In the intricate world of cannabis cultivation, the role of male plants and their pollen often remains overshadowed by their more celebrated female counterparts. Yet, understanding cannabis pollen and its significance is vital for anyone seeking to delve deeper into the art and science of cannabis cultivation. This article explores the often-overlooked realm of cannabis pollen, shedding light on its structure, purpose, and how growers can harness its potential. From the basics of male cannabis plants to the meticulous process of collecting and storing pollen, this comprehensive guide offers insights into the essential aspects of cannabis pollination. Whether you are a novice cultivator or an experienced breeder, this exploration of cannabis pollen will equip you with valuable knowledge to enhance your growing endeavors. Join us on this journey through the intricate world of cannabis reproduction, where every pollen grain holds the potential for new and exciting strains.
- Introduction
- Definition of Cannabis Pollen
- Importance of Male Cannabis Plants in Seed Production
- Types of Cannabis Plants
- Dioecious and Monoecious Plants
- Hermaphroditism in Cannabis Plants
- Understanding Pollen
- Structure and Appearance of Pollen
- Role of Pollen in Cannabis Reproduction
- Uses of Cannabis Pollen
- Seed Production and Genetic Variation
- Breeding New Cannabis Strains
- Collecting and Storing Pollen
- Techniques for Collecting Pollen
- Proper Storage Methods and Viability
- Pollination Process
- How to Pollinate Female Cannabis Plants
- Importance of Pollination Timing
- Reasons for Collecting Pollen
- Creating New Strains vs. Maintaining Mother Plants
- Advantages of Harvesting Your Own Pollen
- Pollinating Autoflowering Cannabis Strains
- Possibilities and Considerations for Autoflowering Seeds
- Cannabis Pollen FAQs
- Viability Period and Proper Storage
- Differences Between Male Pollen and Hash Pollen
- Conclusion
- Importance of Male Cannabis Plants in Cannabis Cultivation
- Tips for Successful Pollen Collection and Usage
Introduction to Cannabis Pollen
Definition of Cannabis Pollen
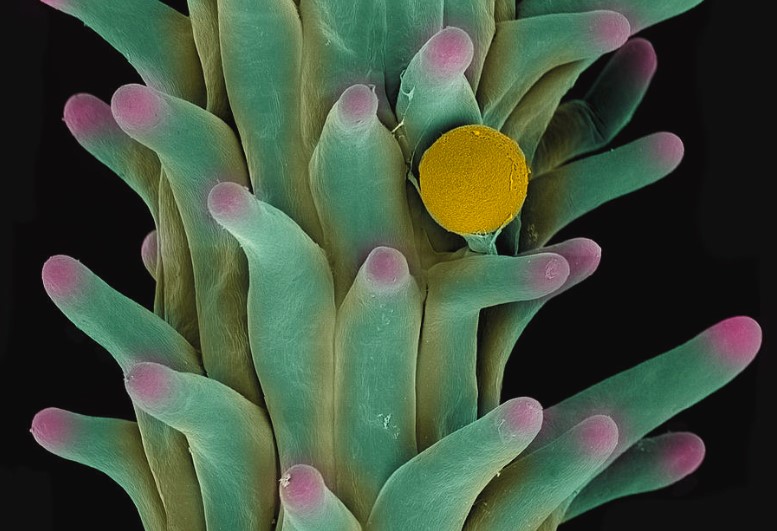
Cannabis pollen, the microscopic powder-like substance, plays a pivotal role in the reproduction of cannabis plants. It originates from the male cannabis plant and contains male gametes essential for fertilization. Unlike female plants that produce buds, male plants develop pollen sacs, which, upon maturity, release pollen into the air. These tiny grains carry the genetic information of the male plant, which combines with female gametes to form cannabis seeds. This fundamental biological process underpins the continuity of cannabis species and serves as the foundation for cannabis cultivation. Understanding the nature and composition of cannabis pollen is crucial for growers and breeders, as it enables them to harness the plant’s genetic diversity, leading to the creation of unique and desirable cannabis strains.
Importance of Male Cannabis Plants in Seed Production
In the realm of cannabis cultivation, both male and female plants have distinct roles. Male cannabis plants are responsible for producing pollen, the life-giving substance that facilitates the fertilization of female plants. This fertilization process is essential for seed production. Seeds, in turn, are the foundation for future cannabis crops, enabling genetic diversity and the development of novel strains. While male plants do not produce the resinous buds sought after by many cannabis enthusiasts, their significance lies in their ability to contribute genetic material crucial for the evolution and variation within the cannabis species. For breeders and cultivators aiming to create specific traits, male plants are invaluable, allowing for controlled cross-breeding and the development of desirable characteristics, including flavors, aromas, and potency levels.
