THC and THCV are both cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant, but they differ in their chemical structures and effects on the body. THC, or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, is the most well-known cannabinoid and is responsible for the psychoactive effects commonly associated with cannabis use. THCV, or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabivarin, is a lesser-known cannabinoid that is gaining attention for its potential health benefits and unique properties.
In this guide, we will delve deeper into the differences between THC and THCV, their effects on the body, and their potential medical applications. By understanding these distinctions, we can gain insights into how these cannabinoids may be used to support various health conditions and improve overall well-being.
Table of Contents
Chemical Differences Between THC and THCV
Mechanism of Action: How THC Works
Mechanism of Action: How THCV Works
Potential Medical Applications of THC
Potential Medical Applications of THCV
Different Types of THC: Exploring Delta-8-THC, Delta-9-THC, and More
What is THC?
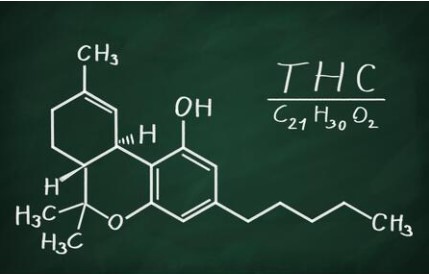
THC, short for delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, stands out as the principal psychoactive compound in cannabis. It triggers the characteristic “high” linked with cannabis use by interacting with the body’s endocannabinoid system, specifically binding to CB1 receptors in the brain and central nervous system.
When THC engages CB1 receptors, it prompts the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter crucial for pleasure and reward. This dopamine surge results in the euphoric and psychoactive effects typically associated with THC use.
THC is renowned for inducing relaxation, elevating mood, enhancing appetite, and delivering pain relief. Its medicinal applications extend to conditions such as chronic pain, nausea, muscle spasms, and sleep disorders. Medical professionals often prescribe THC to alleviate these symptoms, harnessing its therapeutic potential in various healthcare contexts.
What is THCV?
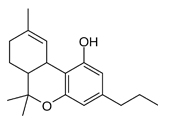
THCV, or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabivarin, is a lesser-known cannabinoid with a chemical structure akin to THC. However, THCV possesses a unique arrangement of carbon atoms, resulting in distinct properties.
Unlike THC, THCV is less psychoactive, offering a different experience. It interacts with both CB1 and CB2 receptors in the endocannabinoid system, but its effects vary with dosage.
At higher doses, THCV acts as a CB1 receptor agonist, similar to THC. However, at lower doses, it functions as an antagonist, countering some of THC’s effects on CB1 receptors.
This unique mechanism makes THCV intriguing, potentially mitigating undesirable THC effects such as impaired cognition and increased appetite. Additionally, THCV’s influence on other receptors and neurotransmitter systems hints at its broad therapeutic potential for various medical conditions.
Chemical Differences THCV vs THC
THC and THCV share similar chemical structures, differing in their side chain arrangements. THC boasts a side chain with five carbon atoms, while THCV features a side chain with three carbon atoms.
This slight variance leads to distinct effects on the body. THC is renowned for its potent psychoactive properties, whereas THCV, especially at lower doses, is less psychoactive and may even act as a CB1 receptor antagonist.
Furthermore, these chemical distinctions contribute to variations in boiling points. THC boils at 155ºC, while THCV possesses a higher boiling point of 220ºC. Understanding these differences sheds light on the diverse effects these cannabinoids exert, offering valuable insights for both recreational and medicinal use.
Mechanism of Action: How THC Works
THC operates by binding to CB1 receptors within the endocannabinoid system, primarily located in the brain and central nervous system. Upon binding, THC activates these receptors, triggering the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine.
This activation of CB1 receptors leads to a range of effects, including euphoria, relaxation, altered perception, and increased appetite. These effects define THC’s psychoactive properties, making it sought after for recreational use.
