Growing cannabis from seed can be an exciting and rewarding experience, but it also comes with its challenges. The seedling stage, in particular, requires careful attention and proper techniques to ensure healthy growth. Whether you’re a novice grower or have some experience under your belt, this comprehensive guide will provide you with the knowledge and steps needed to master the seedling stage of cannabis cultivation.
Step 1: Choosing the Right Genetics, Containers, and Medium
The first step in successfully growing cannabis seedlings is selecting the right genetics, containers, and medium. When sourcing your seeds, consider factors such as your experience and skill level as a grower, budget, grow equipment, preferences in taste and effect, and whether you’re growing indoors or outdoors. Each strain has its own unique characteristics and requirements, so choose one that suits your specific needs.
Best Medium for Cannabis Seedlings
In terms of the medium, it is recommended to grow seedlings in a light, well-aerated, slightly acidic soil with a pH level of 6.3–6.5. Adding 20–50% perlite to your medium can improve soil aeration and nutrient retention. The amount of perlite should be adjusted based on the nutrients you plan to provide your plants. It’s important to note that seedlings, especially autoflowering varieties, are sensitive to nutrients. Avoid planting them in nutrient-rich soil and wait until they’ve grown 3–4 sets of true leaves before starting to feed them.
Best Containers for Cannabis Seedlings
When it comes to containers, different approaches are recommended for autoflowering and feminized seedlings. For autoflowers, it’s best to plant them directly in their final pots to avoid unnecessary stress. Most auto growers use pots between 5–15 liters, depending on the strain and grow space. On the other hand, feminized seedlings can be transplanted since they have more time to recover from the stress. Solo Cups or small germination pots are a popular choice for providing support and robust health from the beginning. Transplant feminized seedlings once they’ve grown sets of true leaves that cover the full circumference of their current container.
It’s important to consider the characteristics of cannabis pots as well. Ensure that your pots have drainage holes to prevent fungal pathogens and root rot. Aeration is another key factor, and fabric pots can improve oxygen exchange, resulting in healthier plants. Additionally, keeping seedlings in appropriately sized pots is crucial to avoid overwatering and promote healthy root growth.
Step 2: Using the Right Germination Techniques
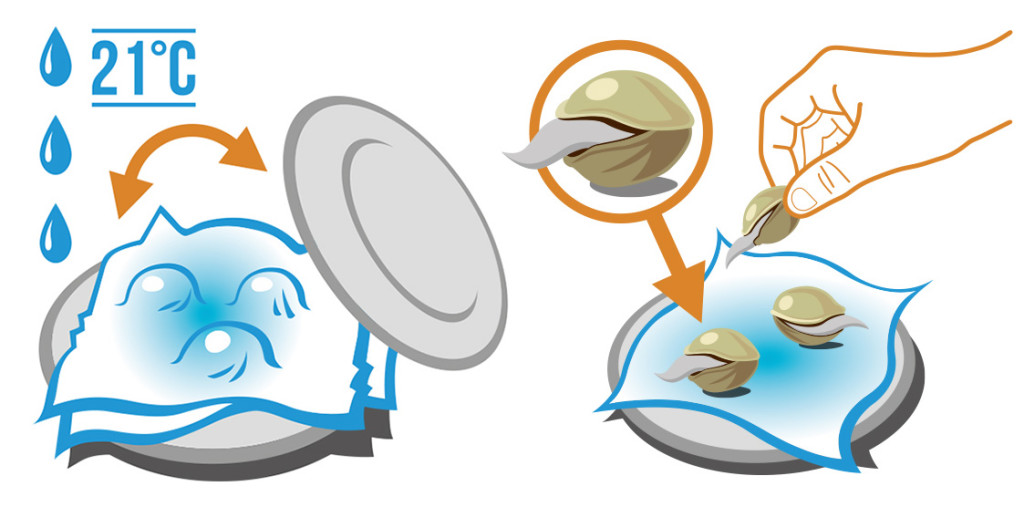
Proper germination is essential for successful seedling development. There are several techniques you can use to germinate cannabis seeds, each with its own advantages. The paper towel method involves placing seeds between moist paper towels in a plastic container. Keep the container in a warm, dark place, ensuring fresh air exchange. Another method is the glass of water technique, where seeds are submerged in water for 24–48 hours. Once taproots sprout, they are ready to be planted. Seedling starter kits are also available to provide optimal conditions for germination.

Step 3: Mastering the Seedling Stage
Now that your seedlings are in the soil, it’s time to focus on their care during the seedling stage. Cannabis seedlings are delicate and require specific environmental conditions to thrive. Understanding their needs and optimizing their environment is key to their healthy growth.
Optimizing Light, Temperature, and Humidity for the Seedling Stage of Cannabis
During the seedling stage, seedlings have specific requirements for light, temperature, and humidity. Providing the right conditions is crucial for their development. Seedlings should be grown in a propagator, where you can easily create the ideal environment for them.
- Light: Seedlings are sensitive to light and can burn under strong HID or LED bulbs. It’s recommended to use CFL bulbs with a blue light spectrum for the first 10–14 days. Once seedlings have developed healthy true leaves and 2–3 nodes, they can be moved under stronger HID or LED lights to promote vegetative growth.
- Temperature: Seedlings prefer daytime temperatures of 20–25°C and nighttime temperatures that are slightly cooler. High temperatures can stress seedlings and stunt their growth, while cold temperatures can freeze their cells and impede nutrient absorption. Maintaining appropriate temperatures is crucial for healthy seedling development.
- Humidity: Seedlings absorb water through their leaves, so it’s important to keep relative humidity levels at 65-70%. Low humidity can stunt growth and cause symptoms similar to nutrient deficiencies, while high humidity can lead to wilting, rot, and the attraction of pests and pathogens. Once seedlings enter the vegetative phase, relative humidity should be kept at 50%.
