Welcome, fellow gardeners and cannabis enthusiasts! The age-old debate between hydro weed vs soil cultivation methods continues to spark curiosity among growers. In this comprehensive guide, we delve deep into the intricacies of both techniques, exploring their impact on cannabis potency. Drawing from years of hands-on experience and scientific insights, we navigate the pros and cons of each method and unravel the mystery behind what truly makes cannabis more potent.
Table of Contents:
- Hydroponic vs. Soil-Based Growing: An Overview
- Understanding the fundamental differences between hydroponic and soil-based cultivation methods.
- The Science of Cannabis Potency
- Exploring the role of cannabinoids, especially THC and CBD, in determining cannabis potency.
- Hydroponic Growing: Pros and Cons
- Delving into the advantages and disadvantages of hydroponic cultivation, from accelerated growth to meticulous maintenance.
- Soil-Based Growing: Pros and Cons
- Unraveling the benefits and challenges of traditional soil-based cultivation, focusing on natural flavor profiles and ease of use.
- Hydroponic Cannabis vs. Soil-Grown Cannabis: Which Is More Potent?
- Analyzing the ongoing debate regarding the potency of hydroponically grown cannabis versus soil-grown cannabis, considering various factors like THC levels and cannabinoid diversity.
- The Science of Hydroponic Growing
- A deep dive into the scientific intricacies of hydroponic cultivation, covering water temperature, nutrient balance, and optimal pH levels.
- Hydroponic Cannabis Equipment For Beginners
- A comprehensive guide to essential hydroponic equipment, including hydroponic systems, grow lights, nutrients, and pH testing kits.
- Conclusion
- Summing up the key points and helping growers make an informed decision based on their unique preferences and goals.
- FAQ
- Addressing frequently asked questions about hydroponic and soil-based growing methods, providing clear insights for growers’ queries.
1. Hydro Weed vs. Soil Growing: An Overview
In the ever-expanding realm of cultivation, two methods stand out: hydroponic and soil-based growing. Each method carries its unique set of advantages and challenges, making the choice between them a pivotal decision for growers. Let’s delve into the core disparities between hydroponic and soil-based growing, enabling you to make an informed choice tailored to your cultivation goals.
Understanding Hydroponic Cultivation:
1. Nutrient Delivery: Hydroponic systems utilize a water-based solution fortified with nutrients, allowing plants to absorb minerals directly. This precise nutrient control fosters accelerated growth and potentially higher yields.
2. Water Efficiency: Hydroponics drastically reduces water usage compared to traditional soil-based methods. The closed-loop systems recycle water, promoting sustainability and conservation.
3. Space Utilization: Hydroponic setups require less space, making them ideal for indoor cultivation. Vertical farming and controlled environments maximize space usage, enabling year-round cultivation.
4. Pest and Disease Management: The absence of soil minimizes the risk of soil-borne pests and diseases. Hydroponic environments are sterile, reducing the need for pesticides and fostering a healthier plant ecosystem.
Understanding Soil-Based Cultivation:
1. Natural Nutrient Source: Soil provides a natural medium rich in organic matter and essential nutrients. Plants extract nutrients from the soil, leading to a diverse and complex cannabinoid profile, potentially enhancing flavors and aromas.
2. Microbial Interaction: Soil teems with beneficial microbes that facilitate nutrient absorption and enhance plant immunity. These symbiotic relationships contribute to the overall health and resilience of plants.
3. Flavor Complexity: Many cultivators argue that soil-grown cannabis exhibits a more nuanced flavor profile due to the intricate interactions between the plant and the diverse microorganisms in the soil.
4. Simplicity and Accessibility: Soil-based growing is often considered more accessible for beginners. It requires less technical knowledge, making it a popular choice for novice growers. The simplicity of soil-based methods can also translate to lower startup costs.
Choosing the Right Method for You:
1. Consider Your Goals: Determine your cultivation objectives. Are you aiming for rapid, high-yield production, or do you prioritize the complexity of flavors and a more natural growing approach?
2. Evaluate Resources: Assess your resources, including space, budget, and expertise. Hydroponic setups might require significant initial investments, while soil-based methods can be more budget-friendly.
3. Environmental Impact: Reflect on the environmental implications. Hydroponics’ water efficiency might align with sustainability goals, while soil-based cultivation supports a more traditional and ecologically balanced approach.
