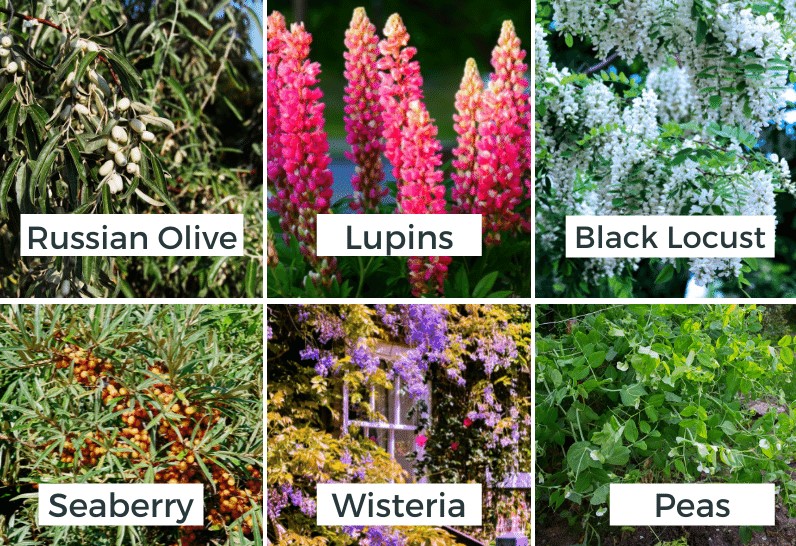
The popularity of cannabis continues to rise, so does the interest in companion planting. Companion planting is the practice of planting different crops together to improve growth and yield. In the case of cannabis, companion planting can enhance its medicinal properties, deter pests, and promote overall plant health.
In this article, we will explore the benefits of companion planting and the different techniques used, including intercropping, trap cropping, banker plants, nitrogen fixing, and biochemical pest suppression. We will also discuss the rules of companion planting and provide a list of the best plants for companion planting with cannabis.
Whether you’re a seasoned cannabis grower or just starting out, incorporating companion plants into your garden can improve your cannabis yield and create a thriving ecosystem for your plants. So let’s dive into the world of companion planting and discover the best cannabis companion plants.
I. Introduction
- Explanation of companion planting and its benefits for cannabis growth and yield
II. Techniques of Companion Planting
- Intercropping: planting multiple crops together for mutual benefit
- Trap cropping: using sacrificial plants to attract pests away from the main crop
- Banker plants: hosting beneficial insects to control pests
- Nitrogen fixing: using plants that fix nitrogen in the soil to benefit cannabis
- Biochemical pest suppression: using plants with natural pesticides to deter pests
III. The Rules of Companion Planting
- Companion planting principles to follow when choosing plants to grow with cannabis
IV. Best Cannabis Companion Plants
- A list of the best companion plants for cannabis, including:
- Herbs and flowers for pest control and soil enrichment
- Vegetables for mutual benefit and pest control
- Cover crops for soil health and pest control
V. Conclusion
- Recap of the benefits of companion planting for cannabis and the importance of selecting the right companion plants.
Introduction: What is Companion Planting
Companion planting is a time-tested agricultural practice that involves growing different plant species together for mutual benefit. This technique can enhance soil health, increase yield, and reduce pest infestations in a natural and sustainable way.
When it comes to cannabis, companion planting offers numerous advantages. For instance, planting certain herbs and flowers alongside marijuana can attract beneficial insects that prey on common cannabis pests like spider mites and aphids. Similarly, planting nitrogen-fixing plants like clover or beans can enrich the soil and promote healthy cannabis growth.
Companion planting also helps to create a diverse and dynamic ecosystem in which plants support each other in various ways. Some plants, for example, release compounds that repel pests, while others provide shade or windbreaks. Additionally, certain plants can attract pollinators like bees and butterflies, which can increase yields in cannabis crops.
Perhaps one of the most famous examples of companion planting is the Native American “Three Sisters” method, which involves planting corn, beans, and squash together. Corn provides support for the climbing beans, which in turn fix nitrogen in the soil to benefit all three plants. The squash, meanwhile, shades the soil to retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Overall, companion planting is a powerful tool for cannabis growers seeking to cultivate a healthy, sustainable, and pest-resistant crop. By choosing the right combination of companion plants and adhering to basic principles of intercropping, growers can optimize their cannabis yield and reduce the need for harmful pesticides and fertilizers.
