Growing healthy and robust weed plants is an art that requires a delicate balance of various environmental factors, with light playing a crucial role in the process. While light is essential for photosynthesis—the lifeblood of plant growth—there exists a fine line between providing adequate illumination and subjecting your cannabis plants to an overdose of light. Just as too little light can hinder their development, excessive light can prove equally detrimental, leading to a myriad of issues that impact the overall health and yield of your plants.
We will explore the nuances of light requirements during different growth stages. Whether you’re a seasoned cultivator or a novice enthusiast, this article aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to foster healthy cannabis plants, steering clear of the pitfalls associated with excessive light exposure. Join us on a journey through the nuanced world of cannabis cultivation, where the right amount of light can make all the difference between lackluster growth and a thriving, vibrant harvest.
Table of Contents:
Understanding Light Requirements
Identifying Signs of Too Much Light
Effects of Excessive Light on Cannabis Growth
Fixing Light | Heat Stress in Cannabis Plants
Myths About More Light Equals Faster Growth
Preventing Light Stress in Cannabis Plants
Understanding Light Requirements
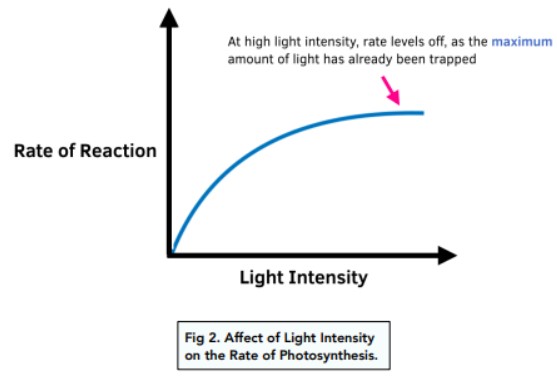
Cannabis plants, like all green organisms, rely on light for photosynthesis, a fundamental process that fuels their growth. Photosynthesis involves the conversion of light energy into chemical energy, providing the necessary fuel for the plant’s metabolic functions. To ensure optimal growth, it’s imperative to understand the specific light requirements of cannabis plants at different stages of their lifecycle.
The Role of Light in Photosynthesis
Light serves as the driving force behind photosynthesis, a complex biochemical process where plants convert light energy into glucose. In the context of cannabis cultivation, this means that without adequate light, your plants won’t produce the energy needed for robust growth. The interplay of light, water, and carbon dioxide is the engine that propels your cannabis plants toward healthy development.
Ideal Lighting Settings for Cannabis Plants
Achieving the ideal lighting settings is a critical aspect of successful cannabis cultivation. The light spectrum required by cannabis plants evolves during different growth stages. During the vegetative phase, plants benefit from a higher proportion of blue light (in the 400-500 nanometer range), promoting leaf and stem development. As the plants transition to the flowering stage, a shift toward red light (in the 600-700 nanometer range) becomes essential for stimulating bud formation.
Different Growth Stages and Light Spectrums
Understanding the distinct light spectrums needed at various growth stages is key to providing your cannabis plants with the right conditions. While blue light encourages vegetative growth, red light supports flowering. Whether you’re using high-pressure sodium (HPS) lights, metal halide (MH) lights, or light-emitting diode (LED) lights, selecting the appropriate spectrum for each growth phase ensures optimal development.
In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into the signs that indicate your cannabis plants might be receiving too much light, and how to navigate these challenges to foster a thriving cultivation environment.
