What is a VPD Chart | Vapor Pressure Deficit?
Vapor Pressure Deficit, or VPD, is a crucial factor in optimizing plant growth in controlled environments. By using a VPD chart, growers can determine the ideal ranges for their plants during different stages of growth. The VPD values help to balance transpiration, or the loss of water through plant leaves, which is vital for nutrient transport. A high VPD value can cause excessive transpiration, while a low value can hinder transpiration and lead to water condensation, which increases the risk of fungal growth and other diseases. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of VPD and how to use a VPD chart to maximize plant health and yields.
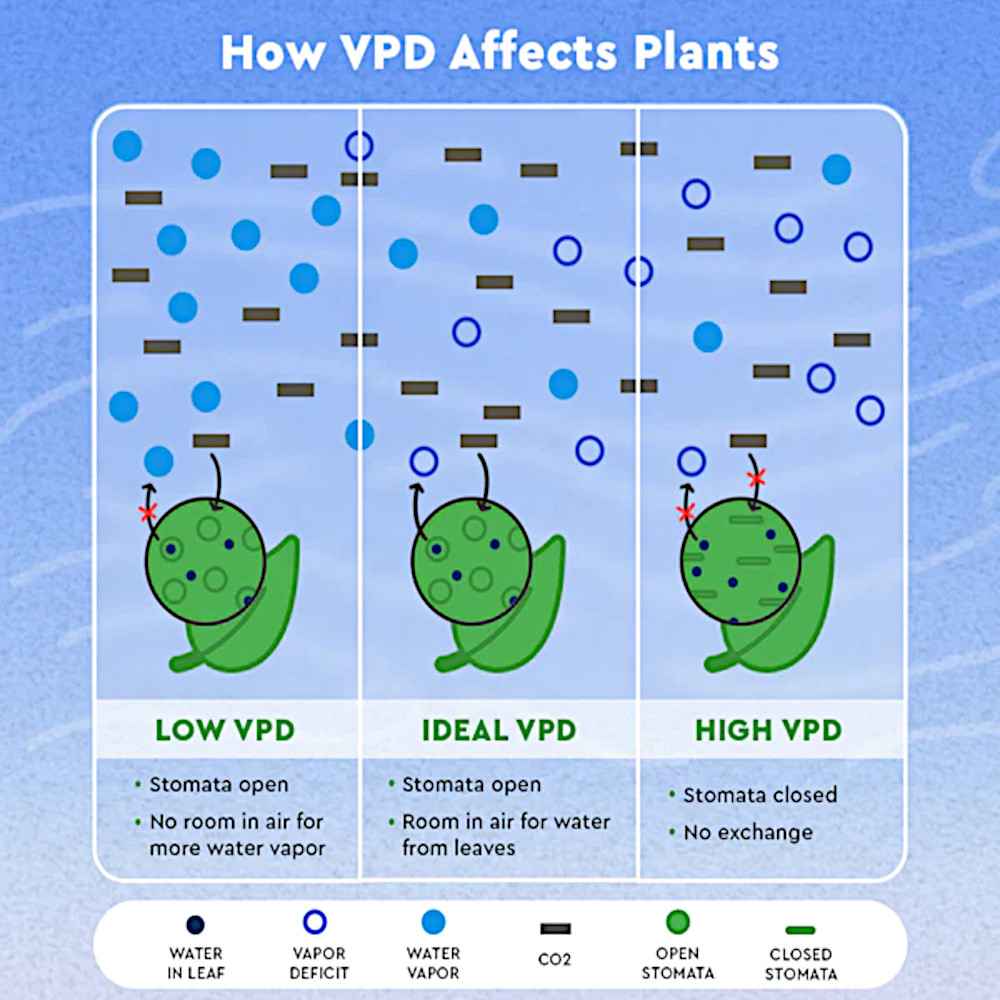
How does VPD affect cannabis growth?
Understanding the effects of Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD) on your cannabis plants is essential to maximizing your yields and producing high-quality buds. VPD is a measure of the difference between the amount of moisture in the air and the amount of moisture the air can hold when it’s saturated. VPD affects plant growth by regulating the amount of water vapor that the plant can lose through transpiration.
One of the first areas of the plant affected by VPD is the stomata, which are small openings on the leaves that allow for gas exchange. Higher VPD levels cause the stomata to constrict to prevent excessive water loss, which reduces the amount of CO2 that the plant can absorb. This, in turn, directly affects photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into organic compounds. Adjusting VPD levels can help fine-tune this process and improve the plant’s growth and yield.
Higher VPD levels also speed up the transpiration of water from the leaf to the air, which increases the ability of the roots to absorb nutrients from the soil. However, excessive VPD levels can stress the plant and negatively affect its quality, growth, and yield. This is where a cannabis VPD chart comes in handy. By using a chart, growers can ensure that their plants are within the optimal VPD range for their specific growth stage, temperature, and humidity levels.
In summary, VPD plays a crucial role in cannabis growth and can significantly impact plant health, quality, and yield. By understanding and controlling VPD levels, growers can fine-tune their plant’s photosynthesis process and improve nutrient uptake, ultimately resulting in healthier and more abundant yields.