4. Experimentation and Innovation: Some growers combine aspects of both methods, utilizing hybrid techniques. Experimentation is key in finding the perfect balance that suits your specific needs and preferences.
In the end, the choice between hydroponic and soil-based growing hinges on your objectives, resources, and the level of control you desire. Whether you opt for the precision of hydroponics or the natural complexities of soil, both methods offer pathways to successful cannabis cultivation. Understanding these differences empowers you to embark on your growing journey with confidence and expertise. Happy cultivating!
The Science of Cannabis Potency
Cannabis potency, the essence of its effects, lies within its chemical composition, predominantly comprising cannabinoids. Among these, Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD) are the frontrunners, each wielding distinct influence on the cannabis experience.
1. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC): THC is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, responsible for the euphoria and altered sensory perception associated with the plant. Higher THC levels often result in more potent and intoxicating effects, making it a focal point for recreational users.
2. Cannabidiol (CBD): CBD, in contrast to THC, does not induce a high. Instead, it offers a more calming, therapeutic influence. CBD-rich strains are popular among medical users seeking relief from various ailments without the intoxicating effects. CBD can balance the potent impact of THC, offering a more harmonious and well-rounded experience.
3. The Entourage Effect: Cannabis’s potency is not solely dictated by THC or CBD alone. The “Entourage Effect” highlights the synergy between various cannabinoids, terpenes, and other compounds present in the plant. This complex interplay enhances the overall effects, accentuating potency and therapeutic benefits.
4. Genetic Variability: Different cannabis strains exhibit varying cannabinoid profiles. Genetics play a pivotal role in determining the ratio of THC to CBD and other cannabinoids. Understanding these genetic differences is crucial for both recreational users seeking specific experiences and medical users pursuing tailored treatments.
5. Impact of Growing Methods: The cultivation method, whether hydroponic or soil-based, influences the cannabinoid composition. Hydroponic environments, with their precise nutrient control, may result in higher THC levels. Conversely, soil-based cultivation, rich in organic complexity, can yield a diverse cannabinoid profile, potentially enhancing CBD content.
6. Harvesting and Curing Techniques: Cannabis potency is further refined during the harvesting and curing phases. Proper timing and techniques preserve and enhance cannabinoids, ensuring the final product retains its intended potency. Factors like light exposure, humidity, and temperature control play pivotal roles in this process.
Understanding the intricate dance of cannabinoids within cannabis offers cultivators and users valuable insights. Whether seeking recreational highs, therapeutic relief, or a balance between the two, comprehending the science behind cannabis potency empowers individuals to make informed choices, leading to a more satisfying and tailored experience.
Hydroponic Growing: Pros and Cons
Hydroponic growing, a modern marvel in agriculture, revolutionizes the way cannabis is cultivated. However, like any method, it comes with its unique set of advantages and challenges. Here, we delve into the pros and cons of hydroponic growing, shedding light on this high-tech approach to cannabis cultivation.
Pros:
1. Precision Nutrient Control: Hydroponic systems offer precise control over nutrient intake, ensuring plants receive an optimal blend of essential elements. This fine-tuning results in faster growth and potentially higher THC levels, enhancing overall potency.
2. Faster Growth Rates: Hydroponically grown cannabis typically experiences accelerated growth compared to traditional soil methods. The controlled environment, coupled with direct nutrient delivery, fosters rapid plant development, leading to quicker harvests.
3. Higher Yields: Thanks to the efficient nutrient uptake and controlled conditions, hydroponic setups often yield more cannabis per square foot. For commercial growers, this translates to increased production and profitability.
4. Water Efficiency: Hydroponic systems use water more efficiently than soil-based cultivation. By recycling nutrient solutions, these systems conserve water, making them environmentally friendly and sustainable options for cannabis cultivation.
5. Space Optimization: Hydroponic setups require less space than traditional soil-based methods. This spatial efficiency is especially advantageous for urban or indoor growers with limited area, allowing for maximized production in confined environments.
Cons:
1. High Initial Investment: Setting up a hydroponic system demands a significant upfront investment. Equipment such as pumps, grow lights, and monitoring tools can be costly, making it a substantial barrier for entry, particularly for small-scale growers.
2. Technical Expertise Required: Hydroponic growing necessitates a deep understanding of the system’s intricacies. Maintaining proper pH levels, nutrient concentrations, and environmental conditions demands expertise. Novice growers might find the learning curve steep.