Types of Cannabis Plants
Dioecious and Monoecious Plants:
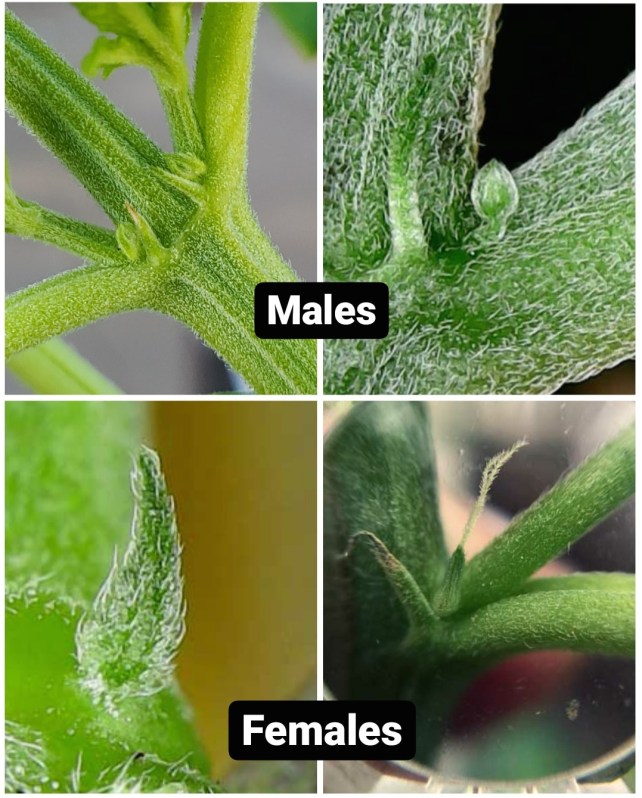
Cannabis plants are categorized into two primary types based on their reproductive structures: dioecious and monoecious. Dioecious plants have distinct male and female individuals, meaning a plant is either male or female. In the context of cannabis cultivation, this implies that some plants exclusively produce male flowers, while others exclusively produce female flowers. Male plants develop pollen sacs, containing pollen grains necessary for fertilizing female plants, leading to seed production. Female plants, on the other hand, develop the resinous buds commonly sought after for consumption.
In contrast, monoecious plants possess both male and female reproductive organs on the same individual. Such plants are also known as hermaphrodites. In the cannabis world, hermaphroditism occurs when a plant, usually female, develops both male and female reproductive parts due to stress or genetic factors. These hermaphroditic plants have the ability to self-pollinate, producing seeds without the involvement of another plant. While dioecious plants are more common, especially in controlled cultivation environments, encountering monoecious cannabis plants is not uncommon and can have significant implications for growers aiming to prevent unintended pollination.
Hermaphroditism in Cannabis Plants:
Hermaphroditism, a natural adaptation mechanism in plants, occurs in response to various environmental stressors, such as abrupt light changes, nutrient deficiencies, or physical damage. When a cannabis plant senses unfavorable conditions or perceives a threat to its survival, it may develop both male and female reproductive parts as a survival strategy. This allows the plant to self-pollinate, ensuring the production of seeds even in challenging circumstances.
For cannabis growers, managing hermaphroditic plants is crucial to prevent unintended pollination and the formation of seeds within buds. Unpollinated female plants, commonly referred to as sensimilla, produce seedless, potent buds highly valued for their resin content. Understanding the triggers for hermaphroditism and implementing proper cultivation practices are essential for maintaining the quality and consistency of cannabis crops, ensuring optimal yields and potent, seed-free flowers for consumption.
