The weed plant, scientifically known as Cannabis, is a member of the Cannabaceae family of plants. For thousands of years, humans have utilized this plant for both therapeutic and recreational purposes, owing to its various benefits. In fact, hemp fiber derived from the plant is used in making an array of products, including paper, clothing, biofuel, and food.
Moreover, cannabis is one of the earliest psychotropic chemicals ever used by humans. It is interesting to note that the plant has three species: Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica, and Cannabis ruderalis, each with unique characteristics.
When it comes to slang terms, weed plants are referred to by different names such as pot, marijuana, ganja, and mary jane, among others. All in all, this plant’s versatility and the numerous benefits it offers have made it a highly valuable and popular crop around the world.
Table of Contents
- Description of the Weed Plant
- Plant Physiology of Cannabis
- Components of Weed Plants and their Effects on the Body
- Cultivation of Weed Plants
- Legality of Weed Plants Worldwide
- How to Use Weed Plants: Recreational, Industrial, and Medicinal Uses
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Description of the Weed Plant
Cannabis sativa is an annual herbaceous plant that blooms and is native to Eastern Asia. Today, it is cultivated globally due to its hardy nature, as it can thrive in a variety of environments. Given its ability to grow almost anywhere, it is often referred to as a “weed”. However, cannabis is much more than a mere weed. It is a multi-purpose crop that can be used for food, recreation, spiritual and religious practices, seed oil, industrial fiber, and medicine. Each part of the plant is harvested and utilized differently based on its intended use. With its versatile and valuable properties, cannabis has been a significant plant in human history and continues to play a crucial role in various cultures and industries worldwide.
Plant Physiology of Cannabis
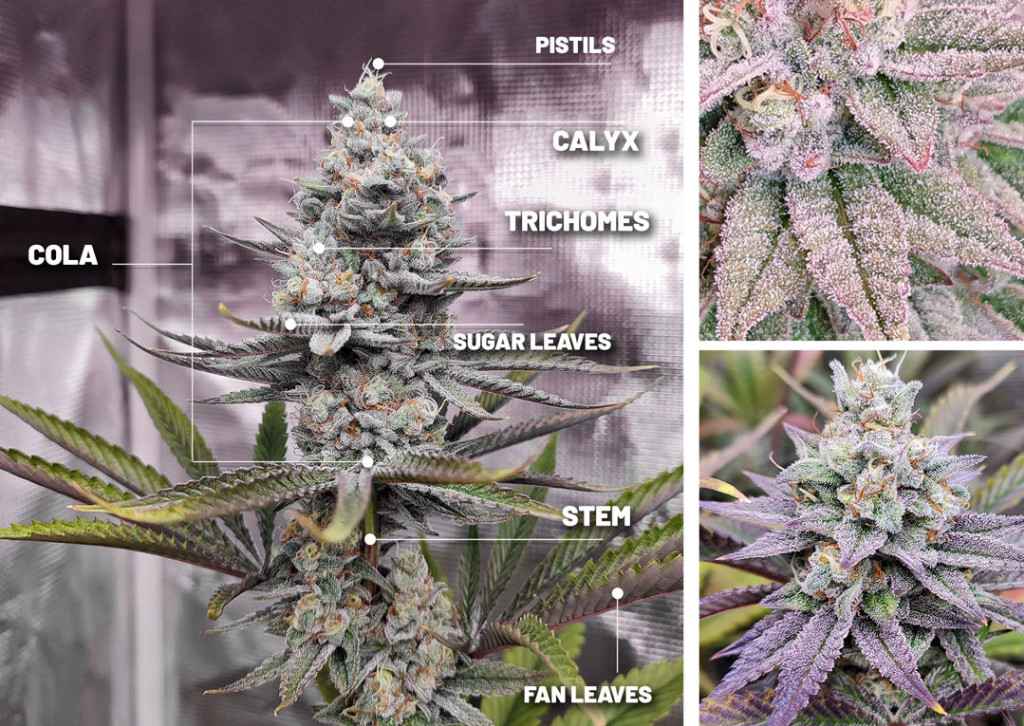
Cannabis plants are dioecious, annual herbs that are known for their distinctive features. They grow on long, slender stems with large fan leaves emerging from nodes, and can reach heights of up to 16 feet. The leaflets of weed plants are usually arranged in a palmate or digitate manner and have serrated edges. The cotyledon leaves are the first to emerge after germination, typically appearing in pairs.