Identifying Signs of Too Much Light
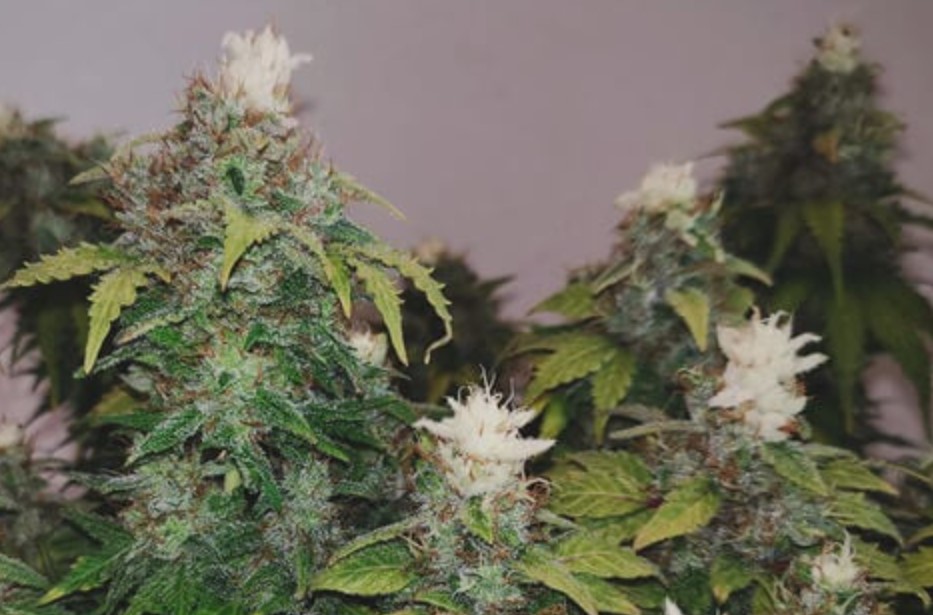
As a cannabis cultivator, vigilance in monitoring your plants is paramount to ensure they receive the optimal amount of light. Recognizing signs of excessive light is crucial for preventing potential harm to your cannabis crop. In this section, we explore the importance of identifying cannabis light burn and delve into visual indicators and practical methods for testing light intensity.
Importance of Recognizing Cannabis Light Burn
Cannabis light burn occurs when your plants are exposed to an intensity of light that surpasses their tolerance. This not only hampers their growth but can lead to various complications, such as nutrient deficiencies and weakened bud development. By promptly identifying and addressing signs of light burn, you can mitigate potential damage and steer your cultivation towards a healthier outcome.
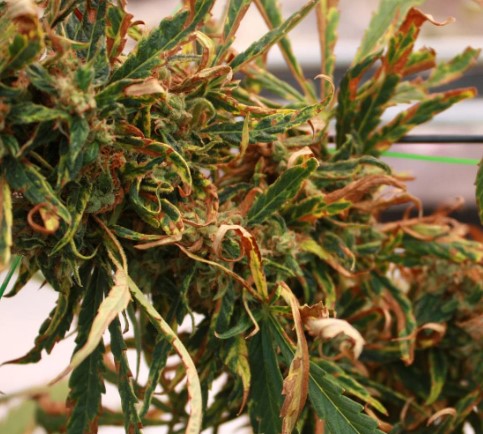
Visual Indicators: Yellowing Leaves and Cannabis Light Stress
One of the most apparent signs of too much light on cannabis plants is the yellowing of leaves, particularly at the tops closest to the light source. While yellowing leaves can be attributed to various factors, in the context of excessive light, it indicates cannabis light stress. Understanding this visual cue is essential for diagnosing and rectifying the issue, ensuring your plants receive the right balance of light for optimal growth.
Testing Light Intensity
Testing the intensity of light in your cultivation space is a practical approach to assess whether your plants are receiving an appropriate amount of illumination. A simple yet effective method involves placing your hand, palm down, at the top of your plant for 10 to 15 seconds. If the heat is uncomfortably high, it signals that the light intensity may be too much for your plants. This hands-on approach provides a quick gauge of the potential risk of light burn.
In the upcoming sections, we’ll explore strategies to optimize light conditions, ensuring that your cannabis plants thrive without succumbing to the negative effects of excessive illumination.