How do I check VPD
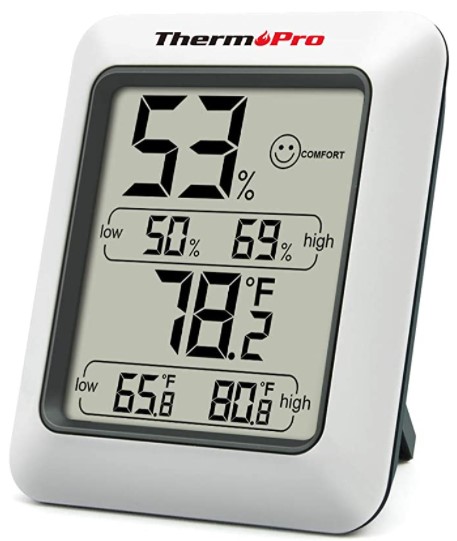
You can check VPD by using a digital hygrometer to measure the temperature and relative humidity in your grow room. Once you have these readings, you can use a VPD chart or calculator to determine the optimal VPD range for your specific growth stage. You can then compare the optimal VPD range with the VPD measurement from your hygrometer to determine if adjustments need to be made to the temperature, humidity, or both.
VPD Chart for Cannabis
| Growth Stage | Temperature (°F) | Humidity (%) | Lights on Optimal VPD Range (kPa) | Lights off Optimal VPD Range (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seedling | 68-77 | 70-75 | 0.3-0.7 | 0.2-0.5 |
| Vegetative | 70-85 | 40-70 | 0.8-1.2 | 0.6-1.0 |
| Early Flower | 70-78 | 40-50 | 1.0-1.5 | 0.8-1.2 |
| Mid Flower | 68-75 | 40-50 | 1.2-1.7 | 1.0-1.5 |
| Late Flower | 65-72 | 40-50 | 1.5-1.8 | 1.2-1.7 |
| Pre-Harvest | 60-68 | 40-50 | 1.2-1.8 | 1.0-1.5 |
Note: The recommended temperature and humidity levels are general guidelines for cannabis growth and may vary depending on the specific strain being cultivated.
During the seedling stage, it’s important to maintain a relatively high humidity level to prevent the young plants from drying out. As the plants move into the vegetative stage, humidity can be gradually reduced to prevent the onset of mold and mildew. During the flowering stage, humidity levels should be kept low to prevent bud rot, but not so low as to cause the plants to dry out.
In general, a VPD range of 0.8-1.2 kPa is recommended for the vegetative stage, while a range of 1.0-1.8 kPa is recommended for the flowering stage. During pre-harvest, a slightly higher VPD range of 1.2-1.8 kPa can help to promote resin production and enhance the potency of the buds.
It’s important to regularly monitor the VPD levels and adjust temperature, humidity, and airflow as needed to ensure optimal plant growth and health. A VPD chart can be a valuable tool for growers looking to maximize their yields and produce high-quality cannabis crops.
How your Grow Light affects VPD
When it comes to indoor cannabis cultivation, selecting the appropriate grow light is crucial for optimal plant growth and yield. Light intensity is a significant factor that indirectly affects VPD by influencing the plant’s temperature.
It is recommended to choose bulbs with a higher intensity from the start, as it’s easier to reduce intensity than to increase it later. Higher light intensity levels can lead to denser plants with higher yields, but it’s important to balance it with other factors like temperature and humidity to avoid excessive VPD levels.
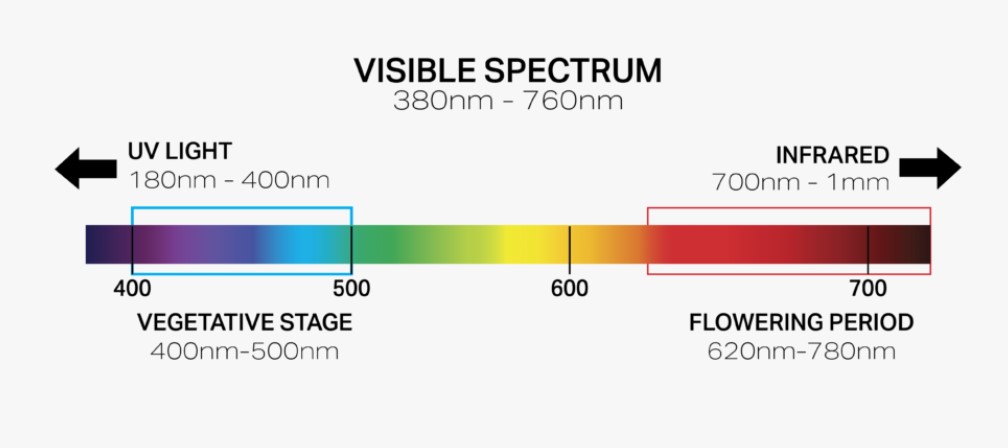
The light color is also a critical consideration when selecting a grow light for cannabis. Different wavelengths of light are required during each growth stage, with the vegetative stage favoring blue light, while the flowering stage requires red light for optimal growth. Choosing the appropriate light spectrum during each growth stage can help ensure that your plants receive the right light for optimal growth and yield.
When selecting a grow light, it’s important to consider factors such as cost, energy efficiency, and the size of your grow space. LED grow lights are a popular choice for indoor cannabis cultivation due to their low heat output, energy efficiency, and customizable light spectrum.
In summary, selecting the right grow light is an essential component of successful indoor cannabis cultivation. By choosing the appropriate light intensity and color for each growth stage, growers can optimize VPD levels and ensure that their plants are receiving the right spectrum of light for optimal growth and yield.


Bookmarked so I can follow along with my grow