Understanding Pollen
Structure and Appearance of Pollen:
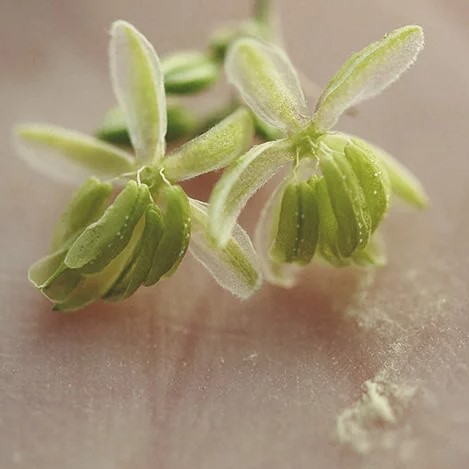
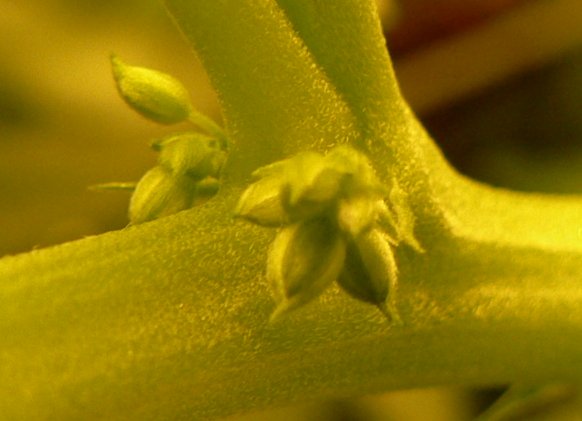
Cannabis pollen, despite its microscopic size, possesses a distinctive structure crucial to its reproductive function. Under a microscope, cannabis pollen grains appear as tiny, powdery spheres, finer than sand particles. These grains, originating from the male cannabis plant, carry genetic information essential for fertilization. Each pollen grain comprises male gametes, representing the male reproductive contribution. Due to its minuscule size and lightweight nature, pollen can be easily carried by the wind, facilitating its dispersal over considerable distances. The appearance of cannabis pollen is typically yellow or gray, and growers must handle it with extreme care to prevent contamination of nearby female plants during the pollination process.
Role of Pollen in Cannabis Reproduction:
Pollen serves a pivotal role in the reproduction of cannabis plants, driving the formation of seeds. When mature, male cannabis plants develop pollen sacs, which contain vast quantities of pollen grains. In nature, these grains are released into the air, where they can be carried by the wind or other natural elements. Female cannabis plants, with their receptive stigma, catch these airborne pollen grains. Upon contact, the pollen grain adheres to the stigma, initiating the fertilization process. The male gametes within the pollen grain combine with the female gametes in the ovule, located within the female plant’s reproductive structure. This fusion forms the foundation of genetic diversity within cannabis species, leading to the development of various strains, each with unique characteristics in terms of flavor, aroma, potency, and growth traits.
Understanding the intricate process of cannabis reproduction, specifically the role of pollen, empowers cultivators and breeders to make informed decisions. By manipulating the interactions between male and female plants, growers can create specific genetic combinations, resulting in cannabis strains tailored to meet diverse consumer preferences and market demands.
Uses of Cannabis Pollen
Seed Production and Genetic Variation:
One of the primary uses of cannabis pollen is in seed production, a fundamental process that ensures the perpetuation of the cannabis species. Pollen, carrying the male genetic material, is indispensable for fertilizing female plants and initiating the formation of seeds. Within the ovule of the female plant, the male and female gametes merge, leading to the creation of a genetically unique seed. These seeds, each carrying a distinct combination of genetic traits from both parent plants, contribute to the rich diversity of cannabis strains available today. Seed production not only facilitates the continuation of the cannabis lineage but also allows for the preservation and exploration of specific genetic characteristics, including cannabinoid profiles, terpene compositions, and growth patterns.
Breeding New Cannabis Strains:
Cannabis breeders harness the power of pollen to create new and innovative cannabis strains tailored to meet various consumer preferences and market demands. By selectively cross-breeding plants with desirable traits, breeders aim to enhance specific characteristics, such as potency, flavor, aroma, and resistance to diseases. Pollen from a chosen male plant can be applied to the receptive buds of a female plant, initiating controlled pollination. Through meticulous selection and hybridization processes, breeders can create unique genetic combinations, leading to the development of novel cannabis varieties. Breeding is an art and a science, requiring a deep understanding of genetics and plant biology. Skilled breeders play a vital role in shaping the future of cannabis cultivation, introducing new strains that captivate consumers and push the boundaries of what the cannabis plant can offer.
Understanding the dual roles of cannabis pollen in seed production and breeding empowers cultivators and breeders to make strategic decisions. By leveraging the genetic diversity encapsulated within pollen grains, growers can contribute to the ever-expanding world of cannabis strains, offering enthusiasts an array of choices and experiences.