3. Maintenance Challenges: Hydroponic systems require meticulous maintenance. Any deviations in nutrient levels or system functioning can rapidly impact plant health. Regular checks and adjustments are vital, making this method labor-intensive and time-consuming.
4. Susceptibility to System Failures: Technical glitches or failures in hydroponic systems, such as pump malfunctions or power outages, can swiftly jeopardize crops. Unlike soil-based methods, where plants have some resilience against temporary adversities, hydroponic plants are entirely dependent on system integrity.
5. Lack of Organic Certification: Achieving organic certification for hydroponically grown cannabis can be challenging. Many certification bodies have stringent criteria, and hydroponic systems, which rely on artificial nutrient solutions, might not meet these standards.
Understanding these pros and cons equips growers with the knowledge needed to weigh the benefits against the challenges. Hydroponic growing, with its potential for high yields and accelerated growth, offers an innovative pathway in cannabis cultivation. However, the initial investments, technical demands, and ongoing maintenance requirements necessitate careful consideration before opting for this method.
Soil-Based Growing: Pros and Cons
Soil-based growing, a time-honored technique, relies on the natural properties of soil to nurture cannabis plants. While it embraces the traditional essence of farming, it presents its own array of advantages and challenges. Let’s explore the pros and cons of this classic method, shedding light on its unique characteristics in cannabis cultivation.
Pros:
1. Rich Flavor Profile: Soil-based cultivation often results in a more complex and nuanced flavor profile in cannabis. The plants draw distinctive characteristics from the soil, leading to a diverse range of tastes and aromas, cherished by connoisseurs.
2. Lower Initial Investment: Soil-based growing typically requires less initial investment compared to hydroponic systems. The simplicity of this method means growers can start with minimal equipment, making it accessible for beginners and small-scale cultivators.
3. Beginner-Friendly: Soil-based cultivation is more forgiving, especially for novice growers. The natural buffer of soil provides some leeway in nutrient management, making it easier for beginners to navigate and learn the ropes of cannabis cultivation.
4. Environmental Friendliness: Soil-based growing is often considered more environmentally friendly. It requires fewer resources in terms of energy, relying on natural processes within the soil. This eco-conscious approach aligns with sustainable farming practices.
5. Tolerance to Variability: Soil-grown plants exhibit a higher tolerance to fluctuations in environmental conditions. Variations in pH levels or minor inconsistencies in nutrient availability are generally absorbed by the soil, providing a buffer that protects plants from sudden stress.
Cons:
1. Slower Growth Rate: Soil-based cultivation typically leads to slower growth rates compared to hydroponic systems. The natural nutrient absorption process in soil takes more time, resulting in a longer cultivation cycle and potentially lower yields.
2. Limited Control Over Nutrients: Unlike hydroponic systems, where nutrient levels can be precisely controlled, soil-based methods rely on the existing nutrient content of the soil. While organic supplements can be added, the control over nutrient intake is inherently limited.
3. Space Requirements: Soil-based cultivation often requires more space due to the larger root systems plants develop in soil. This can be a constraint, especially for indoor or urban growers with limited area.
4. Susceptibility to Pests and Diseases: Soil-based environments can harbor various pests and diseases. Without proper management, these issues can escalate and significantly impact plant health. Vigilant pest control measures are essential to mitigate risks.
5. Soil Quality Dependency: The quality of the final product heavily depends on the soil quality. Poor soil quality can lead to inferior crops, emphasizing the importance of soil testing and amendments to ensure optimal conditions for cannabis growth.
Understanding these pros and cons is vital for growers considering soil-based cultivation. While it offers a natural and flavorful approach to cannabis farming, the trade-offs in terms of growth rate and control over nutrients need to be carefully evaluated. Soil-based growing’s historical significance and potential for rich, nuanced cannabis flavors make it a timeless choice, especially for those valuing tradition and taste diversity.
Hydro Weed vs. Soil Grown. Which Is More Potent?
The quest for potent cannabis has spurred an ongoing debate: is hydroponically grown cannabis mightier than its soil-grown counterpart? Understanding the potency of cannabis involves delving into the intricate world of cannabinoids, primarily THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol), which play pivotal roles in the plant’s effects on users.