II. Techniques of Companion Planting:
1. Intercropping: planting multiple crops together for mutual benefit
Intercropping is a popular technique of companion planting that involves planting two or more crops together in the same space. This technique can be highly beneficial for cannabis growers, as it allows for the efficient use of space and resources, increased biodiversity, and improved soil health.
The idea behind intercropping is to create a mutually beneficial environment where each crop supports the growth of the others. For cannabis growers, this means selecting companion plants that can enhance the soil, suppress weeds, and deter pests without competing for resources with the cannabis plants.
One popular intercropping strategy is to plant cover crops between cannabis rows. Cover crops like clover, alfalfa, or vetch can help to fix nitrogen in the soil, improve soil structure, and suppress weed growth. These plants can also attract beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings, which can prey on common cannabis pests.
Another intercropping strategy involves planting herbs and flowers alongside cannabis plants. Herbs like basil, mint, or rosemary can repel pests with their strong aromas and may attract pollinators like bees and butterflies. Similarly, flowering plants like marigolds or calendula can deter pests and attract beneficial insects, while also adding beauty to the garden.
When intercropping, it’s important to select companion plants that have complementary growth habits and nutrient requirements. For instance, fast-growing plants like radishes or lettuce can be planted between cannabis rows to take advantage of the available space, while slow-growing plants like tomatoes or peppers can be planted around the perimeter of the cannabis garden.
Intercropping can also be used to create a natural barrier against pests and diseases. For example, planting garlic or chives around the perimeter of the garden can repel pests like spider mites and aphids, while also adding flavor to the garden.
In summary, intercropping is a powerful technique of companion planting that can benefit cannabis growers in a number of ways. By selecting complementary companion plants and adhering to basic principles of intercropping, growers can optimize their cannabis yield, improve soil health, and reduce the need for harmful pesticides and fertilizers.
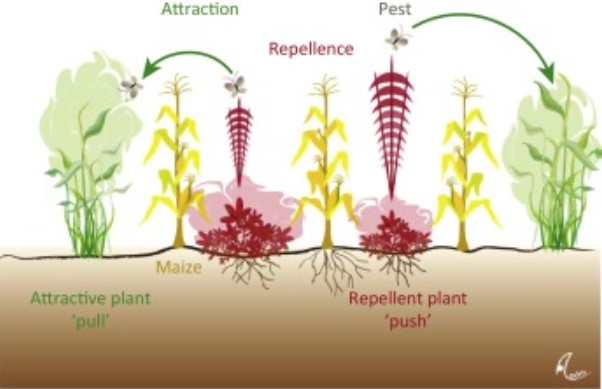
2. Trap cropping: using sacrificial plants to attract pests away from the main crop
Trap cropping is a companion planting technique that involves planting a sacrificial crop to attract and trap pests away from the main crop, which in this case is cannabis. By planting a crop that is more attractive to pests than cannabis, trap cropping can help to reduce the damage caused by pests and minimize the need for pesticides.
The idea behind trap cropping is to use a plant that is highly attractive to the target pest, often called the “trap crop.” The trap crop is planted in close proximity to the main crop, in the hopes that pests will prefer the trap crop and leave the main crop alone.
For cannabis growers, some potential trap crops include plants like clover, radish, or sunflower. These plants are known to attract pests like aphids, whiteflies, and thrips, which can cause significant damage to cannabis plants.
One popular trap cropping technique for cannabis is to plant a row of sunflowers around the perimeter of the garden. Sunflowers are highly attractive to many types of pests, including aphids, thrips, and whiteflies. By planting sunflowers around the garden, cannabis growers can help to divert these pests away from the cannabis plants.
Another effective trap crop for cannabis is clover. Clover attracts a variety of pests, including spider mites and thrips. By planting clover between cannabis rows, growers can help to lure these pests away from the cannabis plants and towards the clover.
In addition to reducing pest damage, trap cropping can also be beneficial for soil health. By planting a diverse range of crops, growers can help to promote beneficial soil microbes and reduce soil-borne diseases.
When using trap cropping, it’s important to select a trap crop that is highly attractive to the target pest, but is not a host for the pest. This means that the trap crop should not provide a suitable environment for the pest to reproduce or feed, and should ideally be a dead-end host.
In summary, trap cropping is a powerful technique of companion planting that can help cannabis growers to reduce pest damage and minimize the need for harmful pesticides. By selecting the right trap crop and planting it strategically, growers can optimize their cannabis yield and promote a healthy, biodiverse garden environment.
3. Banker plants: hosting beneficial insects to control pests
Banker plants are a type of companion plant used in cannabis cultivation that involves using a specific type of plant to attract and sustain a population of beneficial insects. The beneficial insects can then be used to control harmful pests that may threaten the health of the cannabis crop.