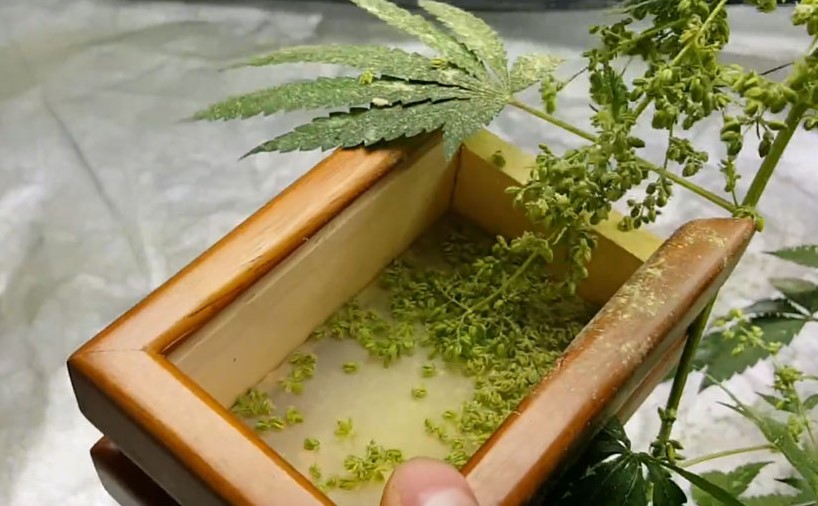

Collecting and Storing Pollen
Techniques for Collecting Pollen:
Collecting cannabis pollen requires precision and caution, as pollen grains are incredibly delicate and easily dispersed. To gather pollen, monitor male plants closely, observing the development of pollen sacs. When these sacs are mature and ready to release pollen, use a gentle shaking motion to encourage pollen to fall into a clean, dry container. Another method involves carefully brushing the male flowers to collect the pollen. Timing is crucial; collecting pollen when it’s at its freshest ensures optimal viability. To prevent accidental contamination, perform this process away from female plants, as even a slight breeze can carry pollen over significant distances.
Proper Storage Methods and Viability:
Proper storage is paramount to preserving the viability of cannabis pollen. Pollen is sensitive to light and moisture, which can degrade its quality. After collection, place the pollen in an airtight container, preferably made of glass, to shield it from light and air. To absorb any excess moisture, include silica gel sachets within the container. For long-term storage, consider keeping the container in the refrigerator, maintaining a cool, dark, and dry environment. It’s crucial to note that pollen viability varies based on storage conditions:
| Temperature/Storage Location | Pollen Viability Duration |
| Room Temperature | Pollen can be stored for 1 to 3 weeks |
| Refrigerator | Pollen remains viable for 2 to 3 months. |
| Freezer | Properly stored pollen can last up to 12 months |
| Liquid Nitrogen | Years |
However, these time frames are estimates, and it’s essential to remove moisture from the pollen before storage. A study conducted at the University of Lethbridge found that by mixing pollen with baked whole wheat flour and preserving agents, freezing it in liquid nitrogen, pollen could possibly remain viable indefinitely.
By following meticulous collection and storage practices, growers and breeders can extend the lifespan of cannabis pollen, ensuring its potency and viability for future breeding endeavors.
Pollination Process
How to Pollinate Female Cannabis Plants:
Pollinating female cannabis plants is a meticulous process that requires careful handling to ensure successful fertilization. Once you have collected viable pollen, there are several methods to pollinate female plants. One approach involves gently shaking the male plant near the receptive female buds, allowing the released pollen to land on the pistils. Alternatively, a soft brush can be used to apply pollen directly onto the stigmas of female flowers. Timing is crucial; pollination should occur when the pistils are fully formed, typically around 3-5 weeks into the flowering stage. During this period, the female plant is most receptive to pollination, enhancing the chances of successful seed development.
Importance of Pollination Timing:
Understanding the optimal timing for pollination is essential for growers and breeders alike. Pollination timing directly impacts seed development and overall crop quality. Pollinating too early, before the pistils are fully developed, can result in incomplete fertilization, leading to underdeveloped seeds or seedless buds. Conversely, pollinating too late may cause the seeds to mature inside overripe, dried-out buds, affecting their viability and quality. By aligning the pollination process with the flowering stage of the female plants, growers can ensure the production of healthy, mature seeds.
Additionally, precise timing is critical for growers aiming to maintain seedless, high-quality buds, commonly referred to as sensimilla. By preventing accidental pollination through timely removal of male plants or the use of feminized seeds, cultivators can focus on producing potent, resinous flowers with optimal cannabinoid and terpene profiles.