One of the most recognizable features of the cannabis plant are the fan leaves, which are quite large and provide ample surface area for photosynthesis. The tiny, resin-coated leaves that surround the buds are called sugar leaves. The buds, or flowers, of the cannabis plant are where it truly shines, as they have complex and intriguing structures such as blazing orange hairs, sweet crystals, and large, encased-in-tiny-leaf blooms.
The cannabis plant is covered in trichomes, which are crystallized resin blankets that are rich in terpenes and cannabinoids. These trichomes can be seen all over the plant, but are particularly concentrated on the buds. A group of closely spaced-apart buds is known as a bud site or cola.
In female cannabis plants, the reproductive organs are enclosed in a bract, which resembles a green, tear-shaped “leaf” and is densely covered in resin glands that produce cannabinoids. The calyx, which is a translucent covering that surrounds the ovule at the base of a flower, is surrounded by these bracts and is invisible to the naked eye.
Male and female reproductive organs are found on different plants in dioecious cannabis plants. Male plants produce pollen sacs close to the base of the leaves, while female plants produce the resin-secreting flowers that are trimmed down into buds. To initiate seed development, male plants pollinate female plants. Understanding the unique characteristics and physiology of cannabis plants is essential for successful cultivation and use of the plant for recreational, medicinal, or industrial purposes.
Components of Weed Plants and their Effects on the Body
Components of Weed Plants
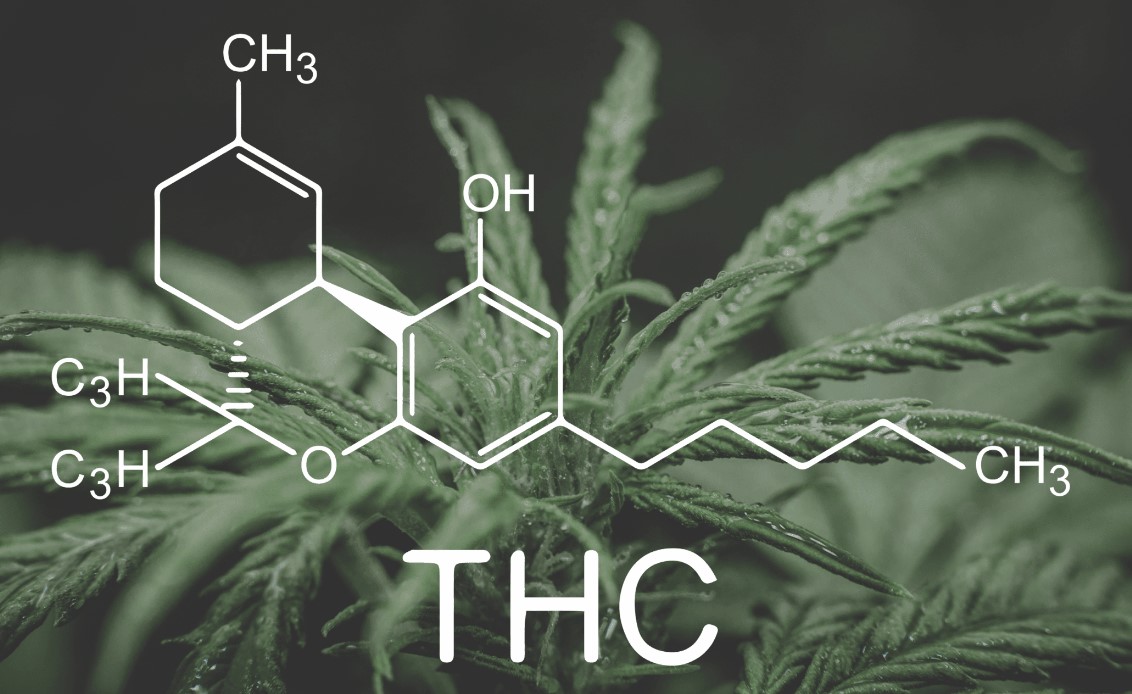
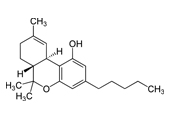
Cannabis is a herbal drug that contains over 100 cannabinoids, including delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). THC is the primary psychoactive compound, responsible for the “high” that most people associate with marijuana, while CBD is non-intoxicating and offers potential medicinal benefits.
CBD is frequently used to relieve inflammation and discomfort, anxiety, migraines, seizures, and nausea. It is also the main component of Epidiolex, the first and only prescription drug containing CBD approved by the FDA to treat specific types of epilepsy.