The idea behind banker plants is to provide a continuous source of food and habitat for beneficial insects, which can help to maintain a stable population throughout the growing season. By using banker plants, cannabis growers can reduce the need for harmful pesticides and promote a more sustainable, eco-friendly growing environment.
One of the most popular banker plants for cannabis cultivation is the ornamental pepper plant (Capsicum annuum). The ornamental pepper plant is a preferred host for the predatory insect species Orius insidiosus, also known as the minute pirate bug. Minute pirate bugs are known to feed on a variety of harmful pests, including thrips, spider mites, and whiteflies. By providing a continuous source of food and habitat for minute pirate bugs, ornamental pepper plants can help to control these pests throughout the growing season.
Another popular banker plant for cannabis is the sweet alyssum (Lobularia maritima). Sweet alyssum is an attractive host for a variety of beneficial insects, including parasitic wasps, hoverflies, and lacewings. These insects are known to prey on a range of pests, including aphids, whiteflies, and thrips.
In addition to attracting beneficial insects, banker plants can also be used to provide a source of nutrition for the cannabis plants themselves. For example, clover is a popular banker plant that can fix nitrogen in the soil, providing a natural source of fertilizer for the cannabis plants.
When using banker plants, it’s important to select a plant species that is well-suited to the growing conditions of the cannabis crop. It’s also important to monitor the population of beneficial insects to ensure that they are effectively controlling pest populations.
In summary, banker plants are a powerful tool for cannabis growers looking to promote a sustainable, eco-friendly growing environment. By providing a continuous source of food and habitat for beneficial insects, growers can reduce the need for harmful pesticides and promote a healthier, more resilient cannabis crop.
4. Nitrogen fixing: planting plants that fix nitrogen in the soil to benefit cannabis
This is a type of companion planting technique used in cannabis cultivation that involves growing plants that have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen into a form that can be used by other plants in the same growing area. Nitrogen is one of the most important nutrients required for healthy plant growth, and is often a limiting factor in many growing environments.
Nitrogen-fixing plants are able to convert atmospheric nitrogen gas into a form that can be used by other plants in the soil. This is achieved through a symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing bacteria that live in specialized root nodules. These bacteria are able to take in atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into ammonium, which can then be used by the host plant.
One of the most popular nitrogen-fixing plants for cannabis cultivation is the clover plant (Trifolium spp.). Clover is a fast-growing plant that is able to fix significant amounts of nitrogen in the soil. By growing clover as a companion plant, cannabis growers can provide a natural source of nitrogen to their crops, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and promoting healthier, more vigorous growth.
Other nitrogen-fixing plants that are commonly used in cannabis cultivation include alfalfa (Medicago sativa), beans (Phaseolus spp.), and peas (Pisum spp.). These plants are all able to fix significant amounts of nitrogen in the soil and can be used to promote healthy growth in cannabis crops.
When using nitrogen-fixing plants as companion plants, it’s important to ensure that they are well-suited to the growing conditions of the cannabis crop. They should also be planted in sufficient quantities to provide an adequate source of nitrogen to the cannabis plants.
In summary, nitrogen fixing is a powerful companion planting technique that can help to promote healthy growth in cannabis crops. By growing nitrogen-fixing plants as companion plants, cannabis growers can provide a natural source of nitrogen to their crops, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and promoting a more sustainable, eco-friendly growing environment.
5. Biochemical pest suppression: using plants with natural pesticides to deter pests
Biochemical pest suppression is a cannabis companion planting technique that involves the use of plants that release natural chemicals or compounds that repel or deter pests. These chemicals can be used to control pest populations without the need for chemical pesticides, which can be harmful to the environment and to human health.
There are a number of plants that have been shown to have natural pest-repelling properties, including marigolds (Tagetes spp.), lavender (Lavandula spp.), and garlic (Allium sativum). These plants release natural chemicals that can repel pests like aphids, spider mites, and whiteflies, which can be major pests in cannabis cultivation.
One of the most popular plants for biochemical pest suppression in cannabis cultivation is the marigold plant. Marigolds release a natural chemical called alpha-terthienyl, which has been shown to be effective at repelling nematodes, a type of pest that can cause significant damage to cannabis plants.
Another plant that is commonly used for biochemical pest suppression in cannabis cultivation is the neem tree (Azadirachta indica). Neem trees produce a natural pesticide called azadirachtin, which can be extracted from the leaves and used to control pests like spider mites, thrips, and whiteflies.
