup and enjoy while it’s warm.
Benefits of Cannabis Leaf Tea:
- Rich in Nutrients: Cannabis leaves are a good source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Potential Health Benefits: Some believe cannabis tea may help with relaxation, pain relief, and sleep.
- Non-Psychoactive: Since it’s made from leaves and not buds, cannabis tea typically doesn’t induce a psychoactive high, making it suitable for those who want to avoid the euphoric effects.
By exploring creative ways to utilize cannabis leaves, individuals can make the most out of the entire plant, promoting sustainable and holistic consumption practices.
Juicing Cannabis Leaves for Health Benefits
Juicing cannabis leaves is gaining popularity as a health-conscious practice due to the potential nutritional benefits without the psychoactive effects associated with THC. Raw cannabis leaves are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. Juicing them preserves these nutrients and allows for easy consumption. Here’s how you can prepare and enjoy cannabis leaf juice:
Ingredients:
- Fresh Cannabis Leaves: Harvest fresh leaves from healthy cannabis plants. Typically, a handful of leaves is enough for one serving.
- Additional Greens: Optionally, add other leafy greens like kale, spinach, or lettuce for enhanced flavor and nutrition.
- Fruits: To balance the flavors, include fruits such as apples, oranges, or pineapples.
- Water: A small amount for consistency, if needed.
Steps:
- Clean the Leaves:
- Thoroughly wash the cannabis leaves and any additional greens or fruits you plan to juice.
- Prepare the Juicer:
- Set up your juicer according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Juicing Process:
- Feed the cannabis leaves, other greens, and fruits into the juicer one at a time.
- If the mixture becomes too thick, add a splash of water to facilitate the juicing process.
- Collect the Juice:
- The juicer will separate the liquid from the pulp. Collect the juice in a clean container.
- Serve Immediately:
- Fresh cannabis leaf juice is best consumed immediately to retain its nutritional value.
Benefits of Cannabis Leaf Juice:
- Nutrient-Rich: Cannabis leaves are a good source of vitamins (such as A, C, and K), minerals (including calcium and iron), and antioxidants.
- Potential Health Benefits: Some proponents claim that raw cannabis juice may offer anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties.
- Non-Psychoactive: Since raw cannabis does not undergo decarboxylation, which activates THC, juicing cannabis leaves does not induce a psychoactive high.
It’s important to note that individual responses to cannabis products can vary. Before incorporating cannabis leaf juice into your routine, consult a healthcare professional, especially if you have underlying health conditions or concerns about potential interactions with medications.
Crafting Thai Sticks: Utilizing Leaves for Smoking
Thai sticks are a traditional method of smoking cannabis, originating from Thailand. This technique involves creating a tightly packed, cigar-like joint using cannabis buds and leaves. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to craft your own Thai sticks:
Materials Needed:
- Cannabis Buds: Select high-quality, fluffy, and soft cannabis buds for optimal packing.
- Cannabis Leaves: Choose large, flexible cannabis leaves that are clean and dry.
- String or Twine: To secure the Thai stick tightly.
- Stick, Skewer, or Stem: Used as a core for wrapping the buds and leaves.
- Hash Oil or Sugar Water: Acts as a glue to hold the buds and leaves together.
- Parchment Paper: Used during the fusion and curing processes.
- Hemp Wick or Lighter: For ignition.
- Optional: Concentrates or Hash Oil: To enhance potency, spread a thin layer of concentrates over the cannabis buds before wrapping.
Steps:
1. Quality Control:
- Open your stash and select the fluffiest and softest buds. These buds pack down effectively and provide a better smoking experience.
2. Prepare the Stick:
- Paint the stick, skewer, or stem with a layer of hash oil or sugar water. This acts as a glue to hold the buds together and enhances potency.
3. Wrap the Buds:
- Skewer the buds and spiral-wrap them tightly from top to bottom using hemp string, ensuring consistent girth along the stick.
4. Fusion Process:
- Wrap the tied buds in parchment paper and refrigerate for 24-48 hours. This allows the buds to fuse together, forming a cohesive unit.
5. Additional Wrapping:
- Unwrap the buds and apply another layer of sugar water or hash oil.
- Wrap the buds in fresh cannabis leaves, repeating this process twice for three layers of leaves. Ensure the substance is applied between each layer.
6. Sealing the Stick:
- Warm the stick over a hot surface, melting the oil/sugar water and allowing it to spread over the leaves. Rewrap the stick tightly in hemp string and parchment paper. Refrigerate for 3-5 days to cure the Thai stick fully, enhancing its shelf life and preserving the strain’s flavor.
7. Final Step:
- Remove the hemp string and the stick from the middle of the Thai stick before lighting it.
Note: Crafting Thai sticks is a detailed process that requires patience and attention to detail. Exercise caution, adhere to local laws and regulations, and enjoy the smoking experience responsibly.
Creative Culinary Uses: Incorporating Cannabis Leaves in Recipes
Cannabis leaves, often overlooked, can be creatively incorporated into various culinary delights, adding unique flavors and potential health benefits to your dishes. Here are some creative culinary uses for cannabis leaves:
1. Cannabis Leaf Pesto:
- Blend fresh cannabis leaves with garlic, pine nuts, Parmesan cheese, olive oil, and a bit of lemon juice to create a flavorful cannabis leaf pesto. Use it as a spread, dip, or pasta sauce.
2. Cannabis Leaf Smoothies:
- Add fresh cannabis leaves to your favorite smoothie recipe. The leaves blend well with fruits, vegetables, yogurt, and juice, offering a nutrient boost and a subtle herbal taste.