Effects of Excessive Light on Cannabis Growth
Understanding the repercussions of subjecting your cannabis plants to excessive light is essential for maintaining a flourishing cultivation environment. In this section, we delve into the specific effects, focusing on nutrient absorption, heat stress, and the intricate relationship between light exposure and bud development.
Impact on Nutrient Absorption
Excessive light can disrupt the nutrient absorption process in cannabis plants, leading to nutrient deficiencies. When plants receive too much light, they may experience accelerated transpiration, causing them to dry out and deplete essential nutrients. This imbalance can result in weaker, airier buds, hindering the overall quality and yield of your harvest.
Heat Stress and Its Consequences
The heat generated by intense light sources poses a dual threat to cannabis plants. Not only does it elevate the overall temperature in the growing environment, but it also exacerbates the risk of heat stress. Elevated temperatures can impede the plants’ metabolic processes, disrupt enzymatic activity, and contribute to nutrient imbalances. Heat-stressed cannabis plants often exhibit wilting, discoloration, and a general decline in overall health.
Relationship Between Light and Bud Development
The intricate dance between light and bud development is a critical factor in cannabis cultivation. While light is essential for photosynthesis and overall plant health, too much of it can lead to undesirable consequences for budding. Excessive light can result in looser, less densely packed buds, diminishing the quality of your harvest. Striking the right balance in light exposure during the flowering stage is crucial for fostering robust bud development.
In the subsequent sections, we’ll explore myths surrounding the notion that more light equates to faster growth and higher yields, shedding light on the nuances of providing the appropriate light cycle and quality for optimal cannabis growth.
Fixing Light | Heat Stress in Cannabis Plants
If your cannabis plants are already experiencing heat stress, immediate intervention is crucial to prevent lasting damage. Follow these steps to rectify heat stress:
- Watering Schedule Adjustment:
- Increase watering frequency during periods of elevated temperature.
- Ensure the soil remains consistently moist, but avoid overwatering.
- Cooling Techniques:
- Introduce additional cooling methods such as portable air conditioners or cool-mist humidifiers.
- Consider placing frozen water bottles near plants for localized cooling.
- Pruning and Defoliation:
- Trim affected leaves to reduce overall plant stress.
- Focus on removing damaged or scorched foliage to promote new growth.
- Shade Placement:
- Temporarily move plants to a shadier location, especially during peak sunlight hours.
- Use shade cloth or create makeshift shading to shield plants from excessive sunlight.
- Hydrogen Peroxide Solution:
- Prepare a diluted hydrogen peroxide solution (1-2 tablespoons per gallon of water).
- Water plants with this solution to alleviate stress and stimulate recovery.
- Mulching:
- Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of plants to regulate soil temperature.
- Mulching helps retain moisture and shields roots from extreme heat.
- Foliar Spray with Aloe Vera:
- Mix aloe vera gel with water (1:10 ratio) and spray it on plant leaves.
- Aloe vera has soothing properties that can alleviate stress and promote healing.
- Temperature Monitoring:
- Continuously monitor ambient temperature and humidity.
- Adjust cooling methods and interventions based on real-time environmental data.
- Nutrient Adjustments:
- Provide a balanced nutrient solution to support recovery.
- Adjust fertilization based on the plant’s immediate needs during the recovery period.
- Patience and Observation:
- Allow plants time to recover after implementing interventions.
- Observe for signs of improvement and adjust care accordingly.
By promptly implementing these measures, you give your cannabis plants the best chance to recover from heat stress and resume healthy growth. Regular monitoring and adjustments are key to ensuring ongoing plant well-being.
Myths About More Light Equals Faster Growth
Dispelling common misconceptions is essential for cultivating cannabis knowledgeably. In this section, we unravel the myth that more light necessarily translates to faster growth. We delve into the intricacies of the optimal light cycle for different growth stages and explore the nuanced relationship between quality and quantity of light concerning overall efficiency.