THC, on the other hand, can cause a pleasant euphoria, relaxation, increased hunger, laughter, and altered perceptions of time when consumed. However, taking large quantities of THC can lead to acute psychosis, which includes hallucinations, delusions, and a loss of self-identity.
| Component | Chemical Name | Potential Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| THC | Tetrahydrocannabinol | Pain relief, muscle relaxation, appetite stimulation, mood enhancement |
| CBD | Cannabidiol | Anxiety reduction, anti-inflammatory, pain relief, antipsychotic |
| CBC | Cannabichromene | Anti-inflammatory, anti-fungal, anti-depressant |
| CBG | Cannabigerol | Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer |
| CBN | Cannabinol | Sedative, antibiotic, appetite stimulant |
| THCV | Tetrahydrocannabivarin | Appetite suppression, anti-convulsive, bone growth stimulation |
| CBDV | Cannabidivarin | Anti-epileptic, anti-nausea, anti-inflammatory, analgesic |
| Delta-8-THC | Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol | Pain relief, appetite stimulation, relaxation, reduced anxiety and paranoia |
| Delta-9-THC | Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol | Pain relief, muscle relaxation, appetite stimulation, mood enhancement |
| THC-A | Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid | Anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, nausea relief |
| CBD-A | Cannabidiolic acid | Anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, pain relief, may enhance CBD’s effects |
| Terpenes | Various | Aromatherapy, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, pain relief, mood enhancement |
| Flavonoids | Various | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, may enhance the effects of CBD |
Effects of Weed on Your Body
When marijuana is smoked, THC and other plant compounds are quickly released into the bloodstream and travel through the body to the brain, where they exert their effects. Some of the most common side effects of marijuana use include euphoria, relaxation, altered perceptions, and increased appetite.
However, cannabis use can also have detrimental effects on physical health, including inflammation of the lungs and bronchitis development, weakened immune system, increased heart rate and pulse, cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (severe nausea, vomiting, and dehydration), and pregnancy-related impairment with fetal development. It may also interfere with adolescent brain development and exacerbate lung diseases like asthma when combined with tobacco use.
On the other hand, there is emerging evidence to suggest that marijuana may have potential therapeutic benefits in treating certain medical conditions, such as chronic pain, epilepsy, and nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy. Additionally, some studies suggest that cannabinoids may inhibit tumor growth and have neuroprotective properties, but more research is needed in these areas.
Cultivation of Weed Plants
The process of growing cannabis requires specific conditions and care to produce a healthy and robust plant with high-quality buds. Here is an overview of the various stages of cannabis growth and cultivation:
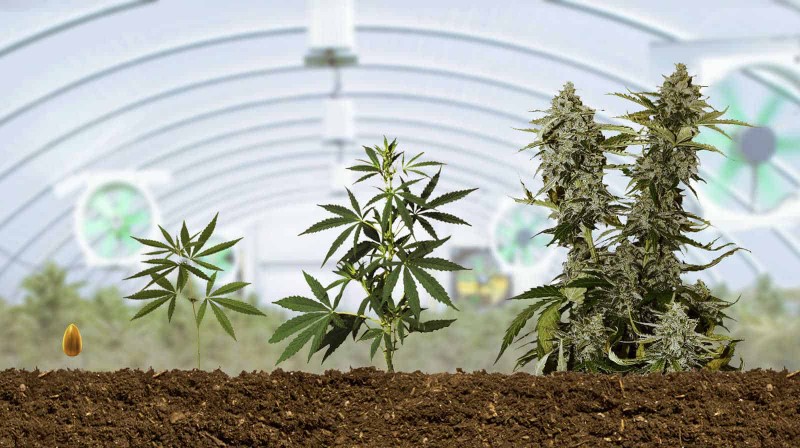
Germination: The first stage of cannabis growth begins with the germination of seeds, which usually takes between three to ten days. During this phase, the seed begins to grow and emerge from the ground, establishing a root system.
Seedling: The next stage is the seedling phase, which is the period between germination and the development of the plant’s initial cotyledon leaves. At this stage, the plant requires a lot of light, but not too much water to prevent overwatering, which can stunt growth.
Vegetative stage: This is the juvenile or immature stage of a cannabis plant and lasts from three to sixteen weeks. During this stage, the plant develops stalks, branches, stems, and fan leaves, preparing for the flowering stage.
Flowering stage: The cannabis plant begins to produce buds during this stage, which usually lasts from eight to eleven weeks. The plant’s development during this stage depends on various factors, including light exposure, temperature, humidity, and nutrient availability.