Factors Influencing Potency:
1. Cannabinoid Profile: Both hydroponic and soil-grown cannabis can yield high-potency buds. The plant’s genetic makeup, combined with the specific cultivation environment, determines the cannabinoid profile. THC, responsible for the psychoactive effects, is often higher in hydroponic varieties due to precise nutrient control, while soil-grown cannabis might exhibit a more diverse range, including elevated CBD levels.
2. Nutrient Management: Hydroponic systems offer meticulous control over nutrient intake, potentially leading to faster growth and higher THC concentrations. Conversely, soil-based cultivation, relying on natural soil properties, might result in a broader spectrum of cannabinoids, including CBD, known for its relaxing effects.
3. Growing Techniques: Techniques such as topping, pruning, and stress training can influence potency. These methods are applicable to both hydroponic and soil-based cultivation, allowing growers to manipulate cannabinoid production based on their desired outcome.
4. Environmental Factors: Light, temperature, humidity, and air quality profoundly impact cannabinoid development. Hydroponic systems, often indoor setups, allow growers to fine-tune these factors, potentially enhancing THC content. Soil-grown cannabis, influenced by outdoor elements, can develop unique cannabinoid ratios, offering a diverse experience for consumers.
5. Harvesting and Curing: Proper harvesting and curing techniques can intensify the potency of cannabis. Both hydroponically and soil-grown plants require careful handling during these phases to preserve cannabinoids effectively. A well-cured harvest ensures maximum potency and optimal effects for consumers.
The Verdict: Quality Over Quantity:
While hydroponic cannabis may excel in THC concentration and faster growth, the choice between hydroponic and soil-grown cannabis ultimately rests on the desired effects and flavor complexity. Hydroponic methods, driven by precision and speed, might cater to those seeking immediate and intense experiences. In contrast, soil-grown cannabis, rooted in tradition, offers a diverse cannabinoid profile, including CBD, contributing to a well-rounded and nuanced encounter.
Understanding the nuanced interplay of factors influencing potency allows growers and consumers alike to make informed choices. Whether it’s the rapid intensity of hydroponically grown THC or the intricate blend of cannabinoids in soil-grown varieties, the cannabis landscape offers a multitude of options, each with its unique charm and allure.
The Science of Hydroponic Growing
Hydroponic cannabis cultivation might sound like a complex scientific endeavor, but at its core, it revolves around mastering three fundamental elements: water, nutrients, and pH levels. Understanding the intricate relationship between these factors is essential for ensuring the successful growth of vibrant and potent cannabis plants.
1. Water: The Lifeblood of Hydroponic Cultivation
In hydroponic systems, water acts as the primary carrier of nutrients, facilitating their delivery directly to the plant roots. Maintaining the right water temperature, typically between 65 and 75 degrees Fahrenheit, is crucial. This optimal range promotes efficient nutrient absorption, fostering robust plant growth. Regularly monitoring and adjusting water levels guarantee a consistent supply of hydration, vital for the overall health of the cannabis plants.
2. Nutrients: Nourishment for Optimal Growth
Unlike soil-based cultivation, hydroponic plants don’t have access to natural nutrients found in the earth. Instead, growers must provide a complete nutrient solution tailored to the specific needs of cannabis plants. This solution typically contains essential elements like nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), along with micronutrients such as iron, manganese, and zinc. Striking the right balance and composition of these nutrients ensures healthy foliage, robust stems, and potent buds.
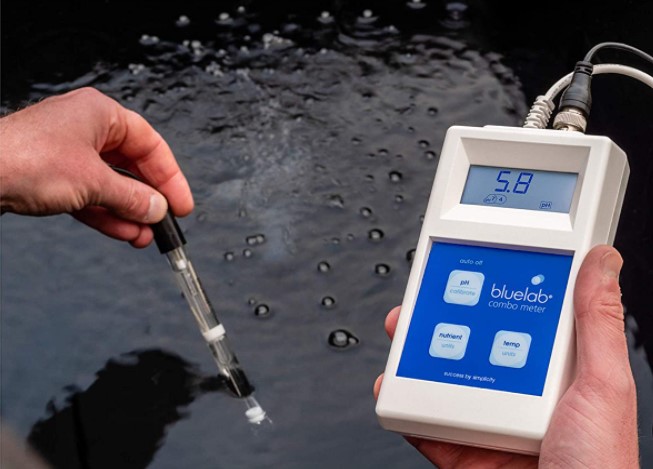
3. pH Levels: Maintaining the Goldilocks Zone
The pH level of the nutrient solution profoundly impacts nutrient absorption. Cannabis plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH range, generally between 5.5 and 6.5. Deviating from this range can lead to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, stunting growth and diminishing potency. Regularly testing and adjusting the pH levels within this optimal range is a meticulous yet crucial task for hydroponic growers. pH fluctuations can disrupt nutrient availability, underscoring the importance of consistent monitoring and adjustment.
