A great part of the medical benefits coming from cannabis is attributed to THC, one of the most abundant chemical compounds found in the plant. The effects of marijuana are well known and appreciated by both medical and recreational cannabis users worldwide.
Most people associate THC solely with the psychoactive high. But as more countries are investing their financial and human resources in research on cannabinoids and the marijuana plant in general, it turns out that THC holds great potential for treating a wide range of serious illnesses and diseases.
Overall, THC has had a long and complicated history as a medicine and recreational drug. Today, many myths around THC resulting from misinformation and the reefer madness propaganda have already been debunked. Yet, some people still fear this complex cannabinoid, mainly because they don’t understand its nature. In this guide, we map out the properties of THC along with its medical benefits and side effects.
What Is THC?
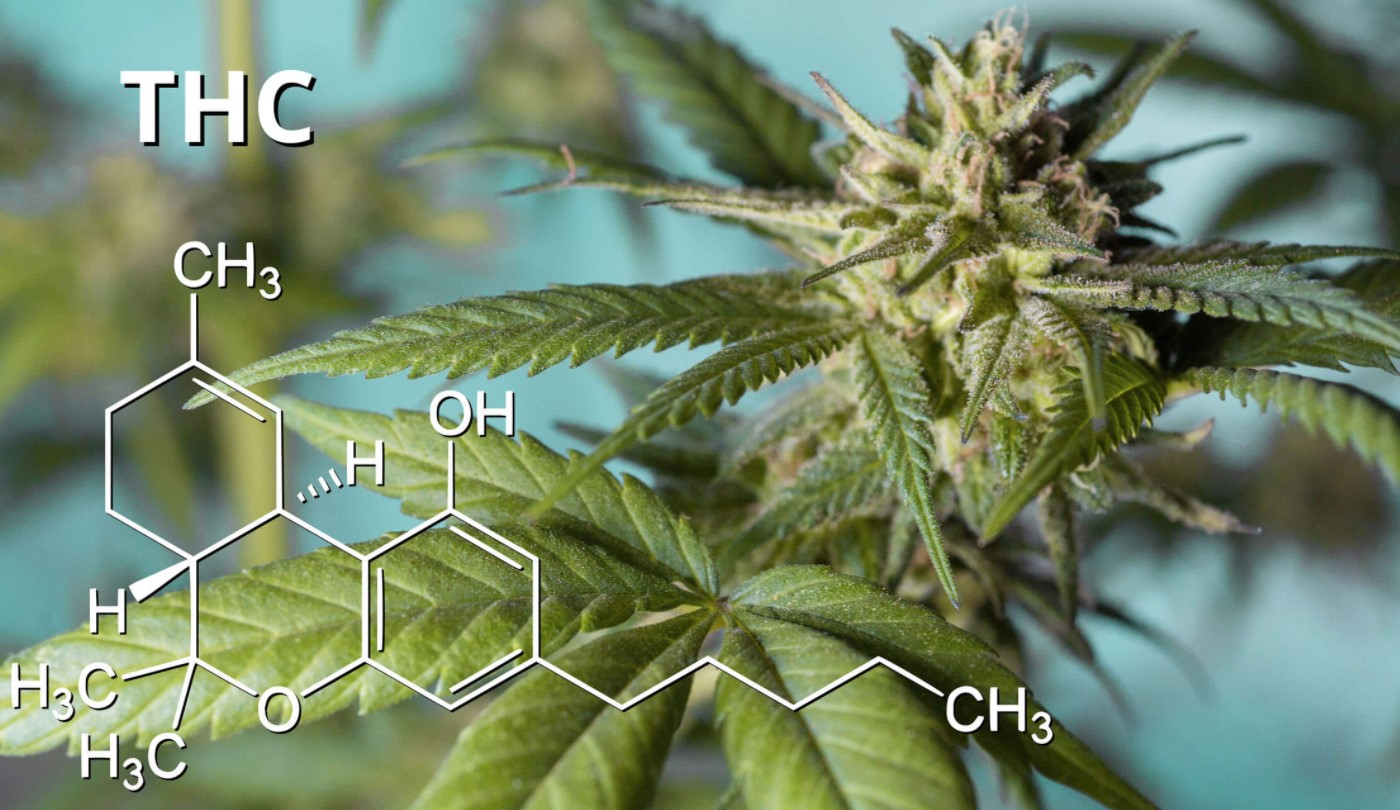
THC, short for delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary compound of cannabis responsible for its psychoactive properties. Molecularly identified in 1964 by Raphael Mechoulam, THC mimics the chemical structure of anandamide, a molecule produced in the brain. Anandamide controls such functions as mood, body temperature, sensory perception, coordination, attention, memory, immune response, and more.
The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) states that THC actually affects the same functions as anandamide. Upon entering the bloodstream, tetrahydrocannabinol alters the neuronal communication in the brain, signalling the increased production of anandamide. THC has long been stigmatized by opponents of marijuana. While fear-mongering was running rampant, research on the medical benefits of this compound was in its infancy. But now that times are changing, and more money is being pumped into cannabis-related studies, it turns out that THC has a plethora of potential medical applications aside from getting you high.

