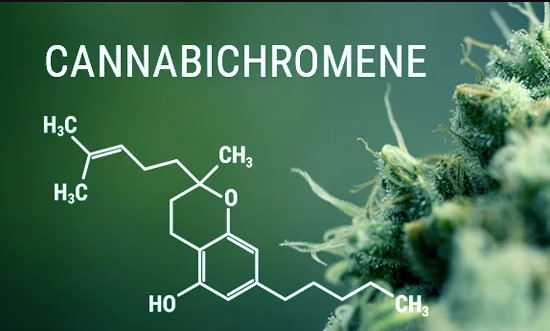
While the names tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) may be reminiscent of something, very few know a cannabis compound called cannabichromene (CBC).
This is unfortunate because cannabichromene is actually the second most abundant cannabinoid in Cannabis, which means that there is probably more CBC in your Cannabis than CBD, even though CBD seems to be getting all the attention.
But research over the last few decades has shown that a number of reasons why we should learn about it the non-psychoactive compound. Here are 5 of them:
Fights bacteria and fungi
One of the first studies to include cannabichromene was published in 1981 by the University of Mississippi. In the study, the researchers found that cannabichromene showed “strong” antibacterial activity in a variety of gram-positive, gram-negative and acid-fast bacteria, including E. coli and Staph (S. aureus). CBC also showed “mild to moderate” activity against various types of fungi, including a common food contaminant, known as black mould (Aspergillus niger).
Anti-inflammatory properties
Recent animal studies show that CBC may reduce swelling (swelling), as well as inflammation of the intestinal tract.
Interestingly, the CBC seems to be fighting inflammation without activating cannabinoid receptors. That could explain why CBC produces a stronger anti-inflammatory effect when combined with other cannabinoids such as THC.
Relieves pain
Cannabichromene has also been found to reduce pain in animals, although its action may not be as strong as that of THC. However, a study published in 2011 concluded that the CBC and the CBD together could fight pain “interacting with several targets involved in its control”. at the level of the spinal cord. Since CBC and CBD are non-psychoactive, scientists are optimistic that these cannabis compounds can be used for the treatment of pain without the presence of “fixation”.
Fights depression
A more recent study from the University of Mississippi found the significant antidepressant effect of cannabichromene in rats, concluding that the CBC and a number of other cannabinoids can contribute to the general properties of Cannabis concerned in raising the mood. Scientists are still trying to understand more on how CBC does this, as it does not appear to activate the same pathways in the brain as THC.
Stimulates brain development
Research on cannabinoids has just been published that highlighted one of its most unique benefits of association: It can really help the brain to grow! In particular, the CBC has been seen to increase the viability of developing brain cells, a process known as neurogenesis.
Contrary to popular belief, neurogenesis does not stop there reaching a certain age. However, this only happens in one specific part of the adult brain called the hippocampus.
The hippocampus is important for memory and learning and deficiency development in this area is believed to contribute to a number of disorders, including depression and Alzheimer’s.
While the ability of cannabichromene to promote neurogenesis is a recent finding, previous studies show that both THC and CBD can do the same.
As Dr. Xia Jiang of the University of Saskatchewan explained, one of the first scientists to discover this remarkable
Cannabis influence in an interview with Science Daily: “Most” abusive drugs “suppress neurogenesis.
Cannabis alone promotes neurogenesis. “Opiates, alcohol, nicotine and cocaine are known to inhibit brain development. Fortunately, the cannabichromene and other elements of Cannabis seem to have the opposite
result.