4. Sterility: Guarding Against Pathogens
Hydroponic systems demand a sterile environment to prevent the proliferation of harmful bacteria and pathogens. Cleanliness is paramount, as any contamination can swiftly damage the plants. Growers must adhere to strict hygiene practices, regularly sterilizing equipment, and ensuring a sanitized growing space. Preventing the growth of detrimental microorganisms is essential for safeguarding the health and potency of hydroponically cultivated cannabis plants.
5. Oxygenation and Water Quality: Ensuring Vigorous Growth
In addition to nutrients, cannabis roots require oxygen for respiration. Hydroponic systems employ various techniques like aeroponics and deep water culture to ensure adequate oxygenation. Well-oxygenated root systems absorb nutrients more efficiently, promoting vigorous growth and maximizing potency. Additionally, using high-quality water, free from impurities and contaminants, is pivotal. Water quality directly affects nutrient solution stability and the overall health of hydroponically grown cannabis plants.
Mastering the science of hydroponic growing involves meticulous attention to these factors. By maintaining precise water parameters, providing tailored nutrient solutions, regulating pH levels, ensuring sterility, and optimizing oxygenation, growers can cultivate cannabis plants with exceptional potency, vibrant health, and impressive yields. In the intricate dance of water, nutrients, and pH, lies the key to unlocking the full potential of hydroponically grown cannabis.
Hydroponic Cannabis Equipment For Beginners
Embarking on a successful hydroponic cannabis cultivation journey necessitates not only expertise in the growing process but also a thorough understanding of the essential equipment required. For beginners, grasping the basics of hydroponic systems, lighting, nutrients, and testing tools is paramount for cultivating potent and healthy cannabis plants.
1. Hydroponic Systems: Tailoring Growth Environments
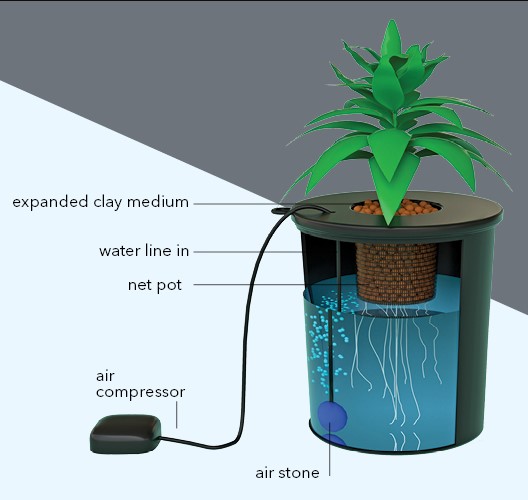
Hydroponic systems form the backbone of your cultivation setup. There are diverse types to choose from, including Deep Water Culture (DWC), Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), and Ebb and Flow systems. Each system offers unique advantages, such as precise nutrient control and efficient space utilization. Selecting the right system depends on your available space, budget, and expertise. Beginners often find DWC systems, where plant roots are submerged directly into the nutrient solution, a user-friendly choice due to their simplicity and effectiveness.
**1. ** Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Overview: DWC is a straightforward yet highly effective hydroponic system. Plants are suspended in net pots above a reservoir filled with a nutrient solution. Air stones provide oxygen to the submerged roots, stimulating rapid growth.
Advantages:
- Optimal Oxygenation: Constant oxygen supply promotes robust root development and nutrient absorption.
- Simplicity: DWC systems are relatively easy to set up and manage, making them suitable for beginners.
- High Yields: The abundant oxygen often leads to faster growth and larger yields.