THC Properties
Every human being has an endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS is a complex communication network comprised of neurotransmitters and receptors spread throughout the brain, nervous system, and immune system. The aim of the endocannabinoid system is to maintain homeostasis — the chemical balance in the body and brain. A well-functioning endocannabinoid system helps a person maintain sanity and good physical health. Specifically, THC is a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor (the one located in the brain) where it attaches and ‘over stimulates’ this system, influencing the aforementioned physiological and mental functions.
When you ingest marijuana — be it through smoking, vaporizing, or eating THC — you can expect:
- Feelings of relaxation and euphoria
- Sedation running through the body
- Enhanced sensory experience
- Altered perception of time
- Improved focus
- Appetite boost
The experience can vary from one cannabis strain to another. There are three major categories of strains: Indica, Sativa, and hybrids
Indica strains induce sedative, whole-body relaxation, and a tingling euphoria without making the user too stimulated. Therefore, Indica buds are recommended for evening or nighttime use.
Sativa strains provide a more cerebral, energizing, and uplifting experience. They can also boost focus and productivity, which makes them a perfect daytime option.
Hybrid strains get you the best of both worlds, combining the effects of sativas and indicas in different ratios.
As you can see, THC is the major (but not the only) cannabis constituent that can affect your experience with marijuana. Some weed strains boast extremely high THC content reaching up to 30%; this can result in a more powerful high and more intensified medical benefits, but it can also bring up some minor side effects.
For now, though, let’s focus on the benefits of THC
THC Medical Benefits:
On the one hand, the scheduling of marijuana indicates that weed has strong potential for abuse and no medical applications. On the other hand, the same government that holds marijuana under the Schedule I category created a patent on the medical use of non-psychoactive cannabinoids. Patent No. 6,630,507 also claims that THC might be an effective antioxidant and neuroprotectant.
Here’s the list of the most remarkable therapeutic properties of this cannabinoid:
THC Benefits Cardiovascular Health
Although marijuana use is typically associated with some unhealthy behaviours like smoking or a high-calorie diet, mechanistic studies found that THC alone may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases in healthy subjects; this is likely due to the THC’s ability to reduce blood pressure.

Medical THC
- THC Is A Potent Pain Killer
It’s one of the best documented properties of THC. A strong base of supporting evidence refers to THC as an effective analgesic that can be used to treat various types of pain, from mild aches to chronic, neuropathic pain and migraines. - THC Stimulates Appetite
THC can promote the release of the hormone ghrelin, which stimulates hunger. If you’ve ever wondered why you can’t stop drooling by simply looking at food, here’s the answer. - Your body can benefit from THC’s appetite-stimulating properties if you maintain healthy eating habits and exercise on a regular basis. Many professional athletes are leaning towards marijuana in their off-season to keep their metabolism running high and stay hungry both metaphorically and literally.
- THC Reduces Inflammation
THC, and cannabinoids in general, have been shown to boost the immune system by reducing inflammation throughout the whole body. That’s the reason why cannabis can prove invaluable for treating autoimmune disorders. - THC Is A Neuroprotectant
THC and CBD are both strong neuroprotectants, which makes them potential medicines for treating neurodegenerative diseases. Studies have found that marijuana may slow or even inhibit the progression of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, as well as provide significant pain relief for some patients. - THC Lowers Intraocular Pressure
Ancient Egyptians have been using marijuana to treat glaucoma and they’ve been doing it for a good reason. - When THC enters the bloodstream, it dilates blood vessels and capillaries, including the ocular capillaries. As a result, the intraocular pressure gets reduced as more blood flows through the system. This is also why you get red eyes after smoking weed.
- THC Reduces Nausea
Numerous studies suggest that THC is an effective antiemetic agent, which means it can prevent vomiting and relieve nausea. - THC Aids Sleep
Marijuana is well known for its sedative effects. By bringing down relaxation to both the body and mind, THC may relieve stress, anxiety, and stave off racing thoughts.