Additionally, THC exhibits analgesic properties, interacting with the body’s pain pathways to alleviate various types of pain, including chronic pain conditions. Understanding how THC engages with the body’s receptors provides crucial insights into its therapeutic potential, guiding its application in medical contexts.
Mechanism of Action: How THCV Works
THCV interacts with both CB1 and CB2 receptors in the endocannabinoid system. Its effects vary with dosage: at higher doses, it functions as a CB1 receptor agonist similar to THC. However, at lower doses, it acts as a CB1 receptor antagonist, blocking some of THC’s effects.
This unique mechanism makes THCV intriguing for potential therapeutic use. By countering THC’s effects, especially in terms of cognitive function and appetite, THCV demonstrates its versatility. Additionally, THCV may influence other receptors and neurotransmitter systems, expanding its potential benefits for various medical conditions.
Effects of THC
THC, or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, exerts a multifaceted impact upon binding to CB1 receptors in the brain. Its effects encompass a diverse range:
1. Euphoria and relaxation: THC induces a profound sense of happiness and relaxation, fostering overall well-being and a calm mental state.
2. Altered perception: THC heightens sensory perception, leading to profound changes in how surroundings are experienced. Colors might appear more vivid, and sounds can be more intense.
3. Increased appetite: Often referred to as the “munchies,” THC has a well-documented ability to stimulate appetite, making it a valuable tool in medical scenarios where appetite stimulation is crucial.
4. Pain relief: With its analgesic properties, THC alleviates various types of pain, including chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia and multiple sclerosis. It works by interacting with the body’s pain pathways, reducing the perception of pain and providing relief for individuals with debilitating pain conditions.
5. Sleepiness and sedation: THC induces drowsiness, making it particularly useful for individuals suffering from insomnia or other sleep disorders. Its sedative effects can promote relaxation and aid in falling asleep.
Crucially, the effects of THC are highly individualized, influenced by various factors such as the individual’s tolerance, dosage, and the specific cannabis strain consumed. While some users find relaxation and relief, others might experience heightened anxiety or paranoia, especially with high THC doses. Understanding these nuances is pivotal for responsible cannabis consumption, ensuring users can make informed decisions about their well-being.
Effects of THCV
THCV has distinct effects that differ from THC, making it an intriguing compound for both recreational and medicinal use. While less psychoactive than THC, THCV can still produce mild psychoactive effects at higher doses. However, at lower doses, it may act as an antagonist to CB1 receptors, potentially counteracting some of the effects of THC.
The effects of THCV include:
- Appetite suppression: THCV has been found to suppress appetite, making it a potential tool in weight management and obesity treatment.
- Increased energy and focus: THCV has been dubbed the “race car” or “sports car” of cannabinoids, as it can provide a short-lasting, energetic high.
- Potential neuroprotective effects: THCV may have neuroprotective properties and could be beneficial for individuals with neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease.
- Possible anticonvulsant properties: THCV has shown promise as an anticonvulsant, with studies suggesting it may help control seizures in certain individuals.
Further research is needed to fully understand the extent of THCV’s effects and its potential applications. As more studies are conducted, we can expect to gain a deeper understanding of the benefits and limitations of THCV.
Potential Medical Applications of THC
THC has been studied extensively for its potential medical applications. Some of the conditions for which THC has shown promise include:
- Chronic pain: THC has analgesic properties and can provide relief for individuals with chronic pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia and multiple sclerosis.
- Nausea and vomiting: THC has antiemetic properties and can help alleviate nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy and other medical treatments.
- Muscle spasms: THC can help reduce muscle spasms and spasticity in individuals with conditions such as multiple sclerosis and spinal cord injuries.
- Sleep disorders: THC can promote sleep and help individuals with insomnia or other sleep disorders achieve restful sleep.
- Appetite stimulation: THC is known to increase appetite, making it useful for individuals with appetite loss or eating disorders.
It’s important to note that the use of THC for medical purposes should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Individual responses to THC can vary, and the potential side effects and risks should be carefully considered.