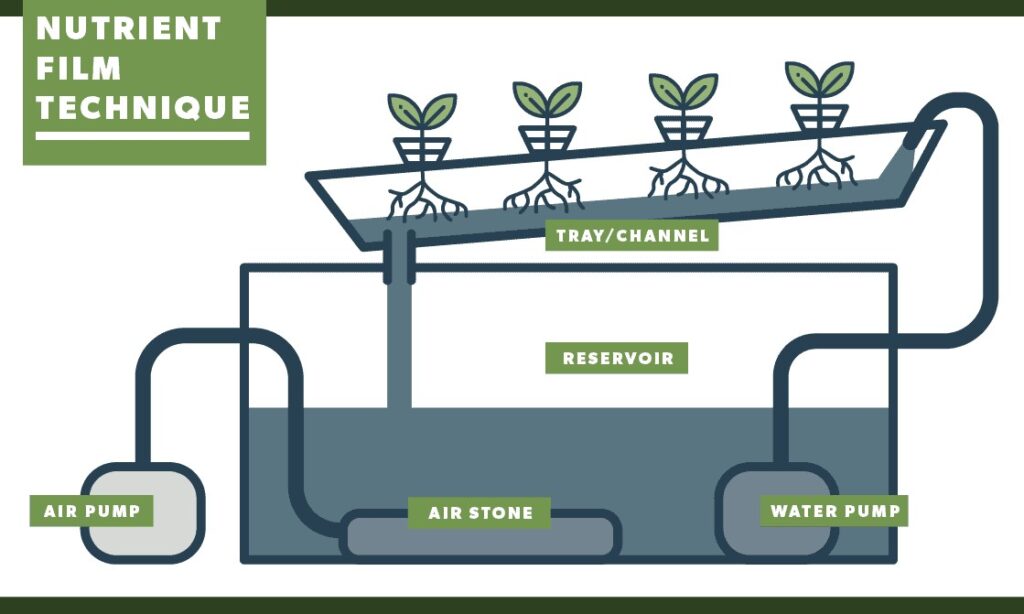
**2. ** Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
Overview: In NFT systems, a thin film of nutrient solution continuously flows over the roots, providing essential elements. Plants are placed in sloping channels, allowing the roots to be partially submerged in the nutrient film.
Advantages:
- Water Efficiency: NFT systems use water efficiently as the nutrient solution is recirculated, reducing waste.
- Space Optimization: NFT systems are compact and suitable for growers with limited space.
- Continuous Nutrient Supply: Plants receive a constant flow of nutrients, ensuring consistent growth rates.
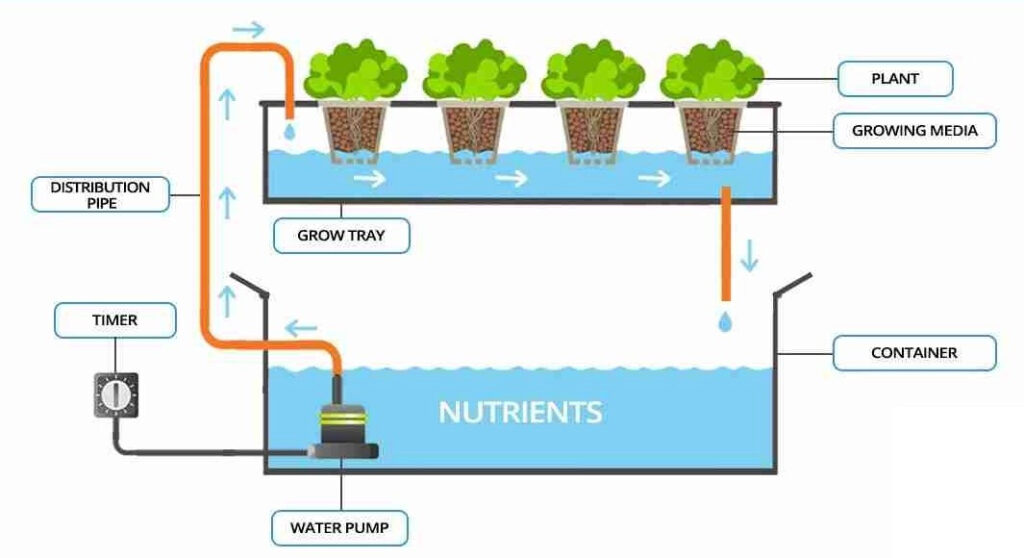
**3. ** Ebb and Flow Systems
Overview: Also known as flood and drain systems, ebb and flow setups periodically flood the plant’s root zone with nutrient solution before draining it back into a reservoir. This cycle ensures ample nutrient absorption and prevents waterlogging.
Advantages:
- Customizable Feeding Cycles: Growers can adjust flood and drain intervals to suit specific plant needs, providing flexibility.