3. Cannabis Leaf Salad:
- Combine fresh cannabis leaves with other greens, vegetables, and your favorite salad toppings. Drizzle with a cannabis-infused vinaigrette for a refreshing and nutritious cannabis leaf salad.
4. Cannabis Leaf Wraps:
- Use large cannabis leaves as natural wraps for rice, vegetables, and protein fillings. Steam or bake the wrapped ingredients for a unique and healthy dish.
5. Cannabis Leaf Chips:
- Coat cannabis leaves with a light layer of olive oil and seasonings, then bake them until crisp. These cannabis leaf chips make a nutritious and crunchy snack alternative.
6. Cannabis Leaf Infusions:
- Steep fresh or dried cannabis leaves in hot water to create a calming and aromatic cannabis leaf tea. Add honey or lemon for flavor. You can also infuse cannabis leaves in warm milk to make a soothing bedtime beverage.
7. Cannabis Leaf Butter:
- Infuse butter with cannabis leaves to create cannabis-infused butter. Use this butter in baking or as a spread for bread and pancakes. Ensure proper decarboxylation for optimal potency.
8. Cannabis Leaf Ice Cream:
- Blend cannabis leaves into the base of your favorite ice cream recipe. The leaves add a mild herbal flavor to the ice cream, creating a unique dessert experience.
Note: When using cannabis leaves in culinary creations, it’s essential to decarboxylate them properly if you desire the psychoactive effects. Experiment with quantities to find the right balance between flavor and potency in your dishes. Always label cannabis-infused foods clearly and keep them out of reach of children and pets.
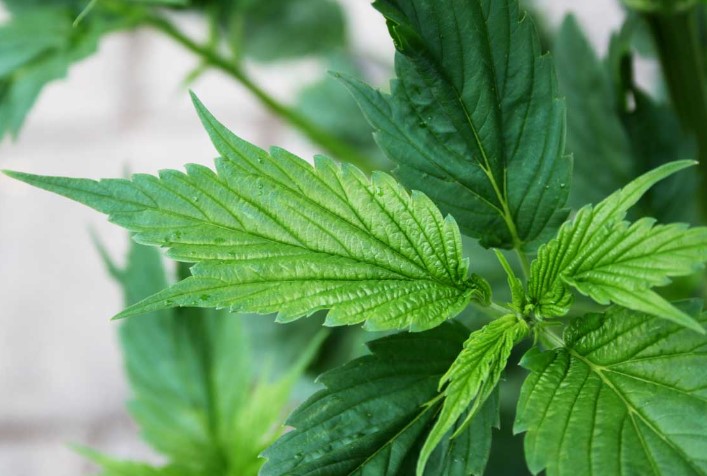
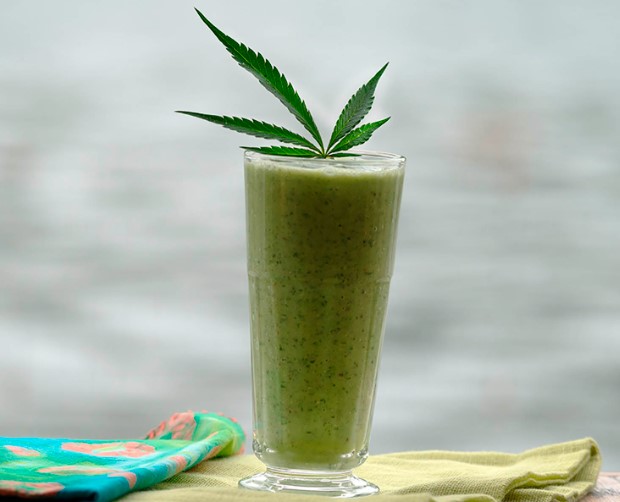
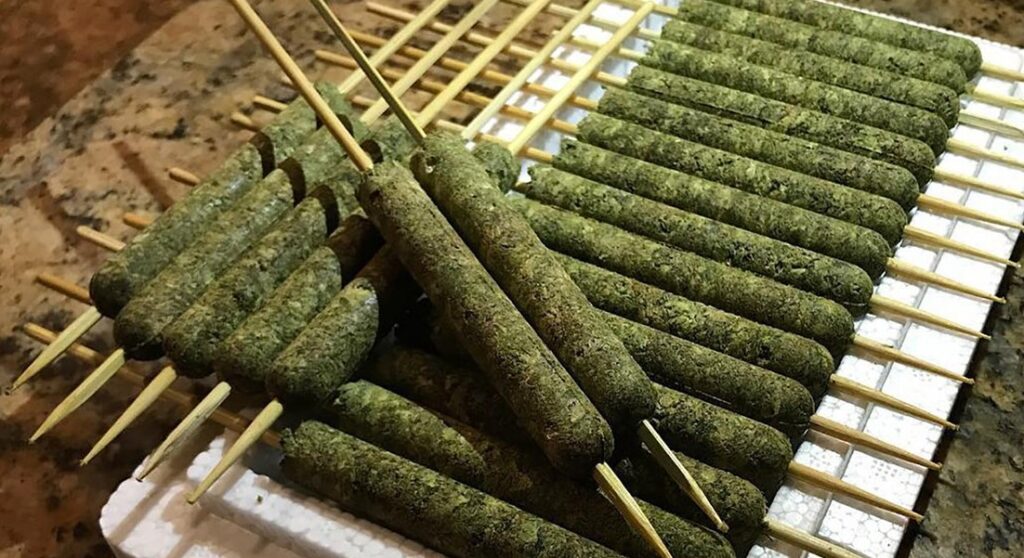





















I tried them in a smoothie, not great flavor but i probably did it wrong.
Trying a smoothie as we speak, very green!