Environmental factors: Cannabis is an annual plant that grows best in warm areas. Its growing time varies between 10 and 32 weeks. For a photoperiod plant, weed prefers temperatures between 65 and 80 °F (18 and 26 °C) during the day and 55 and 70°F (13 to 21 °C) at night. Humidity levels also play a crucial role in cannabis growth, and most producers favor relative humidity levels between 40 to 70 %, depending on the growth stage. Additionally, the ideal pH range for cannabis growth is between 6.3 and 6.8.
Propagation methods: While seed production continues to be the most common method of propagation, tissue culture multiplication has become increasingly essential in the development of medically significant clones. Tissue culture propagation is a cloning process that involves taking a tiny sample from a mother plant and placing it in a sterile medium to grow into a new plant.
In conclusion, the cultivation of cannabis plants requires careful attention to various factors, including environmental conditions, nutrient availability, and propagation methods, to produce a healthy and high-quality plant with potent buds.
Legality of Weed Plants Worldwide
The legality of cannabis varies significantly across the world, with some countries legalizing it for medical or recreational use while others still prohibit its use entirely.
In countries where cannabis is legal for medical purposes, it is often tightly regulated and requires a doctor’s prescription. In contrast, countries where cannabis is legal for recreational use generally have fewer restrictions, but still impose age limits and limits on the amount of cannabis an individual can possess.
Uruguay became the first country in the world to legalize cannabis for recreational use in 2013, followed by Canada in 2018. Many US states, including California, Colorado, and Washington, have also legalized cannabis for both medical and recreational purposes, but it is still illegal under federal law.
In other countries, such as the United Kingdom and Germany, cannabis is legal for medical use only and requires a prescription from a doctor. However Germany recently announced planned legalization for recreationl purposes. In Australia, cannabis is legal for medical use in some states but still illegal for recreational use.
It’s worth noting that even in countries where cannabis is legal, there are often strict regulations on how it can be consumed and who can grow it. For example, in Canada, individuals are only allowed to grow up to four cannabis plants for personal use, and cannabis products must be purchased from licensed retailers.
In countries where cannabis is still illegal, possession, distribution, and cultivation can result in severe criminal penalties, including fines and imprisonment. However, some countries have decriminalized cannabis, meaning that possession of small amounts is treated as a civil offense rather than a criminal one.
Overall, the legality of cannabis continues to evolve, with more and more countries reconsidering their stance on the drug. As research into the potential medical benefits of cannabis continues to grow, it’s likely that more countries will legalize its use for medical purposes in the future.
How to Use Weed Plants: Recreational, Industrial, and Medicinal Uses
Recreational use:
Cannabis is widely known for its recreational use and is the fourth most commonly used drug worldwide, following only alcohol, caffeine, and tobacco. The primary psychoactive component in cannabis is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which causes relaxation and euphoria. Cannabis also produces secondary psychoactive effects such as introspection, philosophical thought, and metacognition. However, overuse can lead to anxiety and paranoia.
Industrial use:
Cannabis is an adaptable plant that is useful in several industrial applications. The plant’s lengthy stems provide fibers that are strong and durable, known as hemp. Hemp is used in the production of paper, rope, cordage, building materials, and apparel. It is more durable than cotton and is also a good source of biofuels and meals, such as hemp milk, hemp seed, and hemp oil.
Medicinal use:
Medical cannabis, also known as medical marijuana, is used to treat various illnesses and reduce their effects. Cannabis has been used for medicinal purposes for centuries. Cannabinoids found in cannabis have been shown to alleviate chronic pain, muscle spasms, nausea and vomiting in chemotherapy patients, reduce inflammation, and treat neurological conditions like multiple sclerosis and movement problems. Medical cannabis can also be used to treat anorexia, arthritis, glaucoma, migraine, Tourette’s syndrome, ADHD, depression or anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder, or psychosis.
FAQ
a. How Long Does Cannabis Stay in Your System?
The length of time that cannabis stays in your system depends on a variety of factors such as your metabolism, frequency of use, and the potency of the cannabis. Generally, cannabis can be detected in urine for up to 30 days, in blood for up to 2-3 days, and in hair for up to 90 days.
b. How to Recognize a Weed Plant?
Cannabis plants have several identifying features. They typically have serrated leaves that are arranged in a palmate pattern with several finger-like structures. The flowers of a cannabis plant are usually green and grow in clusters. Additionally, the plants produce a strong, distinct aroma that is often described as skunky.
c. What are the Differences Between Male and Female Cannabis Plants?