Mastering the art of pollination timing empowers cultivators to manage their cannabis crops effectively, whether the goal is seed production or the cultivation of premium, seedless cannabis flowers.
Reasons for Collecting Pollen
Creating New Strains vs. Maintaining Mother Plants:
Collecting cannabis pollen opens the door to two distinct avenues for growers and breeders: the creation of new strains and the preservation of existing genetic lines through mother plants. Creating new strains involves deliberate cross-breeding of carefully selected parent plants to combine desired traits. Breeders meticulously analyze genetic profiles, aiming to enhance specific characteristics such as potency, flavor, aroma, and resistance. Pollen from male plants carrying desirable traits is used to fertilize receptive female plants, giving rise to unique and innovative cannabis varieties.
On the other hand, maintaining mother plants involves cultivating a stable, known genetic line over successive generations. Mother plants act as a consistent source of cuttings or clones, ensuring the replication of specific traits and characteristics. By collecting and storing pollen from exceptional mother plants, growers can safeguard valuable genetics for future use, allowing for the perpetuation of favored strains and traits.
Advantages of Harvesting Your Own Pollen:
Harvesting your own pollen offers several advantages, making it a preferred choice for many cultivators and breeders. Firstly, it provides growers with complete control over the breeding process, allowing for the creation of tailor-made strains designed to meet specific preferences or market demands. Secondly, home-collected pollen is a cost-effective alternative to purchasing pollen from external sources, reducing expenses associated with breeding endeavors. Additionally, by cultivating and collecting pollen from well-maintained plants, growers can ensure the quality and purity of the genetic material, leading to more predictable and consistent results in subsequent generations.
Furthermore, the process of harvesting pollen allows growers to deepen their understanding of cannabis genetics, enabling them to experiment with different combinations and explore the vast array of possibilities within the cannabis gene pool. This hands-on approach not only fosters a deeper connection with the cultivation process but also encourages innovation and creativity within the cannabis breeding community.
By appreciating the balance between creating new strains and preserving existing ones, cultivators can navigate the world of cannabis breeding with purpose and precision, ensuring the sustainability and diversity of the cannabis plant.
Pollinating Autoflowering Cannabis Strains
Possibilities and Considerations for Autoflowering Seeds:
Autoflowering cannabis strains, renowned for their rapid growth and ability to flower independently of light cycles, present unique opportunities and challenges in the realm of pollination. While autoflowering plants follow their predetermined life cycle, growers have the possibility to pollinate these strains and create autoflowering seeds. However, certain considerations are vital for successful pollination and seed production in autoflowering cannabis.
Autoflowering strains typically have a limited lifespan, often completing their entire growth cycle in 8 to 10 weeks. Pollination needs to occur within this timeframe to ensure viable seeds. Timing is critical; observing the plant’s development closely is necessary to identify the optimal moment for pollination. Pollen should be applied when the female plant’s pistils are fully formed but not yet mature, ensuring successful fertilization.
Additionally, the genetic makeup of the parent plants plays a crucial role. If one parent is an autoflowering strain, the resulting seeds will likely carry autoflowering traits. However, if a photoperiod strain is involved, the offspring might not consistently display autoflowering characteristics. Growers interested in producing pure autoflowering seeds should select parent plants with stable autoflowering genetics, ensuring the progeny maintains the desired traits.
Consideration should also be given to the cultivation environment. While autoflowering plants are robust and resilient, ensuring a stress-free environment enhances the chances of successful pollination. Adequate nutrients, optimal lighting, and suitable temperatures contribute to plant health and, consequently, seed production.
Furthermore, growers need to assess their goals and preferences when pollinating autoflowering strains. Whether aiming for a higher yield, specific cannabinoid content, or unique terpene profiles, careful selection of parent plants is essential. By understanding the possibilities and limitations of pollinating autoflowering cannabis, growers can harness the advantages of these remarkable strains, producing seeds tailored to their specific needs and preferences.
Cannabis Pollen FAQs
Cannabis Pollen FAQs
1. For How Long Is Cannabis Pollen Viable?
Under normal conditions, marijuana pollen remains viable for one to three weeks after being collected from the cannabis pollen sacs. However, sealing and freezing the pollen can extend its lifespan up to a year. It’s crucial to store pollen properly in a dark, airtight container and remove moisture before freezing to maintain its viability.