- Reduced Risk of Overwatering: Excess water drains away, preventing root suffocation and minimizing the risk of diseases.
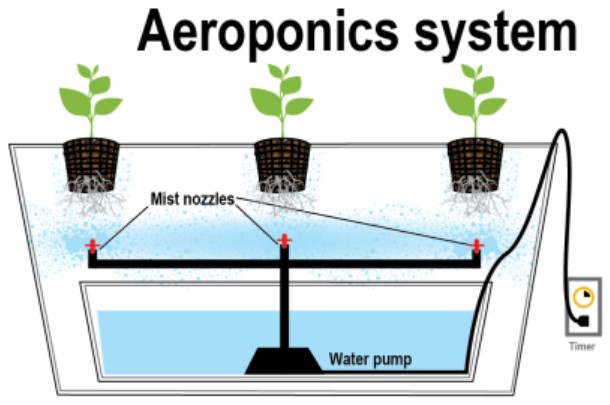
**4. ** Aeroponics
Overview: Aeroponic systems suspend plants in a misty environment where nutrient solution is sprayed directly onto the roots. This method maximizes oxygen exposure, leading to rapid growth and nutrient absorption.
Advantages:
- Maximum Oxygenation: Aeroponics offers unparalleled oxygenation, fostering vigorous root growth and nutrient uptake.
- Water Efficiency: The minimal use of water makes aeroponic systems eco-friendly and resource-efficient.
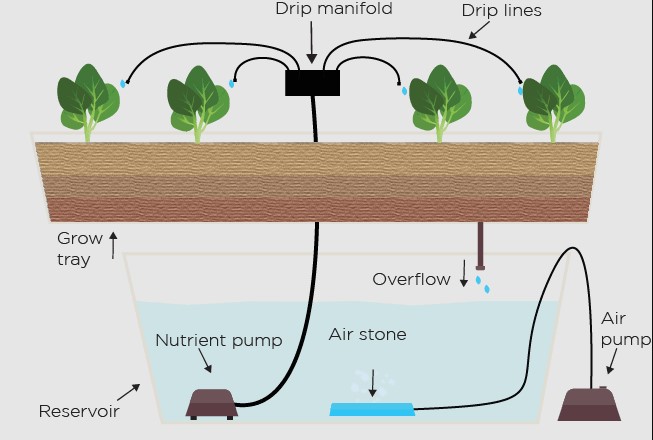
**5. ** Drip Systems
Overview: Drip systems involve a network of tubes that deliver a controlled drip of nutrient solution to each plant. This precise delivery method ensures consistent feeding.
Advantages:
- Precision Feeding: Drip systems allow growers to regulate the exact amount of nutrients delivered to each plant, ensuring tailored nourishment.
- Low Maintenance: These systems are relatively low maintenance, making them suitable for growers seeking efficient solutions.
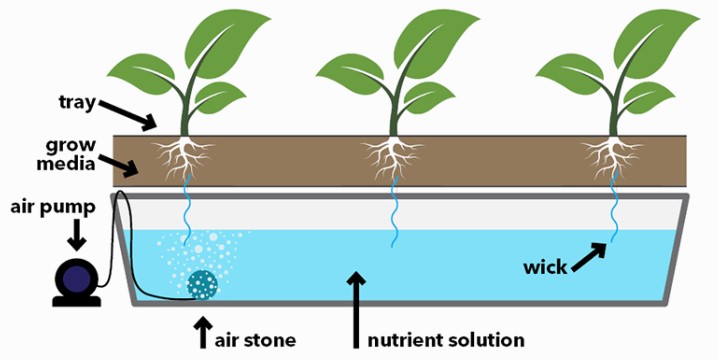
**6. ** Wick Systems
Overview: Wick systems are among the simplest hydroponic setups. A wick, often made of cotton or felt, transports the nutrient solution from a reservoir to the plant’s root zone.
Advantages:
- Low Cost and Low Maintenance: Wick systems are affordable and require minimal maintenance, making them accessible to novice growers.
- Suitable for Small-Scale Cultivation: Ideal for small-scale cannabis cultivation, wick systems offer a basic yet effective approach to hydroponics.