On top of that, marijuana affects the REM phase of sleep, meaning you will experience very few to no dreams at all. The deep sleep phase intensifies, too, which makes weed a strong go-to herbal night cap.
Marijuana Benefits
What Medical Conditions May THC Help Alleviate?
The above health benefits of THC can be used to treat a wide range of conditions. Some notable illnesses that can be treated with marijuana include:
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Arthritis
- Cancer
- Crohn’s disease
- Eating disorders
- Fibromyalgia
- Glaucoma
- HIV/AIDS
- Insomnia
- Metabolic syndrome
- Migraines
- Multiple sclerosis
- Tourette’s syndrome
- Wasting syndrome
Now, let’s elaborate on the potential side effects of THC use for a change.
Common Side Effects of THC Use
THC is known to produce dose-dependent short-term side effects, but these are rather mild ones.
As for the long-term side effects of ingesting the compound, these are yet to be studied, but the current research shows that THC can be habit-forming on top of several other individual-dependent problems.
Short-Term Side Effects
There are plenty of well-documented short-term side effects of marijuana that are popular among most users and considered tell-tale signs that someone has just smoked a generous bowl.
Besides developing tolerance to THC over time, the following minor side effects include:
- Dry and red/bloodshot eyes
- Dry mouth a.k.a. Cottonmouth or the pasties
- Overwhelming sedation
- Short-term motor and cognitive impairment
- Confusion
- Increased heart rate
As we mentioned earlier in the article, THC can cause a range of other side effects when overdosed. Although there has been no record of a marijuana-induced death, there are several side effects that typically occur in cases of very high dosing and/or low THC tolerance:
- General agitation
- Anxiety
- Paranoia or panic attacks
- Nausea and/or vomiting
Keep in mind that these side effects come from consuming extremely high doses of THC. Low-to-moderate doses of this cannabinoid are known to reduce anxiety and prevent nausea/vomiting.
Long-Term Side Effects
Below we list the most common long-term side effects of THC use. However, they are not always linked directly to tetrahydrocannabinol itself but rather to smoking marijuana as the go-to consumption method.
Heart Risks
Smoking marijuana can increase the heart rate from 20-100% for up to 3 hours. People with pre-existing heart conditions or high blood pressure could face a danger of irregular heart rhythms or heart attacks due to the extra tension.
Lung Diseases
As we said, marijuana is most commonly consumed as joints/blunts/spliffs. Simply put, most people just smoke the bud according to their liking. Combustion and inhalation of any compound can cause lung damage and result in such issues as chronic cough, weakened immune function, phlegm, bronchitis, or even cancer. But then again, these side effects are not linked directly to the use of THC. If you eat or vaporize marijuana, you can totally avoid these risks
Negative Impact On Adolescent Brains
A well-known and broadly cited study discussed cannabis use among adolescents and concluded that tetrahydrocannabinol can cause young people to suffer from neural impacts on the developing mind. On the other hand, marijuana can benefit the brains of the elderly thanks to its neuroprotective properties. The bottom line? Start using weed once you’re old enough to benefit from it (21+ should suffice).
Habit Forming
While not physically addictive, THC use is known to form psychological habits and cravings. This, combined with a tolerance buildup, can lead to addictive behaviour. In addition, long-term users may suffer from withdrawal symptoms, such as irritability, sleeplessness, anxiety, decreased appetite, hot flashes, and sweaty hands.

Weed Side Effects
How to Minimize the Potential Side Effects of THC Use
There are certain life hacks you can use to avoid experiencing the negative effects associated with consuming too much THC.
Let’s start with an easy one: don’t smoke too much marijuana at once. It’s not a competition where you have to smoke as many joints as you can in a limited time span. Enjoy weed with baby steps to find your perfect dose, and you’re going to be all good in most cases.
Furthermore, you can find some high-CBD/low-THC strains or at least those that have an even ratio of CBD to THC. CBD is known to mitigate the psychoactivity of THC, allowing you to draw upon its health benefits without getting anxious, paranoid, or couch-locked.
Finally, try to microdose weed. Micro dosing means taking very small (tiny) doses of THC to get yourself on the verge of being high. When micro-dosed, THC exhibits its cognitive-boosting potential, promotes relaxation, and sharpens senses, but it doesn’t make you stoned. Micro dosing works best when the weed is vaporized.
Where Do I Find THC?
THC is one of the easiest phytocannabinoids to obtain. The compound is found in high concentrations in a lot of cannabis strains for those who want to use it recreationally or medically. In addition, you can find THC in other marijuana derivatives, such as concentrates, edibles, oils, capsules, E-liquids, tinctures, and topical creams.
The biggest hurdle on your way to buying marijuana is the current scheduling of the herb. Although more states are legalizing weed every year, it remains illegal on the federal level. Countries that have legalized the medical use of cannabis include Argentina, Australia, Barbados, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Ecuador, Finland, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Jamaica, Lebanon, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malawi, Malta, the Netherlands, New Zealand, North Macedonia, Norway, Peru, Poland, Portugal, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, San Marino, Sri Lanka, Switzerland, Thailand, the United Kingdom, Uruguay, Vanuatu, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
If you want to buy THC-rich cannabis, you must live either in a legal recreational U.S. state, or be a resident of Canada, Uruguay, or one of the countries which have decriminalized the use of marijuana within their borders.

[…] you’re new to the universe of cannabis concentrates, you probably have difficulties maneuvering the maze of different cannabis terms describing various […]
[…] Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the psychoactive substance that produces the “high” you get with smoking marijuana. […]