VPD Chart for Cannabis Seedlings and Early Veg
| Growth Stage | Temperature (°F) | Humidity (%) | Lights on Optimal VPD Range (kPa) | Lights off Optimal VPD Range (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seedling | 68-77 | 65-75 | 0.3-0.7 | 0.2-0.5 |
| Vegetative | 70-85 | 40-60 | 0.8-1.2 | 0.6-1.0 |
Watering Techniques for the Seedling Stage of Cannabis
Proper watering is essential for the health of your seedlings. The frequency and amount of water depend on various factors such as the composition of your soil, temperature, humidity, lighting, and pot size. It’s important to start with a high-quality, well-aerated medium and well-draining pots.
- Watering Method: Seedlings prefer warm and moist conditions. Mist your seedlings regularly (3–6 times a day) to provide moisture. Place a plastic dome or bag over them to trap moisture and facilitate water absorption through the cotyledons and leaves. Avoid watering directly at the stem; instead, pour water around the plant in a circle approximately 3cm from the stem. This promotes healthy root growth and prevents moisture buildup at the stem.
- Watering Frequency: There is no universal watering schedule for seedlings. Water them when the soil has dried out, which can vary from every 3–7 days depending on the factors mentioned above. Test the soil by sticking your finger approximately 2cm into it. Watering in the morning or just before turning on the grow lights allows the plants to take up water during the day and prevents moisture buildup. Get accustomed to how much it weighs when you have just watered it and how it feels when you know its dry and thirsty.
Preventing Damping Off and Nutrient Problems
Damping off, caused by fungi such as Pythium, Botrytis, and Fusarium, can be a common issue during the seedling stage. It occurs in overly wet conditions and can lead to the death of seedlings. To prevent damping off, maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels, avoid overwatering, and ensure good soil drainage.
Nutrient problems can also arise during the seedling stage. It’s important to understand when and how to provide nutrients to your seedlings.
- Feeding Seedlings: Seedlings are fragile and can easily burn in nutrient-rich soil. It’s generally recommended to avoid feeding them during the seedling phase. Allow them to grow in their starting pots until they are ready to be transplanted and start vegetative growth. Transplant seedlings once they have developed at least three nodes and 4–5 sets of true leaves.
- Transitioning to the Vegetative Stage: After transplanting, give your seedlings 3–7 days to adjust before starting to feed them. This allows them to recover from the stress of transplantation. Begin feeding with a mild nutrient solution designed for vegetative growth once you’re confident they have fully recovered.
- Nutrient Burn: Nutrient burn can occur if seedlings are fed too early or with a fertilizer that is too strong. Symptoms include dark green leaves with burnt tips. If nutrient burn occurs, stop feeding for at least one week and water with plain, pH-balanced water. Gradually reintroduce nutrients once the plants show healthy growth.
Organic cannabis gardening is an alternative approach that focuses on building a vibrant soil ecosystem. While it requires more hands-on care, it can result in superior taste and quality. However, organic cultivation typically yields less compared to non-organic methods.
Preventing Pests and Bugs
Pests and bugs can quickly infest and harm seedlings. Maintaining a clean environment and optimal temperature and humidity levels is crucial to prevent infestations. Some common pests to watch out for include fungus gnats, spider mites, leaf miners, and white powdery mildew. Regular monitoring and early treatment are essential to protect your seedlings.
Transplanting Seedlings
Transplanting seedlings is a critical step in their growth. It’s important to pay attention to cues from the plants and perform the process gently to minimize stress. Generally, seedlings are ready for transplanting when their leaves fully cover the circumference of their container. After approximately one week, check the roots to ensure they are well-developed before transplanting.
Bonus Step: Understanding the Seedling Stage of Cannabis
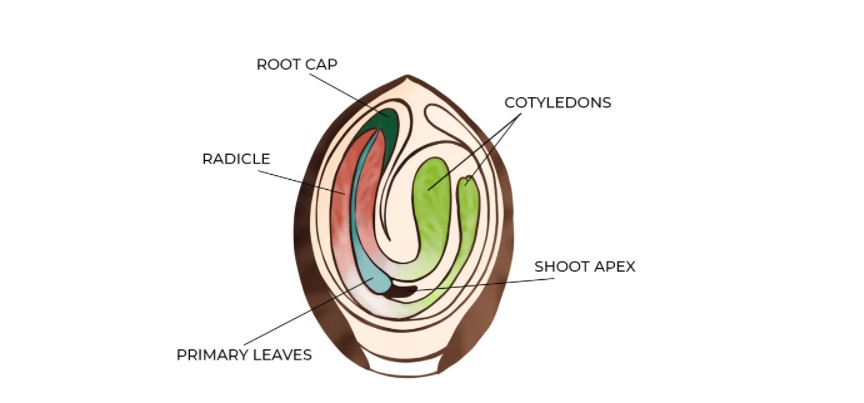
The seedling stage is a crucial phase in the life cycle of cannabis plants. Inside the seed, all the genetic information required for growth is stored. Germination is triggered by imbibition, where water activates enzymes and stimulates the growth of the taproot. The emergence of cotyledons and true leaves signifies the progression from seedling to vegetative growth. Rapid growth and vibrant green foliage are indicators of healthy seedlings.
By following these steps and understanding the essentials of the seedling stage, you can successfully cultivate cannabis seedlings and set the foundation for healthy and robust plants.
Remember to adapt these guidelines to your specific growing conditions, genetics, and preferences. With practice and knowledge, you’ll become a master at nurturing cannabis seedlings and achieving successful cultivation. Happy growing!