2. Grow Lights: Illuminating the Path to Potency
In indoor hydroponic setups, artificial lighting is indispensable. LED lights have gained popularity among growers for their energy efficiency and spectrum customization abilities. Full-spectrum LEDs mimic natural sunlight, providing plants with the ideal light wavelengths for photosynthesis. Proper lighting duration, typically 18-20 hours during the vegetative stage and 12 hours during flowering, is crucial for healthy growth and robust bud development. Investing in high-quality, energy-efficient grow lights ensures your cannabis plants receive the optimal light intensity and spectrum necessary for maximizing potency.
3. Nutrients: Crafting the Perfect Nutrient Cocktail
Hydroponically grown cannabis relies entirely on nutrient solutions for nourishment. These solutions must contain a precise blend of macro and micronutrients, customized for each growth stage. Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium, magnesium, and trace elements are essential components. Pre-formulated hydroponic nutrient mixes are available, simplifying the process for beginners. Regularly monitoring the nutrient solution’s strength (measured in parts per million, PPM) and pH levels guarantees your plants receive the right balance of nutrients, fostering healthy growth and potent bud production.
4. Testing Tools: Precision for Optimal Growth
Accurate testing tools are indispensable for maintaining the delicate balance of hydroponic systems. pH testing kits enable growers to monitor and adjust the acidity of the nutrient solution, ensuring optimal nutrient uptake. Electrical conductivity (EC) or PPM meters measure the nutrient solution’s strength, preventing over-fertilization or nutrient deficiencies. Investing in reliable testing tools empowers growers to make informed decisions, fine-tuning the growing environment for maximum potency and yield.
Navigating the realm of hydroponic equipment might seem overwhelming at first, but with a foundational understanding of systems, lighting, nutrients, and testing tools, beginners can establish a thriving hydroponic cannabis cultivation setup. By selecting suitable equipment, customizing nutrient solutions, and maintaining optimal growing conditions, growers pave the way for potent, healthy, and bountiful cannabis harvests.
Conclusion
In the debate of hydroponic vs. soil-based cannabis cultivation, understanding the nuances of each method is vital for aspiring growers. Hydroponic systems offer meticulous control, enabling faster growth and efficient nutrient absorption. Soil-based growing, on the other hand, embraces the natural complexities of soil, resulting in nuanced flavors and a more traditional approach. Whether you opt for the precision of hydroponics or the organic charm of soil, your choice should align with your goals, resources, and expertise.
FAQ
Q1: Which method yields higher potency, hydroponic, or soil-based growing? A1: Both methods can yield potent cannabis. Hydroponic systems might offer faster growth, but soil-based growing can produce nuanced cannabinoid profiles, including rich THC and CBD concentrations.
Q2: Is hydroponically grown cannabis more susceptible to diseases? A2: Hydroponic systems can minimize the risk of soil-borne diseases, but they require a sterile environment. Proper maintenance is crucial in preventing any potential issues.
Q3: Does soil-grown cannabis taste better than hydroponically grown cannabis? A3: Soil-based cultivation often results in a more complex flavor profile due to the interaction between the plant and the soil. Many enthusiasts appreciate the unique tastes derived from soil-grown cannabis.
Q4: Can I switch my plants from hydroponic to soil-based or vice versa? A4: While it’s possible, transitioning plants between these methods can stress them. Careful adjustments and monitoring are necessary to ensure successful adaptation.
Q5: Which method is more environmentally friendly? A5: Soil-based growing is generally considered more environmentally friendly due to lower energy usage. However, both methods can be sustainable with proper practices in place.
Q6: What are the initial costs associated with hydroponic and soil-based growing? A6: Hydroponic setups often require a higher initial investment due to specialized equipment. Soil-based growing is comparatively more affordable, making it an attractive option for beginners.
Q7: Can hydroponic systems be used outdoors? A7: While hydroponic systems are primarily designed for indoor use, some outdoor setups exist. However, they require careful consideration of environmental factors and may not be as common as soil-based outdoor gardens.
Q8: Which method offers a higher yield? A8: Hydroponic systems generally offer higher yields due to optimal nutrient control and faster growth rates. However, a skilled soil-based grower can also achieve impressive yields through meticulous care and attention.
In the end, the choice between hydroponic and soil-based cultivation boils down to personal preference, resources, and the desired end product. Both methods have their merits, offering unique pathways to successful cannabis cultivation. By harnessing the knowledge about each method’s intricacies and adapting techniques to individual needs, growers can embark on a rewarding journey, cultivating potent and flavorful cannabis tailored to their preferences.