When using biochemical pest suppression as a companion planting technique, it’s important to ensure that the pest-repelling plants are well-suited to the growing conditions of the cannabis crop. They should also be planted in sufficient quantities to provide an effective deterrent against pests.
In summary, biochemical pest suppression is a valuable companion planting technique that can help to control pest populations in cannabis cultivation without the need for chemical pesticides. By using plants that release natural pest-repelling chemicals, cannabis growers can promote a more sustainable and eco-friendly growing environment, while also promoting healthier, more vigorous growth in their cannabis crops.
III. The Rules of Companion Planting
When choosing companion plants to grow with cannabis, it’s important to follow some basic principles of companion planting. These principles can help to ensure that the companion plants provide the intended benefits, and that they do not have any negative effects on the growth and health of the cannabis crop.
- Choose plants with complementary growing requirements: When choosing companion plants, it’s important to select plants that have similar growing requirements to the cannabis crop. This includes factors like sunlight, water, and soil pH. Plants that have vastly different growing requirements may compete with the cannabis crop for resources, or may not thrive in the same growing conditions.
- Consider the height and growth habits of companion plants: Companion plants should be chosen with consideration for their height and growth habits. Plants that are too tall or bushy may shade the cannabis crop and limit its access to sunlight. Similarly, plants with sprawling growth habits may interfere with the growth of the cannabis crop.
- Choose plants with different root systems: Companion plants with different root systems can help to improve soil structure and prevent soil-borne diseases. For example, plants with deep taproots can help to break up compacted soil and improve drainage, while plants with shallow roots can help to stabilize the soil and prevent erosion.
- Use a variety of companion plants: Using a variety of companion plants can help to provide a range of benefits to the cannabis crop. For example, some plants may help to repel pests, while others may provide beneficial nutrients to the soil. Using a diverse range of companion plants can help to ensure that all of these benefits are provided.
- Avoid planting certain plants together: Some plants may have negative effects on the growth and health of the cannabis crop. For example, plants in the nightshade family (like tomatoes and peppers) may attract pests that also target cannabis plants. Additionally, plants that release allelopathic compounds (compounds that can inhibit the growth of other plants) should be avoided.
By following these basic principles of companion planting, cannabis growers can choose companion plants that will provide a range of benefits to their crops. This can help to improve the overall health and yield of the cannabis plants, while also promoting a more sustainable and eco-friendly growing environment.
IV. Best Cannabis Companion Plants
When it comes to choosing the best companion plants for cannabis, there are many options to consider. Companion plants can provide numerous benefits, such as deterring pests, improving soil health, and even increasing yield. Here are some of the best companion plants to consider when growing cannabis:
- Herbs and Flowers for Pest Control and Soil Enrichment Herbs such as basil, rosemary, and thyme are great for deterring pests like spider mites and whiteflies. They also add beneficial nutrients to the soil and can improve the taste and aroma of the cannabis plant. Flowers like marigolds and chamomile are also effective at deterring pests and can attract beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings.
- Vegetables for Mutual Benefit and Pest Control Vegetables like peppers and tomatoes can be grown alongside cannabis plants, as they have similar growing requirements and can provide mutual benefits. Peppers contain capsaicin, which deters pests like aphids and spider mites, while tomatoes can attract predatory insects like ladybugs and parasitic wasps. Additionally, both peppers and tomatoes are rich in nutrients and can improve soil health.
- Cover Crops for Soil Health and Pest Control Cover crops like clover, alfalfa, and rye can be grown in between cannabis plants to improve soil health and prevent weeds. Clover and alfalfa are nitrogen-fixing plants, which means they can add nitrogen to the soil and improve its fertility. Rye is also effective at suppressing weeds and can prevent pests like nematodes from damaging the cannabis roots.
In summary, choosing the right companion plants for cannabis can have numerous benefits for both the cannabis plant and the overall garden ecosystem. By incorporating herbs, flowers, vegetables, and cover crops into your garden, you can create a healthy and thriving environment for your cannabis plants to grow and flourish.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, companion planting is a highly effective method for enhancing the growth, yield, and overall health of cannabis plants. When selecting companion plants, it is crucial to consider factors such as nutrient requirements, growth habits, and pest resistance to ensure optimal results. By carefully selecting the right companion plants, cannabis growers can create a thriving, sustainable ecosystem that supports the health and vitality of their cannabis plants. Overall, companion planting is an excellent way to promote the health and success of cannabis crops while minimizing the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.