The Optimal Light Cycle for Different Growth Stages
Contrary to the belief that flooding your cannabis plants with continuous light accelerates growth, adhering to the appropriate light cycle is paramount. During the vegetative stage, mature plants typically thrive with 12 to 16 hours of light per day. As they transition to the flowering stage or seedling phase, reducing the light exposure to 8 to 12 hours per day is crucial. Beyond these parameters, the risk of light stress increases, potentially stunting growth or, in extreme cases, leading to plant death.
Quality vs. Quantity: Understanding Light Efficiency
While the quantity of light is undeniably important for cannabis growth, the quality of light holds equal significance. Different light sources—fluorescent, LED, or high-pressure sodium lights—emit varying spectrums that influence plant growth differently. For instance, blue light facilitates vegetative growth, while red light is instrumental in flowering. Recognizing the balance between quality and quantity ensures that your cannabis plants receive the right light for their specific growth stage, fostering efficient and healthy development.
Optimizing Light Conditions
Creating an ideal environment for your cannabis plants involves strategic decisions regarding light sources and their management. In this section, we emphasize the significance of selecting the right light source, adjusting the minimum light distance for indoor cultivation, and employing digital monitoring tools to refine light conditions.
Importance of Selecting the Right Grow Light
Choosing the appropriate grow light is a fundamental decision with profound implications for the success of your cannabis cultivation endeavors. Each type of grow light—High-Pressure Sodium (HPS), Metal Halide (MH), and Light-Emitting Diode (LED)—comes with distinct characteristics influencing factors such as running costs, efficiency, and heat generation.
1. High-Pressure Sodium (HPS) Lights:
- Type: HPS lights emit light in the yellow-orange spectrum, making them suitable for the flowering stage of cannabis.
- Running Costs: HPS lights are known for being energy-intensive, leading to higher electricity bills compared to some other options.
- Efficiency (g/Watt): While HPS lights are effective, their efficiency is lower compared to newer technologies like LEDs.
- Heat Generation: HPS lights tend to generate more heat, requiring additional ventilation to maintain an optimal temperature in the grow space.
2. Metal Halide (MH) Lights:
- Type: MH lights emit light in the blue spectrum, making them ideal for the vegetative stage of cannabis growth.
- Running Costs: Similar to HPS lights, MH lights can contribute to higher electricity costs due to their energy consumption.
- Efficiency (g/Watt): MH lights have moderate efficiency, falling between HPS and LED lights.
- Heat Generation: MH lights also produce a significant amount of heat, necessitating proper heat management.
3. Light-Emitting Diode (LED) Lights:
- Type: LEDs offer a broad spectrum of light, allowing growers to tailor the light output to specific growth stages.
- Running Costs: LEDs are known for their energy efficiency, resulting in lower long-term operating costs compared to traditional lights.
- Efficiency (g/Watt): LEDs are highly efficient, converting a significant portion of energy into usable light for photosynthesis.
- Heat Generation: LEDs produce less heat, reducing the need for extensive cooling systems and allowing for more controlled growing environments.
Choosing the right light source involves considering factors such as the growth stage of your cannabis plants, electricity costs, energy efficiency, and heat management. As technology advances, many growers are leaning towards LED lights for their cost-effectiveness, adaptability, and energy efficiency, contributing to healthier and more productive cannabis crops.
Adjusting Minimum Light Distance for Indoor Growing
Maintaining the optimal minimum distance between your light source and cannabis plants is a key factor in preventing light burn. As a rule of thumb, during the vegetative stage, keep the lights at least 18-24 inches above the canopy. In the flowering stage, when the plants require more light, a minimum distance of 12-18 inches is often recommended. These distances can vary based on factors such as the type of light used, plant health, and overall environmental conditions. Experimenting with the minimum light distance helps avoid issues like light burn and ensures your plants receive sufficient light without causing stress.