Potential Medical Applications of THCV
THCV is an emerging cannabinoid with potential medical applications. While research is still in its early stages, some of the conditions for which THCV may be beneficial include:
- Weight management and obesity: THCV has shown promise in suppressing appetite and promoting weight loss, making it a potential tool for individuals struggling with obesity.
- Diabetes management: THCV may help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity, making it a potential treatment for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- Neurological disorders: THCV has been studied for its potential neuroprotective effects and may have applications in the treatment of neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy.
- Seizure control: THCV has shown anticonvulsant properties in animal studies, suggesting it may be beneficial for individuals with epilepsy and other seizure disorders.
It’s important to note that more research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits of THCV and its applications in various medical conditions. The existing studies provide promising results, but further clinical trials are necessary to validate these findings.
Different Types of THC: Exploring Delta-8-THC, Delta-9-THC, and More
In addition to THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) and THCV (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabivarin), it’s crucial to understand the different types of THC, each with its unique properties and effects. Among the various THC variants, delta-9-THC and delta-8-THC are the most well-known. Here’s a closer look at these different types of THC:
1. Delta-9-THC: Delta-9-THC is the primary psychoactive compound found in cannabis. It is responsible for the characteristic “high” that users experience after consuming cannabis products. Delta-9-THC interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system, primarily binding to CB1 receptors in the brain and central nervous system. This interaction results in euphoria, relaxation, altered perception, increased appetite, and potential pain relief.
2. Delta-8-THC: Delta-8-THC is a variation of THC that is chemically similar to delta-9-THC but has a different arrangement of atoms. While delta-8-THC also produces psychotropic effects, they are generally reported to be milder and less anxiety-inducing than those associated with delta-9-THC. Delta-8-THC is gaining popularity due to its legal status in some regions where delta-9-THC is restricted. Users often describe the effects of delta-8-THC as more subtle and less overwhelming.
Other THC Variants: Apart from delta-8-THC and delta-9-THC, there are other THC variants and analogs that researchers continue to study. These variants may have slightly different effects and properties, making them of interest to both the scientific community and consumers.
It’s important to note that the effects of different THC variants can vary based on factors such as individual tolerance, dosage, and consumption method. As with any cannabinoid, responsible use and awareness of local regulations are essential.
As research in the field of cannabinoids progresses, more information about these THC variants and their potential applications may emerge. Staying informed about the latest scientific developments can provide valuable insights into the diverse world of cannabinoids and their effects on the human body.
Legal Status of THC and THCV
The legal status of THC and THCV varies depending on the jurisdiction. THC is considered a controlled substance in many countries and is subject to strict regulations. In some regions, THC is legal for medical and/or recreational use, while in others, it remains prohibited.
THCV, on the other hand, is less regulated and is not explicitly listed as a controlled substance in many jurisdictions. However, its legal status may still vary depending on the specific country or region. It’s important to consult local laws and regulations regarding the use and possession of THCV-containing products.
Conclusion
In conclusion, THC and THCV are two cannabinoids with distinct properties and potential benefits. While THC is known for its psychoactive effects and wide range of medical applications, THCV offers unique properties such as appetite suppression, increased energy and focus, and potential neuroprotective effects.
Both THC and THCV have the potential to be valuable tools in the field of medicine, but further research is needed to fully understand their mechanisms of action, effects, and potential applications. As the scientific understanding of cannabinoids continues to evolve, we can expect to uncover more about the therapeutic potential of these compounds and their role in supporting various health conditions.
It’s important to note that the use of THC and THCV should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional, and individual responses to these compounds may vary. As with any medical treatment, it’s essential to weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks and consider the legal status of these compounds in your jurisdiction.
By staying informed about the latest research and developments in the field of cannabinoids, we can better understand how THC and THCV may fit into our overall health and wellness strategies. As the scientific community continues to explore the potential of these compounds, we can look forward to new insights and discoveries that may shape the future of medical cannabis.