The main difference between male and female cannabis plants is their reproductive organs. Male plants produce pollen sacs, while female plants produce pistils. Female plants are the ones that produce the resinous buds that are commonly used for consumption.
d. What Are Some Common Methods of Consuming Cannabis?
Cannabis can be consumed in a variety of ways, including smoking, vaping, edibles, tinctures, and topicals. Smoking and vaping involve inhaling the cannabinoids through the lungs, while edibles are ingested and absorbed through the digestive system. Tinctures and topicals are applied directly to the skin or under the tongue.
e. What are the Potential Medical Benefits of Cannabis?
Cannabis has been used for medicinal purposes for thousands of years. It is believed to havepotential therapeutic benefits for a variety of conditions, including chronic pain, anxiety, depression, nausea and vomiting, muscle spasms, and inflammation. However, more research is needed to fully understand the medical benefits and potential risks of cannabis use.
f. Is Cannabis Legal?
The legal status of cannabis varies by country and region. In some places, it is completely legal for both medicinal and recreational use, while in others it is illegal for any purpose. It’s important to check the laws in your area before consuming or possessing cannabis.
g. What are the Potential Risks of Cannabis Use?
While cannabis can have potential medical benefits, it also carries some risks, especially when used excessively or inappropriately. Some potential risks of cannabis use include impaired memory and concentration, addiction, respiratory problems, and mental health issues, such as anxiety and psychosis. It’s important to use cannabis responsibly and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
h. Can You Overdose on Cannabis?
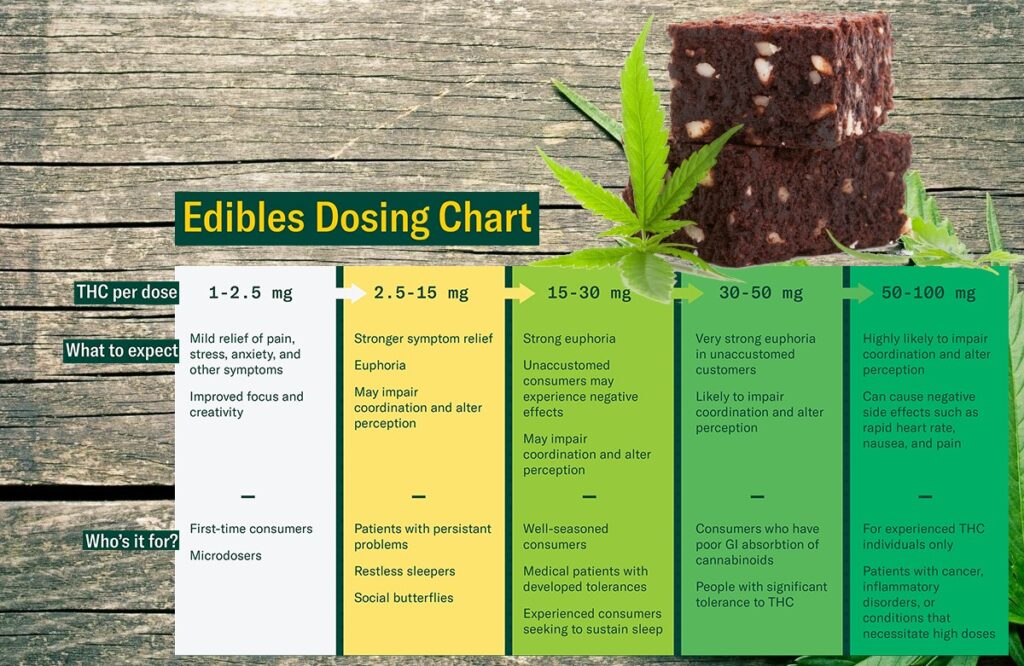
It is unlikely to overdose on cannabis in the way that one can overdose on opioids, for example. However, consuming too much cannabis can result in uncomfortable side effects such as paranoia, anxiety, and rapid heart rate. It’s important to start with a low dose and increase gradually to avoid these side effects.
i. How Can I Store Cannabis Safely?
To maintain the quality and potency of your cannabis, it’s important to store it properly. Keep it in an airtight container, away from light, heat, and moisture. This can help prevent the growth of mold and bacteria, which can compromise the safety of the product. Additionally, it’s important to keep cannabis out of reach of children and pets.






Yeah bookmaking this wasn’t a bad conclusion outstanding post! .