Utilizing Digital Monitoring Tools
In the age of digital precision, monitoring tools offer growers valuable insights into the environmental conditions impacting their cannabis plants. Whether it’s a dedicated light meter or convenient light measuring apps available for your smartphone, these tools enable you to track light intensity accurately. With the convenience of a smartphone app or the precision of a dedicated meter, you can measure and monitor the light levels in your cultivation space. Armed with this data, you can make informed decisions, maintaining your cultivation space within the optimal parameters for robust plant growth.
Preventing Light Stress in Cannabis Plants
Ensuring your cannabis plants thrive requires proactive measures to prevent light stress. In this section, we explore strategies for maintaining ideal light exposure, considerations tailored to indoor growers, and the importance of experimenting with wattage and light distance.
Strategies for Maintaining Ideal Light Exposure
Achieving the perfect balance in light exposure is fundamental to preventing stress in cannabis plants. Beyond adhering to recommended light cycles, consider implementing techniques such as low-stress training to distribute light evenly. This strategic approach helps optimize light absorption and minimizes the risk of specific areas experiencing excessive illumination.
Considerations for Indoor Growers
Indoor cultivation comes with its own set of challenges, especially regarding spatial constraints. Indoor growers should prioritize adequate ventilation and air circulation to disperse heat generated by lights. Additionally, strategically placing reflective materials in the grow space enhances light distribution, ensuring that all parts of the plant receive the necessary illumination without causing undue stress.
Experimenting with Wattage and Light Distance
Fine-tuning the interplay between wattage and light distance is an ongoing process in cannabis cultivation. Consider the specific needs of your plants and the size of your growing space when experimenting with these variables. For smaller spaces like a 2×2 feet area, starting with 200 watts and adjusting light distance accordingly is a common approach. In contrast, larger spaces, such as 8×8 feet, may benefit from 1,000 watts with careful attention to light distance. Regular experimentation and observation allow growers to customize these factors for optimal results.
Outdoor Growing as a Solution
Embracing outdoor cultivation offers a natural and advantageous solution for cannabis growers. In this section, we explore the benefits of growing cannabis outdoors, and draw comparisons with indoor growing practices.
Advantages of Growing Cannabis Outdoors
- Abundant Natural Light: Outdoor cultivation harnesses the power of the sun, providing an abundant and natural light source for cannabis plants. This eliminates the need for artificial lighting and allows plants to thrive under the full spectrum of sunlight.
- Cost-Efficiency: Outdoor growing minimizes the need for expensive indoor lighting setups, resulting in cost savings for growers. Natural environmental conditions contribute to a more economical cultivation process.
- Larger Growth Space: Outdoor cultivation often provides more space for plants to spread their roots and reach their full potential. This can lead to larger yields and healthier plants compared to the confined space of indoor setups.
- Natural Environmental Elements: Cannabis plants benefit from exposure to natural environmental elements like wind and rain, which contribute to robust stem and branch development. Outdoor cultivation mimics the plant’s natural habitat, fostering resilient and hardy growth.
Comparisons with Indoor Growing Practices
While outdoor growing offers several advantages, it’s essential to acknowledge the differences when compared to indoor practices. Factors such as climate control, security, and privacy may vary. Indoor cultivation provides a controlled environment, allowing for year-round production and protection against external elements. Growers often choose between these methods based on their preferences, available space, and the specific needs of their cannabis plants.
Conclusion:
In summary, maintaining a delicate balance in light exposure, whether indoors or outdoors, is crucial for preventing stress and ensuring optimal plant development. Growers should prioritize choosing suitable light sources, adjusting light distances, and leveraging digital monitoring tools to fine-tune the growing environment. Additionally, outdoor cultivation presents distinct advantages, emphasizing the importance of selecting appropriate strains for the chosen environment.
As you embark on your cannabis cultivation journey, continue to refine your practices, experiment with variables, and stay informed about the latest developments in the field. By combining knowledge with hands-on experience, you can cultivate cannabis plants that yield bountiful harvests and exhibit robust, healthy growth.