2. How Long Until Cannabis Plants Produce Pollen?
Male cannabis plants need to mature sexually, typically occurring one to two weeks before female plants. This means growers must wait at least four to six weeks for their plants to mature sexually, followed by an additional two to three weeks for the pollen sacs to develop and release pollen. The exact timing varies by strain but usually takes a minimum of six to seven weeks from seed for plants to produce viable pollen.
3. Is Male Pollen the Same as Hash Pollen?
No, despite both being referred to as pollen, hash pollen is slang for kief. Kief is made by sifting cannabis trichomes from female plants through a fine screen, which can then be pressed into hash or consumed as pollen. In contrast, male cannabis pollen consists of the male gametes used for seed production and cannot be consumed directly.
Understanding these frequently asked questions about cannabis pollen helps growers and breeders make informed decisions, ensuring successful pollination processes and the preservation of genetic diversity within cannabis crops.
4. Can You Store Cannabis Pollen Indefinitely?
While proper storage methods can significantly extend the viability of cannabis pollen, it’s essential to note that pollen, like all biological material, has limitations. While some studies suggest potential methods for long-term storage, there isn’t yet a foolproof way to keep pollen viable indefinitely.
5. How Does Pollination Impact Flowering Time?
When female cannabis plants are pollinated, they redirect their energy towards seed production. This shift can lead to changes in flowering time; pollinated plants may take longer to mature and harvest compared to unpollinated ones. Breeders must account for this extended flowering period in their cultivation timelines.
6. Can Cannabis Pollen Be Used for Breeding Across Different Strains?
Yes, cannabis pollen can be used to breed different strains, allowing growers to experiment with diverse genetic combinations. Crossbreeding different strains can lead to the development of hybrid varieties with unique characteristics. However, understanding the genetic traits of parent plants is crucial to predicting the outcomes accurately.
7. What Are the Environmental Factors That Influence Pollen Production?
Several environmental factors can influence pollen production in cannabis plants, including light cycles, temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, and overall plant health. Stable and optimal environmental conditions promote healthy pollen sac development and, consequently, successful pollination.
8. Is Hand Pollination Feasible for Cannabis Plants?
Yes, hand pollination is a common practice among cannabis breeders and growers. By manually transferring pollen from male to female plants using a brush or other gentle methods, growers can control the pollination process, ensuring specific plants are fertilized. Hand pollination is especially useful in controlled breeding programs.
Conclusion
In the intricate world of cannabis cultivation and breeding, understanding the role of male cannabis plants and the significance of pollen is paramount. Male plants, often overlooked, are the unsung heroes of cannabis cultivation. Their pollen, carrying the genetic information essential for seed production, drives the creation of new strains and the preservation of existing genetic lines. By grasping the unique attributes of male plants, growers and breeders gain the power to shape the future of cannabis cultivation.
Importance of Male Cannabis Plants in Cannabis Cultivation:
Male cannabis plants play a pivotal role in cannabis cultivation by producing pollen necessary for fertilizing female plants. This process not only ensures the continuation of the cannabis species but also empowers breeders to explore endless possibilities in creating novel strains. Through controlled pollination, breeders can enhance desired traits, leading to the development of cannabis varieties tailored to diverse consumer preferences.
Understanding the biological intricacies of male plants allows growers to make informed decisions, whether it’s for creating new hybrids, preserving genetic diversity, or simply maximizing the yield and quality of their cannabis crops. Embracing the significance of male plants elevates the overall cultivation process, paving the way for innovation and excellence in the cannabis industry.
Tips for Successful Pollen Collection and Usage:
Successful pollen collection and usage are the keys to productive breeding endeavors. Cultivators must employ meticulous techniques to collect pollen without contamination, ensuring its viability for fertilization. Gentle shaking or careful brushing techniques, combined with proper timing, are essential for efficient pollen collection. Additionally, the appropriate storage of pollen in airtight containers, shielded from light and moisture, maximizes its shelf life, allowing for future breeding experiments.
Moreover, the understanding of the cannabis pollination process, including optimal timing and techniques, empowers growers to achieve desired outcomes, whether it’s the creation of unique strains, the preservation of cherished genetics, or the production of high-quality, seedless cannabis flowers.
In conclusion, the cultivation and breeding of cannabis are enriched by the knowledge of male cannabis plants and the invaluable role of pollen. By embracing the complexities of plant biology and genetics, cultivators and breeders alike contribute to the ever-evolving landscape of cannabis varieties, ensuring a diverse and vibrant cannabis community for generations to come.